
6.23 LAB: Leap year - functions
A year in the modern Gregorian Calendar consists of 365 days. In reality, the earth takes longer to rotate around the sun. To account for the difference in time, every 4 years, a leap year takes place. A leap year is when a year has 366 days: An extra day, February 29th. The requirements for a given year to be a leap year are:
1) The year must be divisible by 4
2) If the year is a century year (1700, 1800, etc.), the year must be evenly divisible by 400
Some example leap years are 1600, 1712, and 2016.
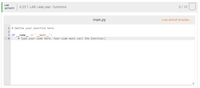
Write a
Ex: If the input is:
1712
the output is:
1712 is a leap year.
Ex: If the input is:
1913
the output is:
1913 is not a leap year.
Your program must define and call the following function. The function should return True if the input year is a leap year or False otherwise.
def is_leap_year(user_year)
Use Python, please.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





