
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
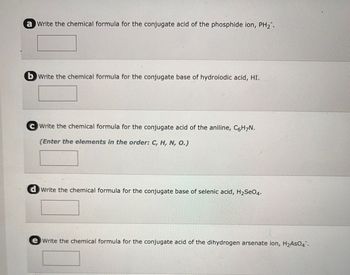
Transcribed Image Text:a Write the chemical formula for the conjugate acid of the phosphide ion, PH₂
b write the chemical formula for the conjugate base of hydroiodic acid, HI.
CWrite the chemical formula for the conjugate acid of the aniline, C6H₂N.
(Enter the elements in the order: C, H, N, O.)
dWrite the chemical formula for the conjugate base of selenic acid, H₂SO4.
Write the chemical formula for the conjugate acid of the dihydrogen arsenate ion, H₂AsO4
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
You didn't answer D&E
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
You didn't answer D&E
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The chemical formulae of some acids are listed in the first column of the table below, and in the second column it says whether each acid is strong or weak. Complete the table. List the chemical formula of each species present at concentrations greater than about 106 mo mo-when about a tenth of a mole of the acid is L dissolved in a liter of water. The chemical formulae of some acids are listed in the first column of the table below, and in the second column it says whether each acid is strong or weak. Complete the table. List the chemical formula of each species present at concentrations greater than about 10-6 mol/L when about a tenth of a mole of the acid is dissolved in a liter of water. acid strong or weak? species present at 10-6 mol/L or greater when dissolved in water ICIO weak H₂SO, weak IICI strong HCIO, strong ☐ x DO....arrow_forwardConsider the following data on some weak acids and weak bases: name nitrous acid acid hypochlorous acid 0.1 M NaI solution 0.1 M KCIO 0.1 M C5H5NHBr 0.1 M NH4CI formula HNO₂ HCIO Ka 4.5 x 104 3.0 × 108 Use this data to rank the following solutions in order of increasing pH. In other words, select a '1' next to the solution that will have the lowest pH, a '2' next to the solution that will have the next lowest pH, and so on. PH choose one choose one ✓ choose one base choose one name formula K₂ -5 ammonia NH3 1.8 × 10 pyridine CHN 1.7 × 10⁹arrow_forward300.0 mL of a 0.385 M solution of NaI is diluted to 700.0 mL. What is the new concentration of the solution? The pH of an acidic solution is 5.43. What is [H⁺]?arrow_forward
- Aluminum has been implicated as a neurotoxic agent for Alzheimer’s patients and is known as harmful for renal failure patients. In 1985, the medical community recommended that no more than 10 mg/L Al3+ be present in drinking water used for dialysis patients. At what pH is the maximum Al3+ concentration equal to 10 mg/L, assuming that the only source of Al3+ is Al(OH)3? How does this compare with the allowable pH of drinking water of 7.8; would we expect to observe this concentration in drinking water?arrow_forwardThe formula for the conjugate acid of HPO42- is? A student weighs out a 2.33 g sample of sodium fluoride, transfers it to a 300 mL volumetric flask, adds enough water to dissolve it and then adds water to the 300 mL tic mark. What is the molarity of NaF in the resulting solution? A student wants to prepare a solution of iron(III) fluoride with a known molarity.How many grams of FeF3 must be weighed out to prepare 250. mL of a 0.245 M aqueous solution of the salt? An aqueous solution has a hydroxide ion concentration of 1.0 x 10^-10 M. What is the hydronium ion concentration in this solution? Concentration = M Is this solution acidic, basic or neutral? An aqueous solution has a hydrogen ion concentration of 1.0 x 10^-6 M. What is the hydroxide ion concentration in this solution? Concentration = M Is this solution acidic, basic or neutral?arrow_forwardWrite the chemical formual of acid: Cl-(aq0+HS04-(aq) HCI(AQ+SO42-(aq)arrow_forward
- Consider the following data on some weak acids and weak bases: name hypochlorous acid nitrous acid acid solution 0.1 M CH3NH3Cl 0.1 M KNO3 0.1 M KCIO 0.1 M NaNO2 formula Ka HCIO 3.0 × 10 HNO₂ 4.5 x 107 Use this data to rank the following solutions in order of increasing pH. In other words, select a '1' next to the solution that will have the lowest pH, a '2' next to the solution that will have the next lowest pH, and so on. X pH -8 choose one ✓ choose one choose one ✓ choose one Ś base K₂ formula methylamine CH3NH₂ 4.4 × 10 4 ammonia NH3 name 1.8 × 10 5 -5arrow_forwardA chemist dissolves 272. mg of pure potassium hydroxide in enough water to make up 100. mL of solution. Calculate the pH of the solution. (The temperature of the solution is 25 °C.) Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits.arrow_forwardOver the past 250 years, the average upper-ocean pH near the Pacific Northwest has decreased by about 0.1 units, from about 8.2 to 8.1. This drop in pH corresponds to an increase in acidity of about 30%. When CO2 levels in seawater rise, the availability of carbonate ion, CO32−, makes it more difficult for marine organisms to build and maintain shells and other body parts from calcium carbonate. Calculate H3O+ and OH− concentrations at pH levels of 8.2 and 8.1. Demonstrate by calculations that this decrease in pH corresponds to an increase in acidity of about 30%. Explain the relationship between the pH of seawater and the availability of carbonate ions. Does the change in pH from 8.2 to 8.1 result in an increase or decrease in the availability of carbonate ions?arrow_forward
- Calculate the pH at 25 °C of a 0.14M solution of sodium hypochlorite (NaC10). Note that hypochlorous acid (HClO) is a weak acid with a pk of 7.50. a Round your answer to 1 decimal place. pH = Ś ? olo Ararrow_forwardWhich of the following chemical formulas corresponds to a base? HCl; KOH; H2SO4; HNO3arrow_forwardWhich of the following is a complete balanced reaction for an Arrhenius base in water? NaOH (s) 2 NaH (s) + O2 (g) →> ○ Mg(OH) 2 (s) → Mg2+ (aq) + OH (aq) ○ HNO2 (aq) → H+ (aq) + NO₂ (aq) KOH (s) →> K+ (aq) + OH¯ (aq)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY