
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
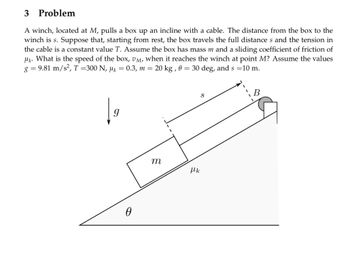
Transcribed Image Text:# Problem
A winch, located at \( M \), pulls a box up an incline with a cable. The distance from the box to the winch is \( s \). Suppose that, starting from rest, the box travels the full distance \( s \) and the tension in the cable is a constant value \( T \). Assume the box has mass \( m \) and a sliding coefficient of friction of \( \mu_k \). What is the speed of the box, \( v_M \), when it reaches the winch at point \( M \)? Assume the values \( g = 9.81 \, \text{m/s}^2 \), \( T = 300 \, \text{N} \), \( \mu_k = 0.3 \), \( m = 20 \, \text{kg} \), \( \theta = 30^\circ \), and \( s = 10 \, \text{m} \).
## Diagram Explanation
The diagram shows an inclined plane with an angle \( \theta \) to the horizontal. A box of mass \( m \) is on the incline, and a cable runs from the box over a pulley at point \( B \) to a winch located at point \( M \). The incline is marked with the distance \( s \) from the box to the winch. The gravitational force \( g \) acts vertically downward, while kinetic friction acts along the plane with a coefficient \( \mu_k \).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Step 1: Write the given data and what is to find
VIEW Step 2: Draw the free body diagram:
VIEW Step 3: Determine the magnitude of the acceleration of the box up the inclined plane:
VIEW Step 4: Apply the Newton's equation of motion to determine the time needed by the box to reach at M:
VIEW Solution
VIEW Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 9 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1 Problem During a particularly snowy winter in Charlotte, a child of mass m slides down a ramp starting at rest from point A and encounters the melted grassy area at B before coming to a full stop at C. Assume the ice is frictionless. The height of point A is hĄ and the distance between B and C is L. What is the coefficient of friction of the grass, k? Assume that g = 9.81 m/s², ha = 5 m, m = 20 kg, and L = 10 m. hA P JA Ice B Grass L Carrow_forwardSituation 5: Suppose the coefficient of kinetic friction between me and the plane as shown in figure is µ = 0.2 and that m = 20 kg and m² = 20 kg 53. What is the acceleration of Block A 0.605 -0.605 0.303 -0.303 60° 54. What is the tension on the chord? 80.31 N 72.12 N 78.17 N 66.71 N 1.1 m/s 52. What is mass of block B in order to move 1m up in an inclined when the block initially at rest 18.83 kg 20.41 kg 15.61 kg 25.12 kg 30° 55. What is the time required for block B to reach the top assuming it is initially 2.5 m away. 4.06 S 1.07 s 2.87 s 3.24 sarrow_forwardA crate has a mass of 120kg and the coefficient of static and kinetic friction is 0.60 and 0.50, respectively. The crate starts from rest and the motor exerts a tension T= 1220 + 200t (N). If the elevation of the dock is 30 degrees from the horizontal, What is the velocity of the crate after 1sec? Compute the power transmitted after 1sec. Provide FBD. Thank you.arrow_forward
- A box with mass m = 2.75 kg rests on the top of a table. The coefficient of static friction between the box and the table is μs = 0.71 and the coefficient of kinetic friction is μk = 0.34. Write an expression for Fm the minimum force required to produce movement of the box on the top of the table. Solve numerically for the magnitude of the force Fm in Newtons. Write an expression for a, the box's acceleration, after it begins moving. (Assume the minimum force, Fm, continues to be applied.) Solve numerically for the acceleration, a in m/s2.arrow_forwardPLEASE ANSWER ASAP. WILL RATE IF CORRECT!arrow_forwardShow complete solutions. Please draw the figure or the illustrations. Problem:Two horses are pulling a barge with mass 2000 kg along a canal, as shown in the Figure. The cable connected to the first horse makes an angle of 30o with respect to the direction of the canal, while the cable connected to the second horse makes an angle of 45.0o. Find the initial acceleration of the barge, starting at rest, if each horse exerts a force of magnitude 600 N on the barge. Ignore forces of resistance on the barge.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY