
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
A wheel is fixed at its center position and allowed to rotate. The moment of inertia of the wheel is J, and the wheel is connected to the fixed center point through a torsional spring with spring constant k(subscript 1) (not shown in the above figure). This wheel is in contact with mass M. The wheel and the mass maintain rolling without sliding condition at the contacting surface. We apply a torque T at the wheel. Derive the Equation of Motion for the system. You should have only one unknown response in your equation. Use x(t) .
I am having a lot of trouble with this problem - please be very detailed and explain fully!
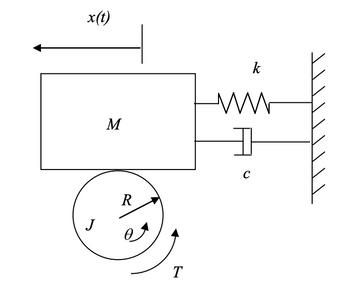
Transcribed Image Text:x(t)
J
M
R
T
k
ww
C
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 1500 kg load is lifted by a hoist using a Ø1.5m drum. The drum is driven by an electric motor through a gearbox with a reduction ratio-25, At a certain instant, 175 m of unwrapped rope is lifling the load and 7.4 m of rope is wrapped on the drum. Drum: diameter ØI5 m IDRUM – 322 kg-m² (includes the inertia effects of the gearbox only) Motor, speed IMOTOR 1200 rpm 1.24 kg-m2 Rope: 3 kel a) Show that the equivalent moment of inertia of the motor and drumgearbox is 2695 kg-m the drum byArthis instant, determine the motor toreue requinedifthe load is accelerating q t the load s accelerating upward at 3.5 s-arrow_forwardplease write neatly and show ALL the steps only HANDWRITTEN answer needed ( NOT TYPED)arrow_forwardProblem 7. We have a line of two equal masses m connected by three springs with spring constants c₁ = 1, c₂ = 1, and c3 = S. Spring 1 is fixed at the top and spring 3 at the bottom, so xo = x3 = 0. (a) Find the stiffness matrix K in the equation Kx = f for the mass displacements. (b) Solve for the displacements x₁ and x2. (c) If the third spring constant S becomes very large or very small (S→∞ and S→ 0) what are the limiting values of the displacements x₁ and .x₂? (d) If the third spring constant S becomes very large or very small (S→∞ and S→ 0) what are the limiting values of the spring forces y1, y2, and y3? 91 www m 3-WW www C₁ X₁ "Xo = 0 C2₂ X2 C3 X3 = 0arrow_forward
- Please solve only 4,5arrow_forwardProblem 2: A car is pushing a barrel to the right. The pushing force P is applied by the front bumper which is level with the center G of the barrel (see figure). The barrel has mass m, radius R, and radius of gyration kG. The coefficients of static and kinetic friction between the bumper and the barrel are µs and µk. The coefficients of static and kinetic friction between the barrel and the road are also µs and µk. 1) If the barrel doesn't slip on the road, find the acceleration of the barrel and the minimum value of us required to ensure no slipping. 2) If the barrel slips on the road, find the acceleration of G and the angular acceleration of the barrel. Hs. Hk. marrow_forwardThe structure of a football goal is shown in the figure below. The bending motion of the structure can be represented by a flexible cantilever beam with tip mass M¡ as shown in the figure. The tip mass M, represents the mass of the horizontal crossbar which is assumed to be rigid in this motion. A single vertical straight beam having mass of MH, shown in the figure below, is the equivalent model for the two symmetrical vertical posts. A soccer ball of mass M, hits the horizontal crossbar with the velocity of Vp. x(t) м, VINGLI SOLAR The response of the horizontal crossbar, mass M, is shown by x(t) in the figure. The vertical beam has a circular cross section of radius r, Young's modulus E and length L. For numerical calculations, use M, = 23.2130 kg, MH = 28.6617 kg. M, = 0.5497 kg, Vý = 8.8974 m/s, L= 2.7757 m, E = 133.5685 GPa andr= 0.0437 m. For circular cross- section I = Tr/4.Considering zero damping and the numerical data given above, obtain the maximum amplitude of response x(t)…arrow_forward
- (3) A circular cam 8-in in diameter rotates off-center with an eccentrity e = 1" & operates the roller follower that is carried by the arm. The roller follower is held against the cam by means of a tension spring attached a third from a fixed pivot point. The force against the cam & roller follower is approximately 50lb @ the low position & 80lb @ high position. The ratio of the coil diameter to that of wire diameter is 7.0. The allowable stress on the spring is S,= 60,000psi. Calculate : P (a) the wire diameter; (b) the outside diameter of spring; (c) the number of active coils recommended.arrow_forwardplease do it neatly and correct and fast pleasearrow_forwardA turbine rotor is mounted on a stepped shaft that is fixed at both ends as shown in The torsional stiffnesses of the two segments of the shaft are given by ka = 3,000 N-m/rad and k2 = 4,000 N-m/rad. The turbine generates a harmonic torque given by M(t) = Mo cos wt about the shaft axis with M, = 200 N-m and w = 500 rads. The mass moment of inertia of the rotor about the shaft axis is Jo = 0.05 kg-m. Assuming the equivalent torsional damping constant of the system as c, = 2.5 N-m-s/rad, determine the steady-state response of the rotor, 6(1). O(1) ke M(1) = M, cos ot Turbine rotor, Joarrow_forward
- 7. 2) The lawn roller has a mass m = 55 kg and a radius of gyration about its gravitational center G, kG = 196 mm. It has a handle that connects to its center axle, and the handle is pushed forward with a force F = 420 N at a 45° angle. The coefficients of static and kinetic friction between the roller and the ground are us = 0.11 and Hk = 0.08, respectively. For the sets of parameters listed below, determine the magnitude of the roller's angular acceleration (in rad/s²). Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point. Take g = 9.81 m/s?. F 45° 200 mm Aarrow_forwardFor two existing torques, what third force at a given distance from the pivot will balance them? Imagine a meter stick set up as in the figure. It hangs from a central bracket, and two hanging masses can hang from it from each of their brackets. At a third location, a force probe can either pull up or pull down on the stick, depending on what is needed to balance the stick. The mass of the meter stick is 120 g. sketch the situation (drawing r1, r2, r3, F1, F2, and F3) and determine the magnitude (value) and direction (+ or -) of each torque. Don't include the mass of a bracket that would hold the hanging mass in place; assume the mass listed is the entire mass hanging at that point. For each trial, use the principle of equilibrium (where the sum of torques is zero) to calculate the third, unknown force acting at x3arrow_forwardA pendulum is made up of a spring with a mass attached to the end. The spring is arranged to lie in a straight line, by wrapping the spring around a massless bar. The equilibrium length of the bar is “l”. Using lagrange’s equations, find the equations of motion.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY