
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
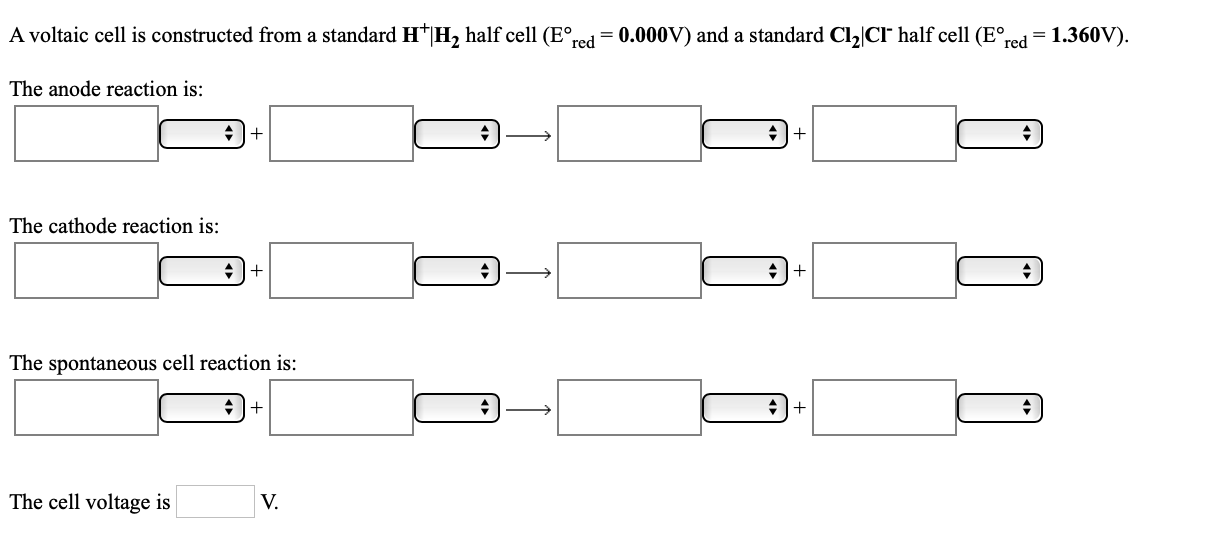
Transcribed Image Text:A voltaic cell is constructed from a standard H*|H, half cell (E°,
red
= 0.000V) and a standard Cl,|CIr half cell (E°,
red
= 1.360V).
The anode reaction is:
+I+
+|+
The cathode reaction is:
The spontaneous cell reaction is:
The cell voltage is
V.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Determine E° for a galvanic (voltaic) cell if AG° = -6.3 kJ/mol and n = 3. (F = 96,500 J/(V•mol)) %D V 1 3 4 6. C 7 8. 9. +/- х 100 + 2.arrow_forwardWhat is the cell notation for the voltaic cell shown below? KD,- Zn²¹ NO, Zo NC₂" NO,- Voltmeter K' Zn2+ ここ So, ² Cu²+ Zn(s) | Zn2+(aq) || Cu2+(aq) | Cu(s) O Zn(s) | Zn2+(aq) || Cu(s) | Cu2+(aq) O Zn2+(aq) | Zn(s) || Cu2+(aq) | Cu(s) O Zn(s) | Cu(s) || Zn2+(aq) | Cu2+(aq) Cu L'u't SC,arrow_forwardA voltaic cell is constructed in which the following cell reaction occurs. The half-cell compartments are connected by a salt bridge.2Fe3+(aq) + Ni(s) 2Fe2+(aq) + Ni2+(aq)The anode reaction is: + + The cathode reaction is: + + In the external circuit, electrons migrate the Ni|Ni2+ electrode the Fe2+|Fe3+ electrode.In the salt bridge, anions migrate the Ni|Ni2+ compartment the Fe2+|Fe3+ compartment. ------ When the following equation is balanced properly under basic conditions, what are the coefficients of the species shown? F- + Cl2 Cl- + F2Water appears in the balanced equation as a fill in the blank 5 (reactant, product, neither) with a coefficient of . (Enter 0 for neither.)Which element is reduced? ---- When the following skeletal equation is balanced under basic conditions, what are the coefficients of the species shown? MnO2 + NO2- N2O + MnO4-Water appears in the balanced equation as a fill in the blank 5…arrow_forward
- A voltaic cell is constructed from a standard Mn2+|Mn half cell (E° red = -1.180V) and a standard Ag+|Ag half cell (E° red = 0.799V). (Use the lowest possible coefficients. Be sure to specify states such as (aq) or (s). If a box is not needed, leave it blank.) The anode reaction is: + + The cathode reaction is: + + The spontaneous cell reaction is: + + The cell voltage is ___ V.arrow_forwardA voltaic cell is constructed in which the anode is a Cu* Cu** half cell and the cathode is a F F2 half cell. The half-cell compartments are connected by a salt bridge. (Use the lowest possible coefficients. Be sure to specify states such as (ag) or (s). If a box is not needed, leave it blank.) The anode reaction is: The cathode reaction is: The net cell reaction is: In the external circuit, electrons migrate ) the Cu"|Cu²* electrode the FF2 electrode. In the salt bridge, anions migrate | the Cu Cu" compartment| the FF2 compartment. from toarrow_forwardA voltaic cell is constructed from a standard Al3+|Al half cell (E°red = -1.660V) and a standard H+|H2 half cell (E°red = 0.000V). The anode reaction is: + + The cathode reaction is: + + The spontaneous cell reaction is: + + The cell voltage is V.arrow_forward
- A voltaic cell is constructed from a standard Zn2+|Zn half cell (E°red = -0.763V) and a standard Ag+|Ag half cell (E°red = 0.799V). The anode reaction is: + + The cathode reaction is: + + The spontaneous cell reaction is: + + The cell voltage is V.arrow_forwardA voltaic cell is constructed from a standard Cu2+|Cu half cell (E°red 0.337V) and %D a standard H+|H2 half cell (E°red 0.000V). %3| The anode reaction is: + + The cathode reaction is: + The spontaneous cell reaction is: + + | The cell voltage is V. + ↑arrow_forwardA voltaic cell is constructed from a standard = Sn2+ Sn half cell (E° red -0.140V) and a standard F2 F half cell (E° red = 2.870V). (Use the lowest possible coefficients. Be sure to specify states such as (aq) or (s). If a box is not needed, leave it blank.) The anode reaction is: + The cathode reaction is: + The spontaneous cell reaction is: + The cell voltage is V. ↑ + + +arrow_forward
- Enter electrons as e A voltaic cell is constructed in which the anode is a Fe2+|Fe3+ half cell and the cathode is a F|F, half cell. The half-cell compartments are connected by a salt bridge. (Use the lowest possible coefficients. Be sure to specify states such as (aq) or (s). If a box is not needed, leave it blank.) The anode reaction is: The cathode reaction is: The net cell reaction is: +. In the external circuit, electrons migrate the Fe2+|Fe3+ electrode the F|F, electrode. from to In the salt bridge, anions migrate the F|F, compartment 3- the Fe2+|Fe+ compartment. +. +. 1arrow_forwardA voltaic cell is constructed from a standard Hg2* Hg half cell (E°red = 0.855V) and a standard Br2 Br half cell (E°red = 1.080V). (Use the lowest possible coefficients. Be sure to specify states such as (ag) or (s). If a box is not needed, leave it blank.) The anode reaction is: + The cathode reaction is: The spontaneous cell reaction is: The cell voltage is V.arrow_forwardFor the Zn-Cu2+ voltaic cell, we have Zn (s) + Cu2+ (aq, 1 M) → Zn2+(aq, 1 M) + Cu (s) Ecell 0 = 1.10 V Given that the standard reduction potential of Zn2+ to Zn(s) is -0.76 V, calculatethe ECu2+/Cu0 for the reduction of Cu2+ to Cu: Cu2+ (aq, 1 M) + 2e- → Cu (s)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY