
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
Two vertical and connected cylindrical tanks of diameter D are open to the atmosphere and they contain water at a height of h in the initial state, as shown in the figure. As the radial blades in the left tank are rotated about the centerline of the tank, some water in the right tank flows into the left tank. Determine the angular velocity of radial blades ? such that half of water in the right tank flows into the left tank. Also, derive a general relation for angular velocity as a function of initial height of water in the tank. Assume water in the tanks would not spill. D = 2R = 45 cm, h = 40 cm and g = 9.81 m/s2.
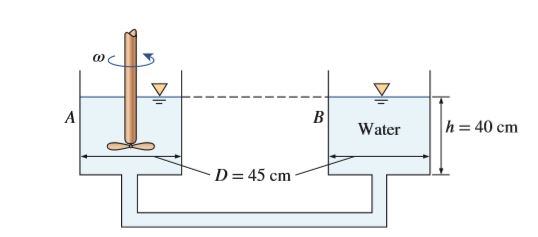
Transcribed Image Text:A
в
Water
h= 40 cm
D = 45 cm-
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For the circular thin plate with a square hole as shown in the image below, its radius R = 0.48 m and the side of the square /= 0.21 m, and the material has a mass per unit area of 12 kg/m2. If at the instant shown, it is subjected to a force P = 38 N, and has a counterclockwise angular velocity of W = 2.6 rad/s, determine magnitude of the support reaction at point O at this instant. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point, and proper unit. Take g = 9.81 m/s?. R Parrow_forwardYou have your bicycle upside down while you adjust the chain. The chain is wound around the rear wheels small gear, which has a radius of 4.0 cm. At the pedals, the chain is wound around the large gear, which has a radius of 11.0 cm. The radius of the rear wheel is 35.0 cm. You spin the pedals initially so they finish two revolutions in 1.0 s, starting from rest. Assume constant acceleration. (a) Find the angular acceleration of the rear wheel in rad/s2. (b) Find the magnitude of the total acceleration of a point at the edge of the small gear at the end of 1.5 s (the sum of the radial and tangential accelerations). (c) What is the tangential acceleration for that point during the first second? (d) Calculate the linear acceleration of the chain.arrow_forwardFor the rotation in two dimensions, both energy, and angular momentum is quantized. Select one: True Falsearrow_forward
- Blocks A and B shown in the figure have masses of 5 kg and 10 kg respectively.If the pulley is treated as a 3 kg solid disk with a 15 cm radius, determine the acceleration of the block A. Disregard the rope mass and any slip on the pulley.Consider that the moment of inertia of the pulley is given by Ip = (1/2)mr² in which m is the mass of the pulley and r is of radius the pulley.arrow_forwardBicycle wheels are manufactured having thin rims and tires of total mass D per unit length, and the spokes and axle may be ignored. Find the angular momentum of one bicycle wheel of radius r when the bicycle is traveling at velocity v, and hence comment upon whether you would prefer large wheels or small wheels to make a bicycle easiest to balance when riding it.arrow_forwardA "swing ride" is shown in the figure. Calculate the necessary angular velocity w for the swings to assume an angle 0 = 44° with the vertical. Neglect the mass of the cables and treat the chair and person as one particle. Assume r = 4.1 m, L = 6.0 m. Answer: W= i rad/sarrow_forward
- I need the answer as soon as possiblearrow_forwardConsider a toy vehicle with a body of mass M = 2Kg on two wheels, each of mass m = 1Kg and radius r = 0.1 m as shown in the figure. It starts from rest on top of a small hill of height H = 10 m and rolls without slipping. What is the linear velocity of the center of mass at the bottom of the hill? HINT: There is rotational and translational kinetic energy in this problem. Vo = 0 M- Vf M-2K m=lKg molkyarrow_forwardA 21 mm diameter glass marble with a mass of 25 g rolls without slipping down a track toward a vertical loop of radius R=15 cm, as shown in the figure. Approximate the minimum translational speed vmin the marble must have in order to complete the loop without falling off the track when it is a height H=25 cm above the bottom of the loop. H R Figure is not to scale.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY