
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
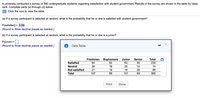
Transcribed Image Text:A university conducted a survey of 390 undergraduate students regarding satisfaction with student government. Results of the survey are shown in the table by class
rank. Complete parts (a) through (d) below.
Click the icon to view the table.
(a) If a survey participant is selected at random, what is the probability that he or she is satisfied with student government?
P(satisfied) =
= 0.59
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
(b) If a survey participant is selected at random, what is the probability that he or she is a junior?
P(junior) =
%3D
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
Data Table
ETTILL
Freshman
Sophomore
Junior
Senior
Total
Satisfied
60
52
63
55
230
Neutral
26
18
20
10
74
Not satisfied
21
19
18
28
86
Total
107
89
101
93
390
Print
Done
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Using the data given below, determine whether it would unusual for a household to have no HD televisions. The number of televisions (HD) per household in a small town Televisions 1 2 Households 26 445 655 1474 P(x) 0.010 0.171 0.252 0.567 Choose the correct answer below. O A. It would be unusual because the probability of having no HD televisions is less than 0.05. OB. It would not be unusual because the probability of having no HD televisions is more than 0.05. O C. It would not be unuşual beçause 26 people have no HD televisions in the town. O D. It would be unusual because 26 people have no HD televisions in the town. Click to select your answer.arrow_forwardBelow, the two-way table is given for a class of students. Freshmen Sophomore Juniors Seniors Total Male 2. Female Total If a student is selected at random, find the probability the student is a freshman. P( Freshman ) =[? ]% Round to the nearest whole percent. Enter DELL home prt sc F10 end F12 F5 F6 F7 Inse F8 F9 F11 6 8. 9.arrow_forwardSolve the last part what is the source of variability in the random variable? B. The sample size was weingarrow_forward
- In an experiment, college students were given either four quarters or a $1 bill and they could either keep the money or spend it on gum. The results are summarized in the table. Complete parts below. Purchased Gum Kept the Money Students Given Four Quarters 33 13 Students Given a $1 Bill 15 30 a. Find the probability of randomly selecting a student who spent the money, given that the student was given four quarters. b. Find the probability of randomly selecting a student who kept the money, given that the student was given four quarters. c. What do the preceding results suggest?choose below A. A student given four quarters is more likely to have kept the money than a student given a $1 bill. B. A student given four quarters is more likely to have kept the money. C. A student given four quarters is more likely to have spent the money than a student given a $1 bill. D. A student given four quarters is more…arrow_forwardThe accompanying table shows the numbers of male and female students in a particular country who received bachelor's degrees in business in a recent year. Complete parts (a) and (b) below. E Click the icon to view the data on business degrees. ..... (a) Find the probability that a randomly selected student is male, given that the student received a business degree. The probability that a randomly selected student is male, given that the student received a business degree, is (Round to three decimal places as needed.) Business Graduates (b) Find the probability that a randomly selected student received a business degree, given that the student is female. The probability that a randomly selected student received a business degree, given that the student is female, is (Round to three decimal places as needed.) Business degrees Nonbusiness degrees Total Male 199,313 600,822 800,135 1,065,757 1,865,892 Female 177,694 888,063 Total 377,007 1,488,885 Print Donearrow_forwardUse the standard normal probability chart, included in this exam, to look up the following numbers and draw the graph for each one. a. - .0492 b. 1.6 c. 1.06 d. -5.2arrow_forward
- The accompanying table describes results from groups of 8 births from 8 different sets of parents. The random variable x represents the number of girls among 8 children. Complete parts (a) through (d) below. Click the icon to view the table. C a. Find the probability of getting exactly 6 girls in 8 births. (Type an integer or a decimal. Do not round.) b. Find the probability of getting 6 or more girls in 8 births. (Type an integer or a decimal. Do not round.) c. Which probability is relevant for determining whether 6 is a significantly high number of girls in 8 births: the result from part (a) or part (b)? O A. The result from part a, since it less than the probability of the given or more extreme result. O B. The result from part a, since it is the exact probability being asked. O C. The result from part b, since it is the complement of the result of part a O D. The result from part b, since it is the probability of the given or more extreme result. d. Is 6 a significantly high number…arrow_forwardThe accompanying table describes results from groups of 8 births from 8 different sets of parents. The random variable x represents the number of girls among 8 children. Complete parts (a) through (d) below. E Click the icon to view the table. a. Find the probability of getting exactly 6 girls in 8 births. (Type an integer or a decimal. Do not round.) b. Find the probability of getting 6 or more girls in 8 births. (Type an integer or a decimal. Do not round.) c. Which probability is relevant for determining whether 6 is a significantly high number of girls in 8 births: the result from part (a) or part (b)? O A. The result from part b, since it is the probability of the given or more extreme result. O B. The result from part a, since it less than the probability of the given or more extreme result. O C. The result from part b, since it is the complement of the result of part a. O D. The result from part a, since it is the exact probability being asked. d. Is 6 a significantly high…arrow_forwardSelect the correct choice below and fill in the answer boxes to complete your choice (Type integers or decimals. Do not round.) A. One can be % confident that the mean drive-through service time of Taco Bell is between seconds and seconds. B. The mean drive-through service time of Taco Bell is of the time. OC. There is a seconds OD. One can be Taco Bell is % % probability that the mean drive-through service time of Taco Bell is between seconds and seconds % confident that the mean drive-through service time of secondsarrow_forward
- Use the data in the following table, which lists survey results from undergraduate school students. Assume that subjects are randomly selected from those included in the table. If one of the students is randomly selected, find the probability that the selected student took online courses and took in-person courses. Round three decimal places. Student Took Online Courses Yes Student took in-person courses 2800 Student have not taken in- 4460 person courses 0.748 354 0.345 O 285 No 720 140arrow_forwardGiven N(23.4, 6.2), the probability that X is less than 23.4, is: 0.25 0.75 0.67 0.5arrow_forwardAnswer Part C only.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman