Question
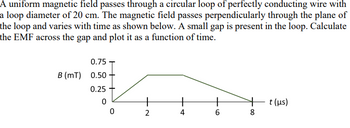
Transcribed Image Text:A uniform magnetic field passes through a circular loop of perfectly conducting wire with
a loop diameter of 20 cm. The magnetic field passes perpendicularly through the plane of
the loop and varies with time as shown below. A small gap is present in the loop. Calculate
the EMF across the gap and plot it as a function of time.
0.75
B (mT) 0.50-
0.25
0
0
+
2
+
4
+
6
+ t (μs)
8
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Consider a straight conductor of length 6.3 cm. The conductor moves at right angles to a magnetic field of uniform strength B = 10-3 T generating e.m.f. of 2.5 × 10-5 v. Calculate the velocity of the straight conductor. Give your answer in SI units. Answer: Choose... + Next page Previous pagearrow_forwardA copper wire is 10.00 m long and has a cross-sectional area of 2.00 ✕ 10-4 m2. This wire forms a one turn loop in the shape of square and is then connected to a battery that applies a potential difference of 0.100 V. If the loop is placed in a uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.400 T, what is the maximum torque that can act on it? The resistivity of copper is 1.7 ✕ 10-8 ·m.arrow_forwardA circular loop of wire has its radius shrink from 3 m to 1.5 m over 5 seconds. The area vector of the wire stays parallel with a magnetic field of magnitude 4 μT. What is the induced emf? 0 V 3.77e-6 V 0.94 V 1.70e-5 Varrow_forward
- b. A 10 cm long solenoid with a radius 1cm has 500 turns. The current in the solenoid is changing at 0.5A per second. Find the followingarrow_forwardSuppose you wish to measure the current in a wire. You have a device that can measure the strength of the magnetic field produced by the wire, but the device does not directly measure the current. If the device is place 1.32m away from the wire, and the magnetic field strength is 0.93μT, what is the current running through the wire in Amps? Note: It is understood that the unit of your answer is in A, however do not explicitly include units in your answer. Enter only a number. If you do enter a unit, your answer will be counted wrong.arrow_forward1. A conducting loop of arca A and resistance R lics at right angles to a spatially uniform magnetic field. At time t = 0, the magnetic field and loop current are both zero. Subsequently, the current increases according to I (t) = bt², where b is a constant with units A/s?. Find an expression for the magnetic field strength as a function of time.arrow_forward
- Q4: Show detailed work and pay attention to the units. There are two different ways to calculate the potential difference across the bar, using the motional EMF expression or Faraday's Law. Show that both methods give the same answer. Use the right hand rule to figure out which end of the bar (A or B) will be at a higher potential due to the motion of the conductor in the field.arrow_forwardA segment of wire 7.9 cm long is moving at a velocity of 5.85 m/s toward a parallel (much longer) wire which carries a current of 9.92 A. At a particular instant the wire segment is 6.9 cm away from the long, current-carrying wire. What is the induced emf (voltage) between the two ends of the wire segment? 5.32E-06 V 1.06E-05 V 1.60E-05 V 1.33E-05 Varrow_forwardA planar coil of wire has a single turn. The normal to this coil is parallel to a uniform and constant (in time) magnetic field of 1.80 T. An emf that has a magnitude of 2.40 V is induced in this coil because the coil's area A is shrinking. What is the magnitude of AA/At, which is the rate (in m²/s) at which the area changes? Number i Unitsarrow_forward
- Here you see a single loop of stiff wire, 10.0 cm on a side, immersed in a magnetic field of 0.225 T. Suppose that you remove the loop from the field in just 0.00208 sec. What emf or voltage will be induced in the loop? Express your answer to three significant figures and in normal notation.arrow_forwardPr1. The figure shows the cross-section of a long, straight, cylindrical coil (solenoid) of radius r = 10 cm. The number of turns per unit length is n = 500 m-1. A direct current I = 1,0 A flows clockwise in the solenoid. A charged particle accelerated by a voltage 1000 V enters into the solenoid through a gap between the coils at point A. The velocity of the particle at point A is pointing along the radius. The particle is traveling inside the solenoid in a plane perpendicular to its axis and exits at point C at an angle a = 60° to its initial direction. 60 Av a) Determine the sign of the charge of the particle. b) What is the radius of the particle's trajectory? c) Find the charge-to-mass (Q/m) ratio of the particle. (The magnetic permeability of vacuum is µo = 47 - 10-7 Vs/Am.)arrow_forwardThe straight wire that has been bent into a perfect circle has been placed in a perpendicular magnetic field has a length of 30.0 cm. The magnetic field is changing at a rate of 13 T/s. If the resistance of the wire loop is 3.6 Ω, the electric current in the wire will be:arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios