
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
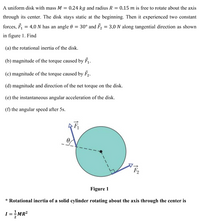
Transcribed Image Text:A uniform disk with mass M
= 0.24 kg and radius R
0.15 m is free to rotate about the axis
through its center. The disk stays static at the beginning. Then it experienced two constant
forces, F, = 4.0 N has an angle 0 = 30° and F, = 3.0 N along tangential direction as shown
in figure 1. Find
(a) the rotational inertia of the disk.
(b) magnitude of the torque caused by F.
(c) magnitude of the torque caused by F2.
(d) magnitude and direction of the net torque on the disk.
(e) the instantaneous angular acceleration of the disk.
(f) the angular speed after 5s.
Figure 1
* Rotational inertia of a solid cylinder rotating about the axis through the center is
=MR?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- An old grindstone, used for sharpening tools, is a solid cylindrical wheel that can rotate about its central axle with negligible friction. The radius of the wheel is 0.330 m. A constant tangential force of 200 N applied to its edge causes the wheel to have an angular acceleration of 0.960 rad/s2. (a) What is the moment of inertia of the wheel (in kg · m2)? b) What is the mass (in kg) of the wheel? (c) The wheel starts from rest and the tangential force remains constant over a time period of 4.50 s. What is the angular speed (in rad/s) of the wheel at the end of this time period?arrow_forwardThe uniform solid block in the figure has mass 33.9 kg and edge lengths a = 0.618 m, b = 1.79 m, and c = 0.0701 m. Calculate its rotational inertia about an axis through one corner and perpendicular to the large faces. Rotation axis Number Unitsarrow_forwardA 2.00 kg solid, uniform sphere rolls without slipping across a level surface, translating at 3.50 m/s. If the sphere's radius is 0.190 m, find the following. HINT Apply the definitions of translational and rotational kinetic energy. Click the hint button again to remove this hint. (a) the sphere's translational kinetic energy (in J) (b) the sphere's rotational kinetic energy (in J)arrow_forward
- what is the correct answer?arrow_forwardWe wrap a light, nonstretching cable around a solid cylinder, of mass 50 kg and diameter 0.120 m, that rotates in frictionless bearings about a stationary horizontal axis (Fig.). We pull the free end of the cable with a constant 9.0 N force for a distance of 2.0 m; it turns the cylinder as it unwinds without slipping. The cylinder is initially at rest. Find its final angular speed and the final speed of the cable.arrow_forwardA wheel of radius 0.159 m, which is moving initially at 45.2 m/s, rolls to a stop in 299 m. Calculate the magnitudes of (a) its linear acceleration and (b) its angular acceleration. (c) The wheel's rotational inertia is 0.298 kg m? about its central axis. Calculate the magnitude of the torque about the central axis due to friction on the wheel. (a) Number Units (b) Number i Units (c) Number Unitsarrow_forward
- A uniform spherical shell of mass M = 3.8 kg and radius R = 7.6 cm can rotate about a vertical axis on frictionless bearings (see figure below). A massless cord passes around the equator of the shell, over a pulley of rotational inertia I = 3.0 x 10-3 kg · m2 and radius r = 5.0 cm, and is attached to a small object of mass m = 0.60 kg. There is no friction on the pulley's axle; the cord does not slip on the pulley. What is the speed of the object after it has fallen 84 cm after being released from rest? Use energy considerations. m/s М, R I, rarrow_forwardA grinding wheel is in the form of a uniform solid disk of radius 6.93 cm and mass 2.06 kg. It starts from rest and accelerates uniformly under the action of the constant torque of 0.608 Nm that the motor exerts on the wheel. (a) How long does the wheel take to reach its final operating speed of 1 260 rev/min? s (b) Through how many revolutions does it turn while accelerating? revarrow_forwardA solid uniform sphere of mass 2.92 kg and diameter 78.6 cm spins about an axle through its senter. Starting with an angular velocity of 11.3 rev/s, it stops after turning through 90.7 rev with uniform acceleration. The magnitude of the net torque (in N m) acting on this sphere as it is slowing down is _________.arrow_forward
- A potter's wheel is a uniform solid disk of radius R = 0.300 m and M = 120 kg. It is initially rotating at 12.0 rad/s. The potter can stop the wheel in 6.00 s by pressing a wet rag against the rim exerting a normal force (radially inward) of 68.0 N. The effect of pressing with the rag produces a frictional torque that brings the wheel to a stop. What is the frictional torque that acts on the wheel while it is %3D slowing down? 125 N-m O - 25.5 N m O - 50.0 N m 12.5 N m O - 10.8 N:m DII 吕口 esc F5 F6 F7 FB F2 F3 F4 @ # $ & Q E R Y D F G K X V 00arrow_forwardTwo wheels have the same mass and radius of 4.6 kg and 0.51 m, respectively. One has the shape of a solid disk. The wheels start from rest and have a constant angular acceleration with respect to a rotational axis that is perpendicular to the plane of the wheel at its center. Each turns through an angle of 13 rad in 9.5 s. Find the net external torque that acts on each wheel.arrow_forwardTwo wheels A and B in the figure are connected by a belt that does not slip. The radius of B is 6.03 times the radius of A. What would be the ratio of the rotational inertias IA/IB if the two wheels had (a) the same angular momentum and (b) the same rotational kinetic energy?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON