
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
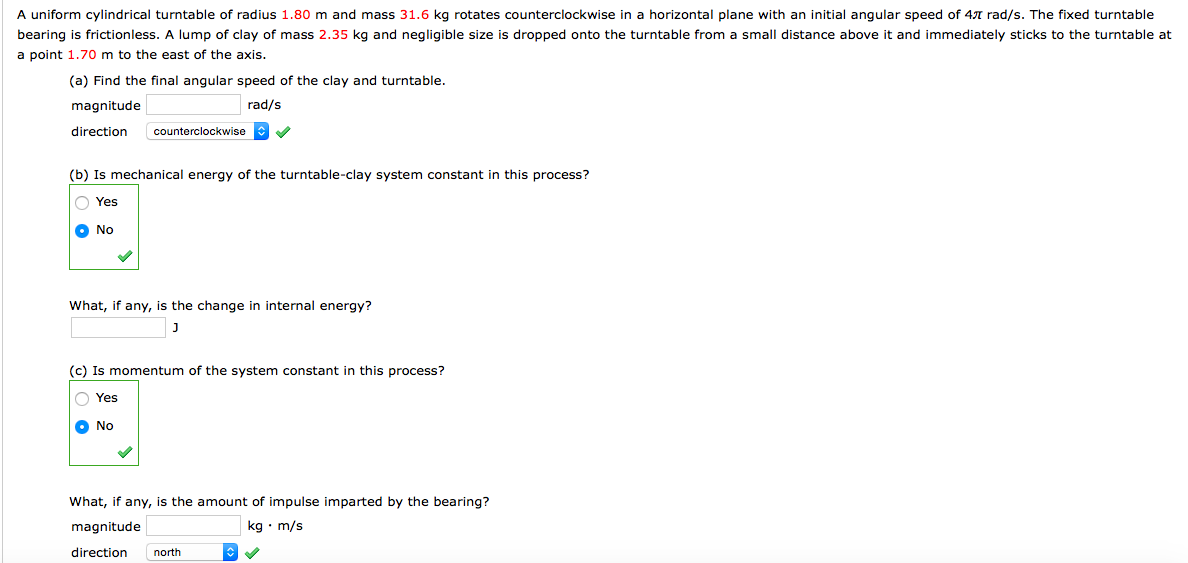
Transcribed Image Text:A uniform cylindrical turntable of radius 1.80 m and mass 31.6 kg rotates counterclockwise in a horizontal plane with an initial angular speed of 47 rad/s. The fixed turntable
bearing is frictionless. A lump of clay of mass 2.35 kg and negligible size is dropped onto the turntable from
small distance above it and immediately sticks to the turntable at
a point 1.70 m to the east of the axis.
(a) Find the final angular speed of the clay and turntable.
magnitude
rad/s
direction
counterclockwise
(b) Is mechanical energy of the turntable-clay system constant in this process?
O Yes
O No
What, if any, is the change in internal energy?
J
(c) Is momentum of the system constant in this process?
O Yes
O No
What, if any, is the amount of impulse imparted by the bearing?
magnitude
kg • m/s
direction
north
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A car is designed to get its energy from a rotating flywheel (solid disk) with a radius of 2.00 m and a mass of 400 kg. Before a trip, the flywheel is attached to an electric motor, which brings the flywheel's rotational speed up to 4500 rev/min. (a) Find the kinetic energy stored in the flywheel. (b) If the flywheel is to supply energy to the car as would a 20.0-hp motor, find the length of time the car could run before the flywheel would have to be brought back up to speed.arrow_forwardA disk of mass M is spinning freely at 4.77 rad/s when a second identical disk, initially not spinning, is dropped onto it so that their axes coincide. In a short time the two disks are corotating. (a)What is the angular speed of the new system (in rad/s)? (b) If a third such disk is dropped on the first two, find the final angular speed of the system (in rad/s).arrow_forwardA horizontal 790-N merry-go-round of radius 1.30 m is started from rest by a constant horizontal force of 45 N applied tangentially to the merry-go-round. Find the kinetic energy of the merry-go-round after 5.0 s. (Assume it is a solid cylinder. Also assume the force is applied at the outside edge.)arrow_forward
- A hollow cylinder has radius 9.5 cm and mass 1.8 kg. The cylinder rolls without slipping at a speed of 1.488 m/s, and begins to roll without slipping up a(n) 11° slope. What is the maximum height the cylinder will reach on the inclined plane when it comes to a stop?arrow_forwardAn electric motor rotating a workshop grinding wheel at 1.08 x 10 rev/min is switched off. Assume the wheel has a constant negative angular acceleration of magnitude 2.06 rad/s? (a) How long does it take the grinding wheel to stop? Note that the time required for the wheel to stop is the same as the time for the wheel to start from rest and reach the given angular speed with the same magnitude angular acceleration, s (b) Through how many radians has the wheel turned during the time interval found in part (a)? It might be helpful to translate this problems into linear variables (a car traveling with an initial speed and then slowing down with a constant negative acceleration), rad Need Help? Road Masterarrow_forwardA uniform solid cylinder of mass M=2 kg and radius R=0.49 m is given an initial angular speed ω=15 rad/s when it is at the bottom of an inclined plane of height h=4.1 m, as shown in the figure. The cylinder rolls without slipping. Find ω if the cylinder comes to rest at the top of the inclined plane. (Take g=9.81 m/s2, Icylinder=1/2MR2 ).arrow_forward
- A ceiling fan can accelerate from rest to 2pi rad/s in 8 seconds. (A) what is the angular acceleration of the fan? (B) find the angular displacement of the fan during the first 5 seconds. (C) at the full angular speed of 2pi rad/s find the corresponding tangential speed of a point at the rim of the wing if the radius of the wing is r=0.5m. (D) what is the centripetal acceleration of a point at the rim (r=0.5 m) when the fan reaches full speed? can you give detailed steps please?arrow_forwardA large wooden turntable in the shape of a flat uniform disk has a radius of 2.00 m and a total mass of 120 kg. The turntable is initially rotating at 3.00 rad/s about a vertical axis through its center. Suddenly, a 70.0 kg parachutist makes a soft landing on the turntable at a point near the outer edge. (a) Find the angular speed of the turntable after the parachutist lands. (As- sume that you can treat the parachutist as a particle.) (b) Compute the kinetic energy of the system before and after the parachutist lands. (c) Are those two kinetic energies equal? If not explain the causes of this difference.arrow_forwardIn the system , a 12.0 kg mass is released from rest and falls, causing the uniform 10.0 kg cylinder of diameter 30.0 cm to turn about a frictionless axle through its center. How far will the mass have to descend to give the cylinder 480 J of kinetic energy?arrow_forward
- The figure shows a uniform disk that can rotate around its center like a merry-go-round. The disk has a radius of 2.3 cm and a mass of 19 grams and is initially at rest. Starting at time t= 0, two forces are to be applied tangentially to the rim as indicated, so that at time t = 1.3 s the disk has an angular velocity of 200 rad/s counterclockwise. Force F, has a magnitude of 0.100 N. What is magnitude F2? Number i Units eTextbook and Media Hint GO Tutorial tv DII DD 888 F12 F10 F11 E7 F8 F9 F6 F4 F5 F1 F2 F3 ) 1 & 23 2$ 4 6 7 8 9. 3 { Q W E Y H K ...- * COarrow_forwardThe figure shows a uniform disk that can rotate around its center like a merry-go-round. The disk has a radius of 2.1 cm and a mass of 16 grams and is initially at rest. Starting at time t = 0, two forces are to be applied tangentially to the rim as indicated, so that at time t = 1.3 s the disk has an angular velocity of 260 rad/s counterclockwise. Force F, has a magnitude of 0.105 N. What is magnitude F2? F Number i Unitsarrow_forwardA horizontal 810-N merry-go-round of radius 1.20 m is started from rest by a constant horizontal force of 55 N applied tangentially to the merry-go-round. Find the kinetic energy of the merry-go-round after 2.0 s. (Assume it is a solid cylinder. Also assume the force is applied at the outside edge.)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON