
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780133923605
Author: Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Electronics
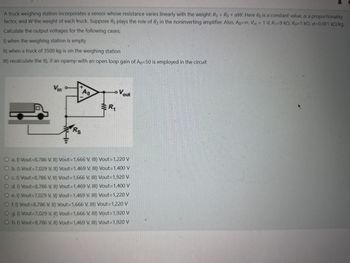
Transcribed Image Text:A truck weighing station incorporates a sensor whose resistance varies linearly with the weight: Rs = Ro+aw. Here Ro is a constant value, a a proportionality
factor, and W the weight of each truck. Suppose Rs plays the role of R2 in the noninverting amplifier. Also, Ap=co, Vin = 1 V, R1=9 ko, Ro=1 ko, a=0.001 kn/kg.
Calculate the output voltages for the following cases;
1) when the weighing station is empty
II) when a truck of 3500 kg is on the weighing station
III) recalculate the II), if an opamp with an open loop gain of A0=50 is employed in the circuit
LoVout
Vin
Ao
R₁
HI
Rs
O a. 1) Vout=8,786 V, II) Vout=1,666 V, III) Vout=1,220 V
O b. 1) Vout-7,029 V, II) Vout=1,469 V, III) Vout=1,400 V
O c. 1) Vout=8,786 V, II) Vout=1,666 V, III) Vout=1,920 V
O d. 1) Vout=8,786 V, II) Vout=1,469 V, III) Vout = 1,400 V
O e. 1) Vout-7,029 V, II) Vout=1,469 V, III) Vout=1,220 V
O f. 1) Vout=8,786 V, II) Vout =1,666 V, III) Vout =1,220 V
O g. 1) Vout-7,029 V, II) Vout=1,666 V, III) Vout=1,920 V
O h. 1) Vout=8,786 V, II) Vout=1,469 V, III) Vout =1,920 V
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 3)please solve! Will upvotearrow_forwardplease show step by step working for this question with circuit diagrams if possible so I can understand the circuit better thank you.(please handwrite the solutions)arrow_forwardThe circuit shown in the following in figure has: VIN= 10 V, Vz = 7.2 V@ Iz-40 mA, Izk =2 mA, IzM= 100 mA and Zz-5 2. Determine a) Maximum output voltage. b) Minimum output voltage. c) The percentage load regulation. d) The minimum permissible load resistor value. c) The maximum permissible load resistor value. R 2211 VISarrow_forward
- Design the fixed bias circuit for the 2N5951 N-channel JFET transistor to achieve an operating point of (Jp=4mA VDS=12 V) if it has a source VDD=24 V, draw the corresponding circuitFrom the datasheet we get VGSOFF=-5V; I_DSS=13 mAarrow_forwardIs the small signal equivalent circuit for this diagram correct? How do we add cg and Cs?arrow_forwardHow did they get this circuit? Break down simplyarrow_forward
- 24. Set up a midpoint bias for a JFET with Ipss = 14 mA and VGs(ofm = -10 V. Use a 24 V dc source as the supply voltage. Show the circuit and resistor values. Indicate the values of Ip, VGs, and Vps-arrow_forwarda. A 5-bit DAC has a current output. For a digital input of 101000, an output current of 10mA is produced. What will be Iout for a digital input of 11101? b. An 8-bit DAC has an output voltage range of 0-2.55V.Determine its resolution in two ways. c. List out and explain any two methods of D to A conversion.arrow_forwardPlease answer in typing format please ASAP for the Please I will like it please I appreciate your support and Iarrow_forward
- please answer all thanks !arrow_forwardTo a measurement range of -4 to 6 V, apply a 4-bit analog-to-digital converter. 1- Identify the assigned voltages to each of the bins. 2- Determine the voltage that will be assigned to a measurement reading -3.25 V. Calculate the percentage ADC error. 3- Determine the voltage that will be assigned to a measurement reading 4.11 V. Calculate the percentage ADC error. Solve step by step properly.arrow_forwardPlease answer ASAP. I will rate Positivelyarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,