
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
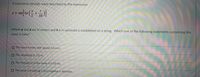
Transcribed Image Text:A transverse periodic wave described by the expression
y = sin
(where y and x are in meters and t is in seconds) is established on a string. Which one of the following statements concerning this
wave is false?
O The wave travels with speed 5.0 m/s.
O The amplitude is 1.0 m.
O The frequency of the wave is 0.10 Hz.
O The wave is traveling in the negative x direction.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The graph below represents the displacement caused by a mechanical wave traveling along a rope (y axis), versus the distance that the wave has traveled along the rope (x axis). displacement / cm 0.5 8distance / m -0.5 If the wave has a frequency of 300 Hz, determine the speed of the wave. O 1200 cm/s O 300 cm/s O 150 cm/s O 2400 cm/s O 600 cm/s O 1800 cm/sarrow_forwardA harmonic wave travels in the positive x direction at 11 m/s along a taught string. A fixed point on the string oscillates as a function of time according to the equationy = 0.021 cos(1t)where y is the displacement in meters and the time t is in seconds. The amplitude of the wave is 0.021 m. What is the frequency of the wave, in hertz?arrow_forwardO y_1 (x,t)=1mm sin(2rx-20Ttt) and y_2 (x,t)=1mm sin(2rx+20rtt) A sinusoidal transverse wave has a wavelength of 2.8 m. It takes 0.2 s for an element of the string at a position x to move from the maximum position of ymax = 0.03 m to the equilibrium position y 0. What is the period of the wave, T, and the wave speed, v? 0.4 sec; 7 m/s O 0.8 sec; 14 m/s O 0.8 sec; 3.5 m/s 0.4 sec; 28 m/s A taut string fixed at both ends is driven by an oscillator at a constant frequency of 100 Hz. The amplitudearrow_forward
- A 38.0-Hz sound wave is barely audible at a sound intensity level of 60.0 dB. The density of air at 20.0°C is 1.20 kg/m3. Speed of sound in air at 20.0°C is 343 m/s. What is the displacement amplitude of a 38.0-Hz sound wave? What is the ratio of the displacement amplitude to the average distance between molecules in air at room temperature, about 3.00 nm?arrow_forwardA transverse wave has a frequency of ν = 74 Hz and a wavelength of λ = 11.5 m. The wave obtains a maximum displacement of ym = 2.5 m and propagates in the -x direction. Given the form y(x,t) = A sin(B) for the displacement of the wave, input an expression for A. Using the same form y(x,t) input an expression for B. How fast is the wave traveling in m/s?arrow_forwardTwo waves are traveling on the same string. The displacement of the first is given by y₁ = (0.200 m) sin [(400л s¯¹)t — (2л m¯¹)×] and of the second by y2 = (0.300 m) sin (400л s¯¹)t − (2ë m¯¹)x + x and y in meters and t in seconds. What is the phase constant of the resultant wave? i - rad wi , witharrow_forward
- Determine the wave speed of a transverse wave that is propagating along the x-axis whose vertical displacement y as a function of position x and time t is y (x,t) = 3.4 cos(4.1x - 2.2t + 7.9) where all quantities are measured in standard SI units of meters, seconds, and radians. O 0.33 m/s O 0.89 m/s O 1.6 m/s O 2.0 m/s O 0.54 m/sarrow_forwardTwo wave pulses A and B are moving in opposite directions, each with a speed v 5 2.00 cm/s. The amplitude of A is twice the amplitude of B. The pulses are as shown at t = 0. Sketch the resultant wave at t = 1.00 s, 1.50 s, 2.00 s, 2.50 s, and 3.00 s.arrow_forwardYour answer is partially correct. A transverse wave on a string has an amplitude of 0.188 m and a frequency of 215 Hz. Consider the particle of the string at x = 0 m. It begins with a displacement of y=0m when t = 0 s. How much time passes between the first two instants when this particle has a displacement of y = 0.0817 m? Number i -0.000332 Units Sarrow_forward
- A certain traveling wave on a string obeys the function: y1(x, t) = 0.5m cos((0.25π rad/m) x + (1.25π rad/s) t) What is the direction and speed of this wave? negative in the x direction and 5m/s 2b. A second wave is traveling on the same string in the opposite direction and is described by the function, y2(x,t) = 1.2m cos((5.75 rad/m) x - (2.50 rad/s)t). What is the direction and speed of this wave? positive in the x direction and 0.43m/s 2c. The two waves overlap at the point x = 0.47 m when t = 3.2 s, what is the amplitude of the string at this point and time? y1(x, t) = 0.5m cos((0.25π rad/m) (0.47) + (1.25π rad/s)(3.2))=? i get 0.47m is this correct? y2(x,t) = 1.2m cos((5.75 rad/m) (0.47) - (2.50 rad/s)(3.2))=? 0.66m is this correct? im looking for guidance on 2c the one that has been answered on the site I don't understand how that answer was attained and need clarificationarrow_forwardThe equation for the displacement of a stationary wave on a string is given by y = 2 (sin 5πt)(cos 6πx), where x and y are in meters, and t is in seconds. Determine: a. wave period!arrow_forwardThe equation for the displacement of a stationary wave on a string is given by y = 2 (sin 5πt)(cos 6πx), where x and y are in meters, and t is in seconds. Determine: b. the amplitude of the point P which lies at a distance of 75 cm from the end of the reflection!arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON