
Concept explainers
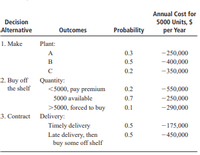
A total of 5000 mechanical subassemblies are needed annually on a final assembly line. The subassemblies can be obtained in one of three ways: (1) Make them in one of three plants owned by the company; (2) buy them off the shelf from the one and only manufacturer; or (3) contract to have them made to specifications by a vendor. The estimated annual equivalent cost for each alternative is dependent upon specific circumstances of the plant, producer, or contractor. The information shown details the circumstance, a probability of occurrence, and the estimated annual cost. Construct and solve a decision tree to determine the least-cost alternative to provide the subassemblies.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

- If the actual production for a month is 216 and the required production is 200, how many units need to be subcontracted?arrow_forwardIt is important to look at the version, variant, and configuration object management capabilities of an SCM solution.arrow_forwardChick-Fil-A is Why I’m Always Over Budget (COB) is trying to decide the best use of its time on the assembly line. Chicken nuggets require 1 labor hour each, but chicken strips require 3 labor hours each. Chicken nuggets sell for $42 with a variable cost of $20. Chicken strips sell for $57 with a variable cost of $24. Calculate the following: Which product should COB focus on when allocating assembly line hours? A. Chicken Fries B. Chicken Nuggets C. Chicken Wings D. Chicken Stripsarrow_forward
- The unit cost for Item #10286 has increased from $90.00 to $120.00. Howdoes this impact the ABC analysis?arrow_forwardYou have developed the following simple product structure of items needed for your gift bag for a rush party for prospective pledges in your organization. You forecast 200 attendees. Assume that there is no inventory on hand of any of the items. Explode the bill of material. (Subscripts indicate the number of units required.) Determine the number of units of each item required. Item K: Item L: Item M: units (enter your response as a whole number). units (enter your response as a whole number). units (enter your response as a whole number). K(1) (5) M(2)arrow_forwardNeed both partsarrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage, Operations ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781259667473Author:William J StevensonPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Operations ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781259667473Author:William J StevensonPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781259666100Author:F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B ChasePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781259666100Author:F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B ChasePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781478623069Author:Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon OlsenPublisher:Waveland Press, Inc.
Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781478623069Author:Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon OlsenPublisher:Waveland Press, Inc.





