
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
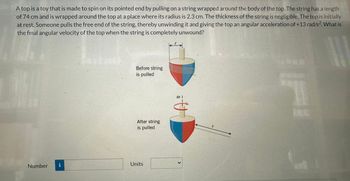
Transcribed Image Text:A top is a toy that is made to spin on its pointed end by pulling on a string wrapped around the body of the top. The string has a length
of 74 cm and is wrapped around the top at a place where its radius is 2.3 cm. The thickness of the string is negligible. The top is initially
at rest. Someone pulls the free end of the string, thereby unwinding it and giving the top an angular acceleration of +13 rad/s2. What is
the final angular velocity of the top when the string is completely unwound?
L
Number
i
Before string
is pulled
After string
is pulled
Units
@ 1
S
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A dragster starts from rest and accelerates down a track. Each tire has a radius of 0.320 m and rolls without slipping. At a distance of 418 m, the angular speed of the wheels is 255 rad/s. Determine (a) the linear speed of the dragster and (b) the magnitude of the angular acceleration of its wheels. (a) v = (b) a= i iarrow_forwardA wind turbine is initially spinning at a constant angular speed. As the wind's strength gradually increases, the turbine experiences a constant angular acceleration 0.140 rad/s2. After making 2870 revolutions, its angular speed is 157 rad/s. (a) What is the initial angular velocity of the turbine? (b) How much time elapses while the turbine is speeding up? (a) Number Units (b) Number Unitsarrow_forwardA wind turbine is initially spinning at a constant angular speed. As the wind's strength gradually increases, the turbine experiences a constant angular acceleration 0.149 rad/s2. After making 2870 revolutions, its angular speed is 151 rad/s. (a) What is the initial angular velocity of the turbine? (b) How much time elapses while the turbine is speeding up?(a) Number Units (b) Number Unitsarrow_forward
- A solid disk of uniform density and mass M = 0.950 kg with radius R = 0.250 m is suspended vertically and is free to rotate about its center without friction. A point object that has the same mass as the disk is placed at an angle 0 = 25.0° clockwise from the top along the rim, causing the disk to rotate. The acceleration due to gravity is g=9.81m/s². What is the angular speed wf of the disk when the point object is directly below the center of the disk? R 0.arrow_forwardA cylindrical fishing reel has a moment of inertia of I = 6.6 x 104 kg-m² and a radius of 4.0 cm. A friction clutch in the reel exerts a restraining torque of 1.3 N-m if a fish pulls on the line. The fisherman gets a bite, and the reel begins to spin with an angular acceleration of 66 rad/s². (a) What is the force of the fish on the line? N (b) How much line unwinds in 0.45 s? cmarrow_forwardA top is a toy that is made to spin on its pointed end by pulling on a string wrapped around the body of the top. The string has a length of 23 cm and is wrapped around the top at a place where its radius is 82.21 cm. The thickness of the string is negligible. The top is initially at rest. Someone pulls the free end of the string, thereby unwinding it and giving the top an angular acceleration of +80 rad/s^2. What is the final angular velocity of the top when the string is completely unwound? Note: Express your answer in whole numbers. No unit is required for the final answer. Set your calculator in radians. Round your answer to 0 decimal places. Add your answerarrow_forward
- A small 0.360-kg object moves on a frictionless horizontal table in a circular path of radius 3.00 m. The angular speed is 4.97 rad/s. The object is attached to a string of negligible mass that passes through a small hole in the table at the center of the circle. Someone under the table begins to pull the string downward to make the circle smaller. If the string will tolerate a tension of no more than 160 N, what is the radius of the smallest possible circle on which the object can move?arrow_forwardA thin rod has a length of 0.537 m and rotates in a circle on a frictionless tabletop. The axis is perpendicular to the length of the rod at one of its ends. The rod has an angular velocity of 0.778 rad/s and a moment of inertia of 1.10 x 10³ kg-m². A bug standing on the axis decides to crawl out to the other end of the rod. When the bug (whose mass is 5 x 10-3 kg) gets where it's going, what is the change in the angular velocity of the rod?arrow_forwardA small pine tree has a mass of 19 kg. Its center of mass is located at 0.87 m from the ground. Its trunk is sawed though at ground level, causing the tree to fall, with the severed trunk acting as the pivot point. At the instant the falling tree makes a 16° angle with the vertical, the angular acceleration of the tree is 2.6 rad/s. What is the moment of inertia of the tree?arrow_forward
- A bicycle wheel initially is spinning with a tangential speed of 9 m/s. The radius of this wheel is 0.737 m, and its mass is 1 kg. The wheel takes 200 s to gradually stop spinning. Assuming the acceleration remains constant as the wheel slows down, through what total angle does it spin? 1175 rad 974 rad 1452 rad 1222 rad 1580 radarrow_forwardA thin rod has a length of .340 m and rotates in a circle on a frictionless tabletop. The axis is perpendicular to the length of the rod at one of its ends. The rod has an angular velocity of. 435 rad/s and a moment of inertia of 1.04 x 10-3 kg.m2. A bug standing on the axis decides to crawl out to the other end of the rod. When the bug ( whose mass is 5 x 10-3) gets where it's going, what is the change in the angular velocity of the rod ?arrow_forwardA uniform disk with radius R = [R} m and mass [M} kg rotates in a horizontal plane on a frictionless vertical axle that passes through the center of the disk. The angle through which the disk has turned varies with time according to 0(t) =3.4t + 1.1t³ rads. What is the angular acceleration (rad/s?) of a point on the rim of the disk at the instant after 1.1 s.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON