
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
A system consists of three identical 13.32-lb particles A, B, and C. The velocities of the particles are, respectively, vA = vA j, vB = vBi, and vC = vCk. The angular momentum of the system about O expressed in ft·lb·s is HO = -1.2k.
a) Determine the velocities of the particles.
b) Determine the angular momentum of the system about its mass center G.
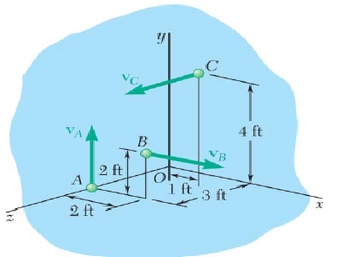
Transcribed Image Text:A
A
2 ft
B
affo
2 ft
NB
1 ft 3 ft
4 ft
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The vehicle shown starts from rest at the bottom of the hill and accelerates up the hill due to the force FR from the road. Note that this is a static friction force and is not dissipative. Vrop = 9.7 m/s m = 1600 kg h = 50 m FR = 7300 N 0 = 25° A) If the vehicle reaches the top of the hill with the speed shown, how much thermal energy is dissipated in the process? B) Assuming that air drag, Fang , is the only dissipative force during this process, try to estimate the cross-sectional area of the vehicle "seen" by the air. In the formula for air drag, regard the car's speed as being a constant v = 5.0 m/s (this speed is roughly half of the starting and ending speeds). Use C = 0.5 for the drag coefficient and p = 1.25 kg/m³ for air density.arrow_forwardPlease include the figure, fbd and formula. An empty freight car with a mass of 10,000 kg rolls at 5 m/s along a level track and collides with a loaded car with a mass of 20,000 kg, standing at rest with brakes released. Friction can be neglected. If the cars couple together, find their speed after the collision. a. Find the decrease in kinetic energy as a result of the collision. b. With what speed should the loaded car be rolling towards the empty car for both to be brought to rest by the collision?arrow_forwardQuestion 9 A car of mass 1200 kg is travelling west with a velocity of 72 kmh=1. It takes a left turn at 50° and continues with the same speed. It takes 5.5 s to turn the corner. a. Find the change in momentum of the car as it rounds the corner. b. Find the force the road applies to the cars tyres as it turns the corner. c. Find the force the car's tyres apply to the road as it turns the corner.arrow_forward
- A 1.5 kg mass is attached to a 1.6 m long rigid rod of negligible mass that is anchored to the ceiling. The mass is pulled back to an initial angle of 45°and released with an initial speed of 3.0 m/s. Note: The mass is initially moving down not up! 2. L m (a) [Hint: The height of the mass above its lowest point is L(1 – cos 0).] How fast is the mass moving at the bottoms of its swing, when 0 = 0°?arrow_forwardk k F Two masses, m¡ and m2 are attached in series by two springs. A force, F is applied to the second mass. Each spring has spring constant, k. The position of each mass is described by x1 and x2, where Fspring 1 = -kx1 and Fspring 2 = -k(x2 – x1) 1. write out the kinetic and potential energy in terms of x1 and x2 2. Use the Lagrange equations to write out two coupled ordinary differential equations here, the force F does virtual work, F8x2arrow_forwardBlock A is initially held at rest. Find how far it will descend before its velocity is momentarily zero. (This is different from finding the point where there would be equilibrium).arrow_forward
- Please asaparrow_forward5.78arrow_forwardFirecracker a. A firecracker is at rest on a frictionless horizontal table. The firecracker explodes into two pieces of unequal mass that move in opposite directions on the table. Before i. Is the net force on the left piece always zero? Explain. After I1. Is the net force on the system consisting of both pieces always zero? Explain. iii. Is the momentum of the left piece conserved? Explain. 1V. Is the momentum of the system consisting of both pieces conserved? Explain.arrow_forward
- A system consists of three particles A, B, and C. We know that *, -1 kg, *, - 2 kg, and mc - 3 kg and that the velocities of the particles expressed in mis ane, respectively, 4 - 34 - 2j + 4k, *g = 4i+3) and vc*-21 + 5j-3k. Determine the angular momentum H, of the system about O.arrow_forwardPart A The 2.2-Mg car increases its speed uniformly from rest to 17 m/s in 40 s up the inclined road. Determine the maximum power that must be supplied by the engine, which operates with an efficiency of e = 0.8. (Figure 1) Express your answer with the appropriate units. HA Pmax = 52.39 kW Submit Previous Answers Request Answer X Incorrect; Try Again Part B Also, find the average power supplied by the engine. Figure 1 of 1 Express your answer with the appropriate units. Pavg = |26.19 kW Submit Previous Answers Request Answer 10 X Incorrect; Try Againarrow_forwardhelp me answer this one pls i need helparrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY