
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
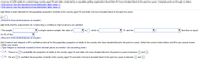
Transcribed Image Text:A survey of 2283 adults in a certain large country aged 18 and older conducted by a reputable polling organization found that 411 have donated blood in the past two years. Complete parts (a) through (c) below.
Click here to view the standard normal distribution table (page 1).
Click here to view the standard normal distribution table (page 2).
(a) Obtain a point estimate for the population proportion of adults in the country aged 18 and older who have donated blood in the past two years.
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
(b) Verify that the requirements for constructing a confidence interval about p
satisfied.
The sample
a simple random sample, the value of
V is I. which is
V 10, and the
V less than or equal
to 5% of the
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
(c) Construct and interpret a 90% confidence interval for the population proportion of adults in the country who have donated blood in the past two years. Select the correct choice below and fill in any answer boxes
within your choice.
(Type integers or decimals rounded to three decimal places as needed. Use ascending order.)
O A. There is a
% probability the proportion of adults in the country aged 18 and older who have donated blood in the past two years is between
and
O B. We are
% confident the proportion of adults in the country aged 18 and older who have donated blood in the past two years is between
and
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A developmental psychologist is interested in studying how long babies gaze at a photograph of a human face. To test this question, she shows a picture to a sample of six babies and records the length of their gaze in seconds. The data are as follows: 12, 17, 18, 20, 20, 29. Calculate the mean, median, mode, range, variance and standard deviation for the sample.arrow_forwardA survey of 2305 adults in a certain large country aged 18 and older conducted by a reputable polling organization found that 411 have donated blood in the past two years. Complete parts (a) through (c) below. Click here to view the standard normal distribution table (page 1). Click here to view the standard normal distribution table (page 2). A Question Help (a) Obtain a point estimate for the population proportion of adults in the country aged 18 and older who have donated blood in the past two years. p= 0.178 (Round to three decimal places as needed.) (b) Verify that the requirements for constructing a confidence interval about p are satisfied. The sample a simple random sample, the value of is which is 10, and the less than or equal to 5% of the (Round to three decimal places as needed.) Enter your answer in the answer box and then click Check Answer. 1 part remaining Clear All Check Answer PAES MAY W 4 F12 F11 F9 F10 F8 F7 F6 吕口 F3 F5 F4 F2 & * $ % 7 8. 2 3 4 T Y U E R Q G H iİŞarrow_forwardAccording to a survey in a country, 32% of adults do not own a credit card. Suppose a simple random sample of 600 adults is obtained. Complete parts (a) through (d) below. Click here to view the standard normal distribution table (page 1). Click here to view the standard normal distribution table (page 2). (a) Describe the sampling distribution of p, the sample proportion of adults who do not own a credit card. Choose the phrase that best describes the shape of the sampling distribution of p below. O A. Not normal because n <0.05N and np(1 – p)< 10 GB. Approximately normal because n<0.05N and np(1 - p) 2 10 CC. Not normal because ns0.05N and np(1 - p) 2 10 D. Approximately normal because n<0.05N and np(1 - p)< 10 Determine the mean of the sampling distribution of p. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) p Enter your answer in the answer box and then click Check Answer. ? 6. parts remaining Clear All Check Answerarrow_forward
- Sixty-two percent of seniors attend a particular school in a school district. Assume 500 seniors within this school district are sampled. a. Can this distribution be approximated using the Normal model? Explain. b. Use the Normal approximation to estimate the probability that at least 290 senior students are enrolled at this particular school. c. Use the Normal model to estimate the probability that between 200 and 300 senior students who are sampled are enrolled at this particular school.arrow_forwardUse the standard normal distribution table to determine the percent of data between z=1.04 and z=1.32. The percent of data between z=1.04 and z=1.32 isarrow_forwardAccording to the Carnegie unit system, the recommended number of hours students should study per unit is 2. Are statistics students' study hours different from the recommended number of hours per unit? The data show the results of a survey of 16 statistics students who were asked how many hours per unit they studied. Assume a normal distribution for the population. 1.5, 2, 2.9, 3.8, 4.6, 1.1, 1.8, 2.6, 1.4, 2.8, 4.5, 1.2, 1, 0.7, 3, 1.2 What can be concluded at the αα = 0.05 level of significance? For this study, we should use Select an answer t-test for a population mean z-test for a population proportion The null and alternative hypotheses would be: H0:H0: ? μ p Select an answer < ≠ = > H1:H1: ? p μ Select an answer < ≠ = > The test statistic ? z t = (please show your answer to 3 decimal places.) The p-value = (Please show your answer to 4 decimal places.) The p-value is ? > ≤ αα Based on this, we should Select an answer reject fail to…arrow_forward
- According to the Carnegie unit system, the recommended number of hours students should study per unit is 2. Are statistics students' study hours more than the recommended number of hours per unit? The data show the results of a survey of 12 statistics students who were asked how many hours per unit they studied. Assume a normal distribution for the population. 1.2, 4.3, 4.5, 1.4, 1.5, 2.7, 1.8, 2.4, 1.3, 2, 2.2, 1.3 What can be concluded at the αα = 0.05 level of significance? A. Thus, the final conclusion is that ... The data suggest the populaton mean is significantly more than 2 at αα = 0.05, so there is enough evidence to conclude that the population mean study time per unit for statistics students is more than 2. The data suggest the population mean is not significantly more than 2 at αα = 0.05, so there is enough evidence to conclude that the population mean study time per unit for statistics students is equal to 2. The data suggest that the population mean study time per…arrow_forwardThanksarrow_forwardIn a survey conducted by a reputable marketing agency, 241 of 1000 adults 19 years of age or older confessed to bringing and using their cell phone every trip to the bathroom (confessions included texting and answering phone calls). Complete parts (a) through (f) below. Click here to view the standard normal distribution table (page 1). Click here to view the standard normal distribution table (page 2). (a) What is the sample in this study? What is the population of interest? Determine the sample in this study. Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box within your choice. O A. The sample is all adults with a cell phone. O B. The sample is all adults 19 years of age or older. O C. The sample is the adults 19 years of age or older. (Type a whole number.) O D. The sample is all adults.arrow_forward
- The 2018 General Social Survey contains information on the number of 1F poor mental health days adults in the US had in the last month. The data arę below. Calculate the standard error of the mean number of poor health days for females. Table 1. Mean number of poor mental health days in the last 30 days by sex Male Female Total Mean S.D. 3.55 6.78 1408 3.02 4.06 6.43 7.07 678 730 Source GSS 2018 Your answerarrow_forwardAn immunologist wants to compare two rabies vaccines. People who had previously received the vaccine were divided into two groups. The first group received a booster dose of type I vaccine and the second group received a booster dose of type II vaccine. Two weeks later the antibody level was measured. The average number of antibodies in each group appears in the following table Do these data indicate that there is a difference in the effectiveness of the two vaccines used for booster doses? Assume a normal distribution and equal population variances. The test statistic that will determine if there is a difference in the effectiveness of the two vaccines..... A. 2,579 B. 2.76 C. 0.58 D. 0.787arrow_forward9. If we take samples of size 110 from a population with proportion 0.39, comment on whether the sampling distribution follows a normal distribution. Explain.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman