
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
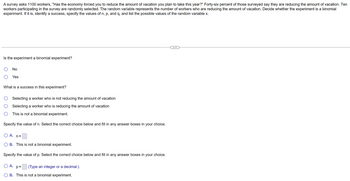
Transcribed Image Text:A survey asks 1100 workers, "Has the economy forced you to reduce the amount of vacation you plan to take this year?" Forty-six percent of those surveyed say they are reducing the amount of vacation. Ten
workers participating in the survey are randomly selected. The random variable represents the number of workers who are reducing the amount of vacation. Decide whether the experiment is a binomial
experiment. If it is, identify a success, specify the values of n, p, and q, and list the possible values of the random variable x.
Is the experiment a binomial experiment?
No
Yes
What is a success in this experiment?
Selecting a worker who is not reducing the amount of vacation
Selecting a worker who is reducing the amount of vacation
This is not a binomial experiment.
Specify the value of n. Select the correct choice below and fill in any answer boxes in your choice.
O A. n=
B. This is not a binomial experiment.
Specify the value of p. Select the correct choice below and fill in any answer boxes in your choice.
O A.
(Type an integer or a decimal.)
p=
B. This is not a binomial experiment.
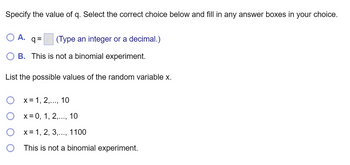
Transcribed Image Text:Specify the value of q. Select the correct choice below and fill in any answer boxes in your choice.
O A. q=
(Type an integer or a decimal.)
B. This is not a binomial experiment.
List the possible values of the random variable x.
O x= 1, 2,..., 10
x = 0, 1, 2,..., 10
O x= 1, 2, 3,..., 1100
This is not a binomial experiment.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A statistics instructor wants to measure the effectiveness of his teaching skills in a class of 102 students (N = 102). He selects students by waiting at the door to the classroom prior to his lecture and pulling aside every third student to give him or her a questionnaire. Is this sample design an example of random sampling? Explain. Assuming that all students attend his class that day, how many students will the instructor select to complete his questionnaire?arrow_forwardIf you know the names of the remaining seven students in the spelling bee, what is the probability of randomly selecting an order and getting the order that is used in the spelling bee? P(selecting the correct spelling bee order) = %3D (Type an integer or a simplified fraction.)arrow_forwardA coach is interested in how many slam dunks the average college freshman at his university can do. Ten volunteers from the senior class step forward. After observing their performance, the coach concluded that college seniors can do an average of 10 slam dunks in a row without missing. what is the sample? what is the population?arrow_forward
- Homework 7.2 1. Four students are randomly selected from an algebra class and asked whether they suffer from math anxiety. Find the sample space for the possible outcomes of the survey using a tree diagram.arrow_forwardclaim: most adults would erase all of their personal information online if they could. A software firm survey of 403 randomly selected adult showed that 50% of them would erase all of their personal information online if they could. Find the value of the test statistic.arrow_forwardA small shop owner wants to see how much people are spending at her store, so she numbers all the receipts from the past week and uses a computer program to generate a list of 20 random numbers. She samples the receipts that correspond to those numbers. What type of sample was taken? convenience sample simple random sample systematic sample cluster sample quota sample voluntary response samplearrow_forward
- A bowl of candy contains 21 green, 8 white, and 16 orange candies. TWO candies are randomly selected from the bowl. d) Find the number in the sample space of this experiment. n(S)= ? Write your answer as a whole number. e) Find the probability of event E: selecting 1 white candy and 1 orange candy. p(E)= ? Write your answer as a percent rounded to one decimal place.arrow_forwardA store owner wants to know if he sells more sandals or sunglasses during the summer. He records the number of sales for both products for the entire month of June. What is the data-gathering technique used? A experiment randomized survey observational study D voluntary survey Carrow_forwardFind the indicated probability. Round to three decimal places.A company purchases shipments of machine components and uses this acceptance sampling plan: Randomly select and test 29 components and accept the whole batch if there are fewer than 3 defectives. If a particular shipment of thousands of components actually has a 7% rate of defects, what is the probability that this whole shipment will be accepted? Group of answer choices 0.280 0.546 0.668 0.190arrow_forward
- Determine if the following probability experiment represents a binomial experiment. If not, explain why. If the probability experiment is a binomial experiment, state the number of trials, n, and probability of success, p. A basketball player who makes 86% of his free throws is asked to shoot free throws until he misses. The number of free throws attempted is recorded. Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer boxes to complete your answer. O A. Yes, because the experiment satisfies all the criteria for a binomial experiment, n = and p = (Type integers or decimals. Do not round.) O B. No, because the experiment is not performed a fixed number of times. O C. No, because the trials of the experiment are not independent since the probability of success differs from trial to trial. O D. No, because there are more than two mutually exclusive outcomes for each trial.arrow_forwardYou are doing research on balance and fitness. To complete this research you will need a watch with a second hand. Identify a random sample of n = 12 men and n = 8 women. You must answer this question: How do you establish that this sample is truly random? Have each subject perform the following task: Have the subjects stand with their hands at their side, raise one knee, cross their ankle over the other knee, squat and bring their hands palms together in front of their chest. Time the subject until they put their foot back down on the floor. b) Ask the following questions: i) How many days per week do they exercise? ii) What is their favorite exercise? You will analyze your data and compute the following statistics for each group: 1) The Mean and standard deviation of the number of seconds the subject stayed balanced 2) The Median number of days per week exercised 3) The Mode of the favorite exercise 4) The 90% confidence interval of the mean Construct a complete…arrow_forwardDuring a basketball game, Sebastián is shooting two free throws. He makes 95% of his free throws. Assuming that his free throws are independent events, find the percent chance that he... (Note: Do not round your answers.) is in the groove and makes both free throws. makes the first and then misses the second. misses the first and then makes the second. struggles and misses both of his free throws. What is the sum of these four answers? % % % do %arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman