
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
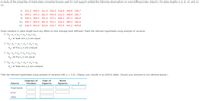
Transcribed Image Text:A study of the properties of metal plate-connected trusses used for roof support yielded the following observations on axial stiffness index (kips/in.) for plate lengths 4, 6, 8, 10, and 12
in:
4: 331.2 409.5 311.0 326.5 316.8 349.8 309.7
6: 409.1
347.2 361.0 404.5 331.0 348.9 381.7
8: 390.4 366.2
351.0 357.1 409.9 367.3
382.0
10: 344.7 452.9 461.4 433.1 410.6 384.2 362.6
12: 418.4 441.8 419.9 410.7 473.4 441.2
465.8
Does variation in plate length have any effect on true average axial stiffness? State the relevant hypotheses using analysis of variance.
H: at least two u's are equal
H: all five u's are unequal
SH = trl = Et = = :°H O
O Ho: H1 # H2 # H3 # H4 * H5
H: all five u's are equal
H: at least two u's are unequal
SH = *r = Et = Zyt = ' :°H O
Test the relevant hypotheses using analysis of variance with a = 0.01. Display your results in an ANOVA table. (Round your answers to two decimal places.)
Degrees of
freedom
Sum of
Mean
Source
Squares
Squares
Treatments
Error
Total

Transcribed Image Text:Give the test statistic. (Round your answer to two decimal places.)
f=
What can be said about the P-value for the test?
O P-value > 0.100
0.050 < P-value < 0.100
O 0.010 < P-value < 0.050
0.001 < P-value < 0.010
P-value < 0.001
State the conclusion in the problem context.
O Fail to reject H. There are differences in the true average axial stiffness for the different plate lengths.
Reject H. There are no differences in the true average axial stiffness for the different plate lengths.
Reject Ho. There are differences in the true average axial stiffness for the different plate lengths.
Fail to reject Ho: There are no differences in the true average axial stiffness for the different plate lengths.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the accompanying data on flexural strength (MPa) for concrete beams of a certain type. 8.3 7.4 7.0 6.8 7.8 9.7 5.0 6.3 6.8 9.0 7.7 7.3 7.4 11.8 6.3 7.7 11.6 7.2 11.3 9.7 10.7 7.0 7.9 8.7 7.9 8.1 6.5 (a) Calculate a point estimate of the mean value of strength for the conceptual population of all beams manufactured in this fashion. [Hint: Σxi = 218.9.] (Round your answer to three decimal places.) MPa(b) Calculate a point estimate of the strength value that separates the weakest 50% of all such beams from the strongest 50%. MPa(c) Calculate a point estimate of the population standard deviation ?. [Hint: Σxi2 = 1851.35.] (Round your answer to three decimal places.) MPa(d) Calculate a point estimate of the proportion of all such beams whose flexural strength exceeds 10 MPa. [Hint: Think of an observation as a "success" if it exceeds 10.] (Round your answer to three decimal places.)(e) Calculate a point estimate of the population coefficient of variation ?/?. (Round…arrow_forwardConsider the accompanying data on flexural strength (MPa) for concrete beams of a certain type. 5.5 7.2 7.3 6.3 8.1 6.8 7.0 7.0 6.8 6.5 7.0 6.3 7.9 9.0 8.6 8.7 7.8 9.7| 7.4 7.7 9.7 8.0 7.7 11.6 11.3 11.8 10.7 The data below give accompanying strength observations for cylinders. 6.3 5.8 7.8 7.1 7.2 9.2 6.6 8.3 7.0 8.7 7.4 8.1 7.4 8.5 8.9 9.8 9.7 14.1 12.6 11.6 ., Xm and the cylinder strengths by Y,, .., Yo. Suppose that the X's constitute a random sample from a distribution with mean u, Prior to obtaining data, denote the beam strengths by X,, and standard deviation o, and that the Y,'s form a random sample (independent of the X's) from another distribution with mean µ, and standard deviation o,. (a) Use rules of expected value to show that X – Y is an unbiased estimator of µ, - Hg. EX – ) = (E(X) - EC) = H1 - 42 O E(X – ) = V E(X) - E(Y) = H1 - H2 E(X) – E(Y) - O E(X – ): = H1 - H2 nm O E(X – Y) = nm E(X) – E(Y) = H1 - H2 O E(X – Y) = E(X) – E(Y) = µ1 - H2 Calculate the estimate (in…arrow_forwardAnswer the whole questionarrow_forward
- Values of modulus of elasticity (MOE, the ratio of stress, i.e., force per unit area, to strain, i.e., deformation per unit length, in GPa) and flexural strength (a measure of the ability to resist failure in bending, in MPa) were determined for a sample of concrete beams of a certain type, resulting in the following data: МОЕ 29.9 33.3 33.6 35.4 35.6 36.0 36.3 36.4 37.6 37.6 Strength 6.0 7.1 7.4 6.2 8.2 6.9 6.9 7.7 6.7 6.6 МОЕ 38.8 38.9 39.7 40.9 42.7 42.7 43.4 45.5 46.1 47.0 Strength 6.9 6.4 7.8 9.1 8.3 8.8 7.7 9.8 7.3 7.6 МОЕ 48.1 49.2 51.8 62.5 69.9 79.6 80.1 Strength 9.8 7.7 7.6 11.5 11.2 11.7 10.8 Fitting the simple linear regression model to the n = 27 observations on x = modulus of elasticity and y = flexural strength given in the data above resulted in ŷ = 7.595, s; = 0.186 when x = 40 and ŷ = 9.706, = 0.263 %3D for x = 60. The simple linear regression model also resulted in a value of s = 0.9008. (a) Explain why s; is larger when x = 60 than when x = 40. The farther x is from…arrow_forwardQ3: Shear strengths of 60 spot welds in a titanium alloy follow: 5408 5431 5475 5442 5376 5388 5459 5422 5416 5435 5420 5429 5401 5446 5487 5416 5382 5357 5388 5407 5469 5416 5377 5454 5375 5409 5459 5445 5463 5408 5481 5453 5422 5354 5421 5406 5399 5391 5477 5447 5329 5445 5436 5454 5453 5428 5444 5423 5441 5412 5384 5473 5418 5465 5427 5421 5396 Construct a Frequency Distribution Table (FDT) for the weld strength through finding: 1) Range 2) Number of Classes 3) width of Classes 4) all classes 5) only the frequency of fifth class. 5457 5429 5466arrow_forwardConsider the accompanying data on flexural strength (MPa) for concrete beams of a certain type. 7.0 7.2 6.8 6.5 7.0 6.3 7.9 9.0 9.7 8.1 7.7 11.6 11.3 11.8 10.7 observations for cylinders. 5.9 7.2 7.3 6.3 8.1 6.8 8.4 8.7 7.8 9.7 7.4 7.7 The data below give accompanying strength 6.7 5.8 7.8 7.1 7.2 9.2 6.6 8.3 7.0 8.1 7.0 8.1 7.4 8.5 8.9 9.8 9.7 14.1 12.6 11.4 Prior to obtaining data, denote the beam strengths by X₁,..., Xm and the cylinder strengths by Y₁,..., Y. Suppose that the Xi's constitute a random sample from a distribution with mean ₁ and standard deviation 0₁ and that the Y's form a random sample (independent of the X;'s) from another distribution with mean ₂ and standard deviation ₂. (a) Use rules of expected value to show that X - Y is an unbiased estimator of μ₁ - μ₂. O E(X)=√E(X) - E(Y) = μ₁ - H₂ ⒸE(XY) = E(X) - E(X) = 14₁ 14₂ O E(X-= E(X) - E(X) = 11 - 12 nm E(X - Y = nm(E(X) - E()) = μ₁ − 44₂ | E(X) = (E(X) - E(M)² = Calculate the estimate for the given data. (Round your…arrow_forward
- An experiment to compare the tension bond strength of polymer latex modified mortar (Portland cement mortar to which polymer latex emulsions have been added during mixing) to that of unmodified mortar resulted in x = 18.19 kgf/cm? for the modified mortar (m = 42) and y = 16.85 kgf/cm? for the unmodified mortar (n = 30). Let u, and u, be the true average tension bond strengths for the modified and unmodified mortars, respectively. Assume that the bond strength distributions are both normal. Assuming that o, = 1.6 and o, = 1.3, test Hn: 4, - H, = 0 versus H: u, - u, > 0 at level 0.01. Calculate the test statistic and determine the P-value. (Round your test statistic to two decimal places and your P-value to four decimal places.) P-value = Compute the probability of a type II error for the test of part (a) when 4 - Hz = 1. (Round your answer to four decimal places.) Suppose the investigator decided to use a level 0.05 test and vwished B = 0.10 when u, - uz = 1. If m = 42, what value of n…arrow_forwardANSWER D AND E ONLYarrow_forwardYou investigate the relationship between height and dbh (diameter at breast height) of oak trees. You get the following results: dbh (cm): 26 49 52 32 15 15 39 41 20 30 46 42 21 40 17 38 13 26 49 26height(m): 10.2 13.5 16.3 10.8 8.9 10.0 14.2 11.3 9.7 11.4 13.5 13.6 11.6 11.2 7.7 13.1 7.9 10.4 15.6 9.0 Read the data into R. (a) Calculate the following using R: ̄x , ̄y , SSx, SSy. (Note that to get SSy or SSx, you can just ask R for the variance (var) or standard deviation, and then do the appropriate calculation).(b) Perform a complete test of the hypothesis that there is no difference in height as dbh increases. Write out all the appropriate steps of a regular hypothesis test (give H0, H1, α, your decision, etc.)(c) Give the equation of the least squares linearrow_forward
- A router is used to cut locating notches on a printed circuit board. The vibration level at the surface of the board as it is cut is considered to be a major source of dimensional variation in the notches. Two factors are thought to influence vibration: bit size (A) and cutting speed (B). Two bit sizes (1/16 and 1/8 inch) and two speeds (40 and 90 rpm) are selected, and four boards are cut at each set of conditions shown below. The response variable is vibration measured as a resultant vector of three accelerometers (x, y, and z) on each test circuit board. (a) Analyze this experiment assuming that each one of the four replicates represent a block. (b)arrow_forwardPlease don't provide handwritten solution ....arrow_forwardConsider the accompanying data on flexural strength (MPa) for concrete beams of a certain type. 8.7 7.2 7.7 6.5 7.8 7.0 11.8 9.7 7.9 8.1 6.3 7.6 7.8 6.0 11.6 7.0 10.7 7.3 6.8 9.0 6.8 7.7 9.7 6.3 8.6 7.4 11.3 (a) Calculate a point estimate of the mean value of strength for the conceptual population of all beams manufactured in this fashion. [Hint: Ex; = 220.3.] (Round your answer to three decimal places.) MPа State which estimator you used. O s/x (b) Calculate a point estimate of the strength value that separates the weakest 50% of all such beams from the strongest 50%. MPа State which estimator you used. O s/X (c) Calculate a point estimate of the population standard deviation o. [Hint: Ex;² = 1868.85.] (Round your answer to three decimal places.) MPа Interpret this point estimate. This estimate describes the spread of the data. This estimate describes the bias of the data. This estimate describes the center of the data. This estimate describes the linearity of the data.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman