
Concept explainers
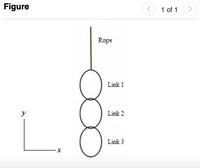
A student suspends a chain consisting of three links, each of mass m = 0.210 kg, from a light rope as shown in (Figure 1). The rope is attached to the top link of the chain, which does not swing. She pulls upward on the rope, so that the rope applies an upward force of 9.50 N to the chain.
(I) Draw a free-body diagram for the entire chain, considered as an object, and one for each of the three links.
(II) Use the diagrams of part (I) and Newton's laws to find (i) the acceleration of the chain, (a) the force exerted by the top link on the middle link, and (b) the force exerted by the middle link on the bottom link. Treat the rope as massless.
(III)There are four objects of interest in this problem: the chain as a whole and the three individual links. For each of these four objects, identify the external forces acting on them. Besides the force of gravity, you should include only forces exerted by other objects that touch the object in question. Throughout this problem, assume the positive y-axis points upwards. (Drag the appropriate forces to their respective bins.)

Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

- The traffic light shown in (Figure 1) has a mass of21 kg . Take h= 3.5 mm.arrow_forward2-Determine the magnitude ( P) of the B W=30 N horizontal force required to initiate motion of the block of mass (m.) for the cases : a-Pis applied to the right. b-Pis applied to the lift. u=0.5 30° P(a) mg P(barrow_forward2. The 6-kg frame AC and 4-kg uniform slender bar AB of length / is free to slide along a smooth fixed horizontal rod. a. Find the tension in the wire BC for a static case where the frame and bar are stationary. b. Now, with the the 80 N force applied find the tension in the wire BC. 60° to Q B 60° -80 N -xarrow_forward
- Please answer this within 30 mins! I will upvote !arrow_forwardQuestion 1 Member ABC of negligible weight is supported by a pin and bracket at B and by an inextensible cord attached at A and C and passing over a frictionless pulley at D. For the loading shown and neglecting the size of the pulley, calculate the tension in the cord ,the horizontal and vertical reactions at point B. (X,XX,XXX represents the last digits number of your IC). 1 257mm 75 N 167mm B 127 mmarrow_forwardA uniform ladder 8 meters long and weighing 350 N rest against a smooth vertical wall at an angle of 30° to the wall. A 700-N man stands 6 meters up from the bottom of the ladder. Find the horizontal force necessary at the base to keep the ladder from slipping. Ps: Include Given, Free-Body Diagrams and Formulaarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





