
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:MALEKS
T
LI
X b Answered: Ⓒ ELECTROCHEMISTR X +
www-awu.aleks.com/alekscgi/x/Isl.exe/1o_u-lgNslkr7j8P3jH-lvdw7xgLCkqMfg8yaFKbD9GafJstkYLIJnusptTd4BMWR5tqw8EEwiGTTdyzfqHFomOky9feFge9QQitSAMuOKacSVpwDeo?1... Q
Type here to search
ALEKS - Rafia Riaz - Learn
=
Recognizing consistency among equilibrium constant, free...
O ELECTROCHEMISTRY
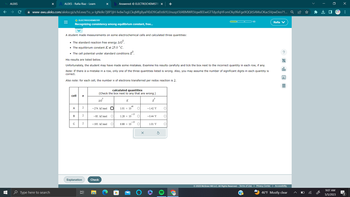
A student made measurements on some electrochemical cells and calculated three quantities:
• The standard reaction free energy AGⓇ.
• The equilibrium constant K at 25.0 °C.
• The cell potential under standard conditions º
His results are listed below.
Unfortunately, the student may have made some mistakes. Examine his results carefully and tick the box next to the incorrect quantity in each row, if any.
Note: If there is a mistake in a row, only one of the three quantities listed is wrong. Also, you may assume the number of significant digits in each quantity is
correct.
Also note: for each cell, the number n of electrons transferred per redox reaction is 2.
cell
A
B
w
с
Explanation
n
2
2
2
발
calculated quantities
(Check the box next to any that are wrong.)
AG
-274. kJ/mol
-85. kJ/mol O
-195. kJ/mol O
Check
K
48
1.01 x 10
-15
1.28 x 10
6.88 × 10
-35
O
O
O
E
-1.42 V
-0.44 V
1/3
1.01 V
Rafia V
allo
© 2023 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility
(?)
46°F Mostly clear
*
J
9:07 AM
5/5/2023
x
:
M
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A student made measurements on some electrochemical cells and calculated three quantities: • The standard reaction free energy AG. • The equilibrium constant K at 25.0 °C. • The cell potential under standard conditions E°. His results are listed below. Unfortunately, the student may have made some mistakes. Examine his results carefully and tick the box next to the incorrect quantity in each row, if any. Note: If there is a mistake in a row, only one of the three quantities listed is wrong. Also, you may assume the number of significant digits in each quantity is correct. Also note: for each cell, the number n of electrons transferred per redox reaction is 1. calculated quantities (Check the box next to any that are wrong.) cell n AGº K A 1 -19. kJ/mol 4.69 × 10 0 E 0.20 V 13 B 1 77. kJ/mol 3.09 × 10 0.80 V -14 C 1 75. kJ/mol 7.25 X 10 0.78 Varrow_forwardA student made measurements on some electrochemical cells and calculated three quantities: • The standard reaction free energy AG. The equilibrium constant K at 25:0 °C. The cell potential under standard conditions E His results are listed below. Unfortunately, the student may have made some mistakes. Examine his results carefully and tick the box next to the incorrect quantity in each row, if any. Note: If there is a mistake in a row, only one of the three quantities listed is wrong. Also, you may assume the number of significant digits in each quantity is correct.. Also note: for each cell, the number n of electrons transferred per redox reaction is 2. cell n A B C 2 2. 2 calculated quantities. (Check the box next to any that are wrong.) .0 AG 172. kJ/mol J 127. kJ/mol - 170. kJ/mol K -31 7.36 X 10 5:63 X.10 - 23 29 6.06 × 10 - O O E -0.89 V. 0:66 V -0.88. V 5arrow_forwardBatteries are charged and discharged due to the concentration of the solutions inside. Calculate the voltage of a battery made from zinc in a 0.5M solution of Zn2+ and a metal X in a 1 M X2+ solution using the table of reduction potentials and Eq. 6 at 25 degrees C. Answer with the unit V, to two decimal places. The standard reduction potential of X is -0.19 volts. Your Answer:arrow_forward
- Give a clear explanation handwritten answer ...arrow_forwardBased on the sign of the standard cell potential, Eel, classify these reactions as spontaneous or nonspontaneous as written. Assume standard conditions. Refer to the list of standard reduction potentials. Spontaneous as written Nonspontaneous as written Answer Bank Pb2*(aq) + H2(g) - Pb(s) + 2 H*(aq) Ni?*(aq) + s? (aq) Ni(s)+S(s) Al3+(aq) + 3 Na(s) → Al(s) + 3 Na*(aq)arrow_forwardA student made measurements on some electrochemical cells and calculated three quantities: • The standard reaction free energy AGº. • The equilibrium constant K at 25.0 °C. me 1. ? • The cell potential under standard conditions E°. 00 2. His results are listed below. Ex Unfortunately, the student may have made some mistakes. Examine his results carefully and tick the box next to the incorrect quantity in each row, if any. 000 Note: If there is a mistake in a row, only one of the three quantities listed is wrong. Also, you may assume the number of significant digits in each quantity is correct. Also note: for each cell, the number n of electrons transferred per redox reaction is 2. 10 Ar cell n calculated quantities (Check the box next to any that are wrong.) K 0 E 27 A 2 156. kJ/mol O 2.14 X 10 0.81 V 11 B 2 66. kJ/mol O 3.65 × 10 -0.34 V C 2 -264. kJ/mol 46 1.78 x 10 -1.37 V K So Na G 4. 3.arrow_forward
- Given the balanced electrochemical reaction below (M and N represent generic metals), what is the cell potential (Ecell), in volts, for this reaction at 35.4 °C when [M+] = 0.00533 M and [N2+] = 0.725 M? Enter your answer to the thousandths place. Do not include units. 2M+(aq) + N(s) → 2M(s) + N2+(aq) E°cell = 0.128 Varrow_forwardA student made measurements on some electrochemical cells and calculated three quantities: • The standard reaction free energy AG • The equilibrium constant K at 25.0 °C.. The cell potential under standard conditions E His results are listed below. Unfortunately, the student may have made some mistakes. Examine his results carefully and tick the box next to the incorrect quantity in each row, if any. Note: If there is a mistake in a row, only one of the three quantities listed is wrong. Also, you may. assume the number of significant digits in each quantity is correct. Also note: for each cell, the number n of electrons transferred per redox reaction is 1. cell A B C₁ n 1 1. 1 calculated quantities (Check the box next to any that are wrong.) ·a AG 77. kJ/mol O 64. kJ/mol 35. kJ/mol O O K 3.09 X 10 6:13 X 10 13. 6 1.35 X 10 - 12. O X 0. 0.80 V 0.66 V -0.36 V Śarrow_forwardA student made measurements on some electrochemical cells and calculated three quantities: • The standard reaction free energy AG". • The equilibrium constant K at 25.0 °C. • The cell potential under standard conditions E. His results are listed below. Unfortunately, the student may have made some mistakes. Examine his results carefully and tick the box next to the incorrect quantity in each row, if any. Note: If there is a mistake in a row, only one of the three quantities listed is wrong. Also, you may assume the number of significant digits in each quantity is correct. Also note: for each cell, the number n of electrons transferred per redox reaction is 1. calculated quantities (Check the box next to any that are wrong.) cell n 46° K 1 - 124. kJ/mol 5.30 x 10 21 -1.28 V -18 4.53 x 10 B 1 - 99. kJ/mol -1.03 V -7 2.20 x 10 1 - 38. kJ/mol 0.39 Varrow_forward
- Calculate the K and AG for the following reaction at 25 °C: с Zn(s) + CuSO₂ (aq) = ZnSO₂(aq) + Cu (s) Note: Reference the Standard reduction potentials at 25 °℃ and Fundamental constants tables for additional information. Part 1 of 2 Round your answer to 3 significant digits. K с Part 2 of 2 = AGO = x10 Round your answer to 4 significant digits. kJ mol X Ś x10arrow_forwardA student made measurements on some electrochemical cells and calculated three quantities: • The standard reaction free energy AG⁰. • The equilibrium constant K at 25.0 °C. • The cell potential under standard conditions º His results are listed below. any. Unfortunately, the student may have made some mistakes. Examine his results carefully and tick the box next to the incorrect quantity in each row, if Note: If there is a mistake in a row, only one of the three quantities listed is wrong. Also, you may assume the number of significant digits in each quantity is correct. Also note: for each cell, the number n of electrons transferred per redox reaction is 1. cell n A B C 1 calculated quantities (Check the box next to any that are wrong.) AGⓇ 37. kJ/mol - 66. kJ/mol -47. kJ/mol K 6 3.03 × 10 2.74 × 10 5.83 × 10 12 9 X 0 E -0.38 V 0.68 V -0.49 V Sarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY