
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
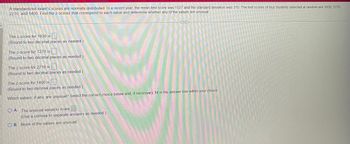
Transcribed Image Text:A standardized exam's scores are normally distributed. In a recent year, the mean test score was 1527 and the standard deviation was 315. The test scores of four students selected at random are 1930, 1270,
2210, and 1400. Find the z-scores that correspond to each value and determine whether any of the values are unusual.
The Z-score for 1930 is
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
The Z-score for 1270 is
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
The Z-score for 2210 is
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
The Z-score for 1400 is
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
Which values, if any, are unusual? Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box within your choice.
OA. The unusual value(s) is/are
(Use a comma to separate answers as needed.)
OB. None of the values are unusual.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Use z scores to compare the given values. The tallest living man at one time had a height of 246 cm. The shortest living man at that time had a height of 116.2 cm. Heights of men at that time had a mean of 170.86 cm and a standard deviation of 8.41 cm. Which of these two men had the height that was more extreme? and the z score for the shortest man is z = ☐, the man had the height that was more extreme. Since the z score for the tallest man is z = (Round to two decimal places.)arrow_forwardGrace has a dog and its weight is z = -0.5lbs. Her current weight is 47 lbs. The average weight for medium-sized dogs is 50 lbs. What is the standard deviation for a dog of her size?arrow_forwardAs reported in Runner's World Magazine, the times of finishers in the New York City 10-km run are normally distributed with a mean of 60 minutes and standard deviation of 7 minutes. What would a runner's finishing time have to be for his/her finishing time to be 1.6 standard deviations above the mean of 60 minutes? You must use the z- score formula and solve for X. Round to the 10ths place.arrow_forward
- Find the indicated IQ score. The graph to the right depicts IQ scores of adults, and those scores are normally distributed with a mean of 100 and a standard deviation of 15.arrow_forwardUse z scores to compare the given values. The tallest living man at one time had a height of 233 cm. The shortest living man at that time had a height of 89.9 cm. Heights of men at that time had a mean of 176.34 cm and a standard deviation of 5.47 cm. Which of these two men had the height that was more extreme? Since the z score for the tallest man is z= height that was more extreme. (Round to two decimal places.) and the z score for the shortest man is z = the man had thearrow_forwardOn a nationwide math test, the mean was 58 and the standard deviation was 4. If Roberto scored 70, what was his z-score? Use the formula Z where is the mean, o is σ the standard deviation, and x is Roberto's score. Round to 4 decimal places. X н =arrow_forward
- Note: The standard deviation is defined as the average distance of the class scores from the mean. Note: The variance is defined as average squared distance of the class scores from the mean. Sameer's score in a quiz was 25 and he was five standard deviations above the mean in this quiz. The mean was 20. The average squared distance of the scores from the mean in this quiz is: Select one: a. -3 b. 2 c. 3 d. -2 e. 1 f. -1arrow_forwardThe annual rainfall in a town has a mean of 54.57 inches and a standard deviation of 12.84 inches. Last year there was rainfall of 71 inches. How many standard deviations away from the mean is that? Round your answer to two decimal places.arrow_forwardOne of the z-score formulas will help on this question. Scores on the SAT test are normally distributed with a mean of 500 and standard deviation of 100 points. Pretend someone scored 400 on the math portion of the SAT test. What would be the z-score cut off for this score? A. 1.0 B. -1.0 C. 0 D. 2.0arrow_forward
- In the School of Medicine at Florida State University, the mean IQ is 116 with a standard deviation of 14. Given this information, what IQ score would correspond to a z-score of -1.5? 123 118 104 95arrow_forwardMario's weekly poker winnings have a mean of $353 and a standard deviation of $67. Last week he won $185. How many standard deviations from the mean is that?arrow_forwardFind the indicated IQ score. The graph to the right depicts IQ scores of adults, and those scores are normally distributed with a mean of 100 and a standard deviation of 15. Click to view page 1 of the table. Click to view page 2 of the table. The indicated IQ score, x, is (Round to one decimal place as needed.) A 0.55 X Qarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman