
Concept explainers
A spring with a spring constant k = 30 N/m is on a frictionless incline with an angle of 40º. A 4.0 kg object is hung on the spring and allowed to slide down the incline. What is the speed of the object after it has slid a distance D = 0.7 m? Hint: Make potential energy zero at the stretch of D.
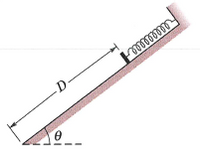
According to the law of conservation of energy , energy can neither be created nor destroyed but can only be converted from one form to another . Thus the initial potential energy of the object will be converted to the spring potential energy and kinetic energy of the object as it reaches distance , thus , where is the mass of the object , is the acceleration due to gravity , is the height , is the spring constant and v is the final velocity .
The height of the object is calculated by using the trigonometric formula ,
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

- A box is pressed against a horizontal spring, compressing the spring from its relaxed length. The box is then released and the spring launches the box horizontally along a track that ends in a ramp, as shown above. The box has enough speed to leave the ramp, and the box reaches a maximum vertical height above the floor. Assume there is negligible friction between the box and the track and air resistance is negligible. K = spring constant of spring X = distance the spring is compressed M = mass box Theta = angle of ramp from horizontal H = maximum height reached by box Does the mechanical energy of the box-spring-earth system increase, decrease, or remain the same from the moment the spring is released until just before the box hits the ground? Justify your answer. If air resistance were not negligible, how would that affect your answer, if at all? Justify your answer.arrow_forwardA bungee cord exerts a nonlinear elastic force of magnitude F(x) = k1x + k2x°, where x is the distance the cord is stretched, k1 = 205 N/m and k2 = -0.223 N/m³. How much work must be done on the cord to stretch it 16.7 m? W = kJ Submit Questionarrow_forwardAs shown in the figure, a 0.490kg object is pushed against a horizontal spring of negligible mass until the spring is compressed a distance x. The force constant of the spring is 450 N/m. When it is released, the object travels along a frictionless, horizontal surface to point A, the bottom of a vertical circular track of radius R = 1.00 m, and continues to move up the track. The speed of the object at the bottom of the track is va = 12.8 m/s and the object experiences an average frictional force of 7.00 N while sliding up the track. (a) What is x? (b) If the object were to reach the top of the track, what would be it’s speed at that point? (c) Does the object actually reach the top of the track, or does it fall off before reaching the top?arrow_forward
- 10. A 4.0 kg block is pushed against a spring with negligible mass and force constant k = 700 N/m, compressing it 0.20 m. When the block is released, it moves along a frictionless, horizontal surface and then up a frictionless incline with slope 40°. (a) What is the speed of the block as it slides along the horizontal surface after having left the spring? (b) How far does the block travel up the incline before starting to slide back down? (c) Redo part b. if there is a non-zero coefficient of kinetic friction k = 0.10 on the incline (but not on the horizontal surface). k m 30ºarrow_forwardPart A (Figure 1) shows the potential energy of a 260 g particle as it moves along the x-axis. What is the maximum speed the particle could have at r = 2.0 m and never reach r = 6.0 m? %3D %3D Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. HA Umax = Value Units Submit Request Answer Figure K1 of 1 Provide Feedback U() 16 12 8. 4 x (m) 0. 4. 6 8arrow_forwardA 26 kg object is acted on by a conservative force given by F = (-2.9)x + (-5.9)x2, with F in newtons and x in meters. Take the potential energy associated with the force to be zero when the object is at x = 0. What is the potential energy of the system associated with the force when the object is at x = 2.0 m? If the object has a velocity of 5.5 m/s in the negative direction of the x-axis when it is at x = 5.0 m, what is its speed when it passes through the origin?arrow_forward
- The first figure gives spring force FX versus position x for the spring-block arrangement of the second figure. The scale is set by F₂ = 200 N. We release the block at x = 13.0 cm. How much work does the spring do on the block when the block moves from x; = +8.0 cm to (a)x +7.0 cm, (b) x = -7.0 cm, (c) x = -8.0 cm, and (d) x = -11.0 cm? F -x (cm) -2 -1 0 1 -F x=0 Ę=0 00000000 x positive F negative (a) Number i Units (b) Number i Units (c) Number i Units (d) Number i Units (a) d Block attached to spring (b) x negative Ę positive (c)arrow_forward14. A block is sent sliding down a frictionless ramp. Its speeds at points A and B are 2.00 m/s and 2.60 m/s, respectively. Point A is higher up the ramp than point B. Next, it is again sent sliding down the ramp, but this time its speed at point A is 4.00 m/s. What then is its speed at point B? (a) 2.5 m/s (b) 4.3 m/s (c) 5.4 m/s (d) 6.1 m/sarrow_forwardA 0.90 kg brick compresses a spring 0.35 meters at point A and the spring has a spring constant of 75 N/m. How much elastic potential energy does the brick possess? A В hA = 0 he = 0 VA = 0 Vв > 0 A 3.20 Joules 984 Joules 4.59 Joules 675 Joules O O O Oarrow_forward
- The spring in a retractable ballpoint pen is 1.8 cm long, with a 320 N/m spring constant. When the pen is retracted, the spring is compressed by 1.0 mm. When you click the button to extend the pen, you compress the spring by an additional 5.0 mm. How much energy is required to extend the spring?arrow_forwardA 0.40 kg block can slide up and down a rough 10-m-high, 30-m-long slope. At the bottom, a stiff spring with spring constant 800 N/m is compressed 0.50 m and used to launch the block up the slope. The friction force on the block from the slope is 1.2 N. What is the speed of the block when it reaches the top of the slope? When apply the following energy principle to this question, assuming the system is block+earth+spring+slope, which of the energy term is positive? Select all apply. ΔK + ΔUg + ΔUsp + ΔEth + ΔEch = Wexternal Answers choices ΔK ΔUg ΔUsp ΔEth ΔEch Wexternalarrow_forwardThe figure shows an 8.4 kg stone at rest on a spring. The spring is compressed 12 cm by the stone. (a) What is the spring constant? (b) The stone is pushed down an additional 30 cm and released.What is the elastic potential energy of the compressed spring just before that release? (c) What is the change in the gravitational potential energy of the stone-Earth system when the stone moves from the release point to its maximum height? (d) What is that maximum height, measured from the release point? k (a) Number i Units (b) Number i Units (c) Number Units (d) Number Units > > >arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





