
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
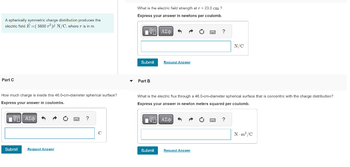
Transcribed Image Text:A spherically symmetric charge distribution produces the
electric field E=( 5600²) N/C, where r is in m.
Part C
How much charge is inside this 46.0-cm-diameter spherical surface?
Express your answer in coulombs.
IVE ΑΣΦ 3
Submit
Request Answer
wwww.
C
What is the electric field strength at r = 23.0 cm ?
Express your answer in newtons per coulomb.
[V=| ΑΣΦ
Submit
Part B
^
Submit
Request Answer
= ?
What is the electric flux through a 46.0-cm-diameter spherical surface that is concentric with the charge distribution?
Express your answer in newton meters squared per coulomb.
IV—| ΑΣΦ ^ A
Request Answer
N/C
?
N-m²/C
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1 ! 7 A skát с A spherically symmetric charge distribution produces the electric field E=( 5400 r²) N/C, where r is in m. Z mylabmastering.pearson.com/?courseld=12649908&key=55673220682936520262024#/ 2 pos W S X 3 20 F3 E D $ 4 C 888 R F What is the electric field strength at r= 16.0 cm ? Express your answer in newtons per coulomb. VG ΑΣΦ 4 Submit Part B Submit Part C What is the electric flux through a 32.0-cm-diameter spherical surface that is concentric with the charge distribution? Express your answer in newton meters squared per coulomb. ΕΠΙ ΑΣΦ % [VG| ΑΣΦ 5 Request Answer V FO Request Answer T How much charge is inside this 32.0-cm-diameter spherical surface? Express your answer in coulombs. G 4 a ^ 6 C 244 MacBook Air Y B SMC & ? 7 H ? N/C 80 F7 N-m²/C U C N H 8 - DII FS 1 ( 9 M DD K chegg.com X C ☆ O O MOSISO O 4 Parrow_forwardThe following diagram shows a solid insulating sphere with a radius "a" and a charge +3Q surrounded by a spherical conducting shell with inner radius "b", and outer radius "c", and a net charge -20. What is the electric field (direction and magnitude) in the region where aarrow_forwardThe figure gives the magnitude of the electric field inside and outside a sphere with a positive charge distributed uniformly throughout its volume. The scale of the vertical axis is set by Es = 4.3 × 107 N/C. What is the charge on the sphere?arrow_forward
- You are working as an intern for a meteorological laboratory. You are out in the field taking measurements with a device that measures electric fields. You measure the electric field in the air immediately above the Earth's surface to be 194 N/C directed downward. (Assume the radius of the Earth is 6.37 x 106 m.) (a) Determine the surface charge density (in C/m²) on the ground. C/m² (b) Imagine the surface charge density is uniform over the planet. Determine the charge (in C) of the whole surface of the Earth. C (c) Determine the Earth's electric potential (in V) due to the charge found in (b). V (d) Determine the difference in potential (in V) between the head and the feet of a person 1.50 m tall. (Ignore any charges in the atmosphere.) Varrow_forwardNCS-1 A non-conducting sphere of radius R=0.300m has a total charge q-100μC that is evenly distributed throughout its volume. a) Find the charge within a radius of r=0.100m. Hint: first find the volume charge density p. b) Find the electric field strength at r=0.100m. c) Find the charge within a radius of r-0.200m. d) Find the electric field strength at r-0.200m. e) Find the charge within a radius of 1-0.300m. f) Find the electric field strength at r-0.300m. g) How does E change with increasing radius? Rarrow_forwardA thin, square, conducting plate 47.0 cm on a side lies in the xy plane. A total charge of 3.50 10-8 C is placed on the plate. You may assume the charge density is uniform. (a) Find the charge density on each face of the plate. C/m2(b) Find the electric field just above the plate. magnitude N/C direction (c) Find the electric field just below the plate. magnitude N/C directionarrow_forward
- A thin, square, conducting plate 49.0 cm on a side lies in the xy plane. A total charge of 3.70 x 10-8 C is placed on the plate. You may assume the charge density is uniform. (a) Find the charge density on each face of the plate. C/m² (b) Find the electric field just above the plate. magnitude N/C direction -Select--- ✓ (c) Find the electric field just below the plate. magnitude N/C direction -Select--- ✓arrow_forwardA flat surface of area 3.10 m² is rotated in a uniform electric field of magnitude E = 6.65 x 105 N/C. (a) Determine the electric flux through this area when the electric field is perpendicular to the surface. N. m²/c (b) Determine the electric flux through this area when the electric field is parallel to the surface. N. m²/carrow_forwardWhat is the magnitude of the electric field 15 mm from the center? Give the numerical value when calculated in units of N/C.arrow_forward
- An infinitely long object consists of an inner cylinder of radius a which has a uniform positive volume charge density p > 0 and a concentric thin cylinder of radius b which has a uniform negative surface charge density o0 Figure 7: A cross-sectional view of two cylinders c) Calculate the electric field for r > b. b 0 <0 d) Calculate the electric potential difference for rarrow_forwardA uniformly charged disk of radius R=25 cm carries a total charge of Q=2 μC. R P 1 Find the magnitude of the electric field E created by the disk at the point P located at distance 40 cm from the center of the disk. E = [N/C] 2. What is the direction of the electric field E created by the disk at point P. Direction: 3. Write the expression of the electric filed E created by the disk at point P. Ē =< [N/C] 4. Find the magnitude of the electric field E created by the disk at the point P located at distance 8 m from thearrow_forwardQuestion 2 A 43.8 cm long rod has a nonuniform charge density given by the equation A(z) = Ae-2/b, where A = 2.50 nC/cm and b= 14.0 cm. What is the total charge on the rod? Hint: This problem requires integration! + + + + ++ Total charge on rod: +arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON