Question
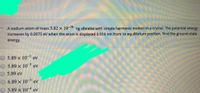
Transcribed Image Text:- A sodium atom of mass 3.82 x 10-20 kg vibrates with simple harmonic motion in a crystal. The potential energy
increases by 0.0075 eV when the atom is displaced 0.014 nm from its equilibrium position. Find the ground-state
energy.
O 5.89 x 10 ev
5.89 x 103 ev
5.89 eV
6.89 x 10-3 ev
O 5.89 x 10 ev
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 1arrow_forwardChapter 39, Problem 017 An electron in the n, state in the finite potential well of of Figure (a) absorbs 650 eV of energy from an external source. U U(x) Ug L. (a) Using the energy-level diagram of Figure (b), determine the electron's kinetic energy after this absorption, assuming that the electron moves to a position for which x > L.arrow_forwardMass of electron m₀ : 9.1 × 10⁻³¹kg Avogadro number N₂ : 6.02 × 10²³ Charge of electron ℯ : 1.6 × 10⁻¹⁹ C 1 ℯV = 1.6 × 10⁻¹⁹ J Boltzman costant k₃ : 1.38 × 10⁻²³ J/K = 8.6 × 10⁻⁵ ℯV/K R = 8.314 J/K·mol Q. The equilibrium interatomic spacing and melting point of sodium halide are as follows. Explain the reasons for the observed trend. NaF NaCI NaBr NaI interval(nm) 0.23 0.28 0.29 0.32 meltingpoint(℃) 988 801 740 660arrow_forward
- Suppose you recently discovered a hydrogen like element that has only one electron orbiting around a nucleus containing a proton and a neutron. You found the ground state energy of the electron to be -16 eV. What will be the energy of this electron when it is on the excited state shown in the sketch? Note that all other possible intermediate states are shown by dashed lines. Electron is here Ground state 1.0 eV 16 eV - 1.0 eV -4.0 eV 4.0 eVarrow_forwardConsider the energy levels of the Hydrogen atom. The allowed H-atom energy levels are given by the equation: En - 13.6 eV n² What is the energy gap between the two lowest energy levels in the Hydrogen atom? 10.2 eV 6.40 eV 12.1 eV 13.6 eV 3.40 eVarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios