
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
thumb_up100%
Of the three forces acting on the rock as it slides down the bowl, which (if any) are constant and which are not? Explain.

Transcribed Image Text:A small rock with mass 0.12 kg is released from rest at point A,
which is at the top edge of a large, hemispherical bowl with
radius R = 0.54 m (the figure (Figure 1)). Assume that the size
of the rock is small compared to R, so that the rock can be
treated as a particle, and assume that the rock slides rather than
rolls. The work done by friction on the rock when it moves from
point A to point B at the bottom of the bowl has magnitude 0.22
J.
%3D
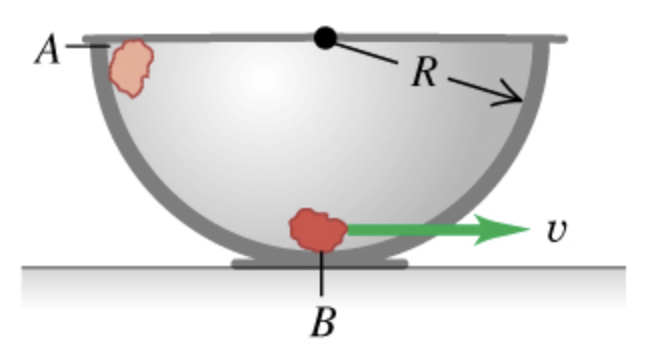
Transcribed Image Text:A-
B
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 61. A 6-newton force and an 8-newton force act concurrently on a box located on a frictionless horizontal surface. Which top-view diagram shows the forces producing the smallest magnitude of acceleration of the box? 8 N 6 N Top of box Top of box 8 N 6N V (1) (3) 6N Top of box 8 N Top of box 8 N6 N (2) (4) INarrow_forwardQUESTION 21 A block of mass M is suspended at rest by two strings attached to walls, as shown in the figure. The left string is horizontal with tension force T2 and and the right string with tension force T1 makes an angle with the horizontal. g is the magnitude of the gravitational acceleration. Which of the following statements is true? Select all apply. T₁ M T₂ M The acceleration along the y-component is zero. The acceleration along the x-component is zero. The net force along the x-component is zero. The net force along the x-component is non-zero. The acceleration along the y-component is non-zero. The net force along the y-component is non-zero. The net force along the y-component is zero. The acceleration along the x-component is non-zero.arrow_forwardA) A woman exerts a constant horizontal force on a large box. As a result, the box moves across a horizontal floor at a constant speed "v0". The constant horizontal force applied by the woman: has the same magnitude as the weight of the box. is greater than the weight of the box. has the same magnitude as the total force which resists the motion of the box. is greater than the total force which resists the motion of the box. is greater than either the weight of the box or the total force which resists its motion. B) If the woman in the previous question doubles the constant horizontal force that she exerts on the box to push it on the same horizontal floor, the box then moves: with a constant speed that is double the speed "v0" in the previous question. with a constant speed that is greater than the speed "v0" in the previous question, but not necessarily twice as great. for a while with a speed that is constant and greater than the speed "v0" in the previous question, then with a…arrow_forward
- REMARKS Unlike its value on a horizontal surface, n is less than the weight of the sled when the sled is on the slope. This is because only part of the force of gravity (the x-component) is acting to pull the sled down the slope. The y-component of the force of gravity balances the normal force. QUESTION Consider the same scenario on a hill with a steeper slope. Would the magnitude of the tension in the rope get larger, smaller, or remain the same as before? O The magnitude of the tension force would be greater. The magnitude of the tension force would be smaller. The magnitude of the tension force would remain the same. How would the normal force be affected? O The magnitude of the normal force would be greater. O The magnitude of the normal force would be smaller. O The magnitude of the normal force would remain the same.arrow_forward1. Two blocks of mass m1 and m2 are held at rest by a wire directed down a frictionless inclined plane as shown in the figure. At times t < 0 the wire provides a constant force Fo. (i) What value of Fo is needed so that both blocks remain at rest? At time t = 0 the external force starts to increase according to F(t) = Fo + at, where a is a positive constant. (ii) What is the speed of block m2 as a function of time? Law m1 F(t) = Fo + at Application m2arrow_forwardAn object of mass m = 1.00 kg is observed to have an acceleration of a with a magnitude of 21.0 m/s² in a direction = 70.0° east of north. The figure below shows a view of the object from above. The force F, acting on the object has a magnitude of 7.18 N and is directed 2 north. Determine the magnitude and direction of the force F, acting on the object. 1 N magnitude direction ---Select--- ↑ m Ө F₁ iarrow_forward
- An elevator accelerates upward at 4 m/s^2. The cable can safely handle a tension up to 5000 N. Suppose the elevator itself weighs 1000 N. How many 75 kg. People can the elevator safely carry upward like this? a) 3 people b) 4 people c) 5 people d) 2 people e) 6 peoplearrow_forwardA net force F is required to give an object with mass m an acceleration a. If a net force 8F is applied to an object with mass 2m, what is the acceleration on this object? A 16a 8a 4a 2аarrow_forwardThree blocks on a frictionless horizontal surface are in contact with each other. A force F is applied to the first block. a) What is the acceleration of the system? b) What are the forces of contact between the first and second block, and the second block and third block? c) What is the net force acting on each block? Choose |F|= 12N, m₁ = 2.3kg, = 1.2kg and ma = 3.7kg. 1₂arrow_forward
- *69. A damp washcloth is hung over the edge of a table to dry. Thus, part (mass = mm) of the washcloth rests on the table and part (mass = m) does not. The coefficient of static friction between the table and the wash- cloth is 0.40. Determine the maximum fraction [ma/(mon + moa)] that can hang over the edge without causing the whole washcloth to slide off the table.arrow_forward1. In each case, three forces act on a 1 kg object to give it the specified acceleration, but only two are shown. Note that the grid has units of 1 N. Draw in the missing vector (F3). F,(N) Fy(N) F, (N) T F1 F;(N) F(N) F(N) a) b) c) = 0 m/s? az = 0 m/s² az = +1 m/s² Ax ay = +2 m/s² Ay = –1 m/s² ay = -2 m/s² %3Darrow_forwardA 4.0-kg square block is on an incline plane of 30 degrees angle with respect to the ground. 1)What is the minimum coefficient of static friction (μs)min is need to prevent it from sliding down the incline? 2) When the surface μs is 0.30 to prevent the block sliding, a horizontal force F, parallel to the ground, is applied to the block. find the minimum magnitude of F required to keep the block from moving. 3) When a 20 N uphill force is applied to the block, the block starts to move up along the incline. Find the acceleration of the blockarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON