
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781259696527
Author: J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
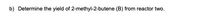
Transcribed Image Text:b) Determine the yield of 2-methyl-2-butene (B) from reactor two.

Transcribed Image Text:A simultaneous dehydration reaction of liquid 2-methyl-2-butanol (A) produces 2-methyl-2-
butene (B) and 2-methyl-1-butene (C) as shown in Figure 1 was carried out in a two continuous
stirred tank reactor (CSTR) connected in series. The dehydration of A to B occur in second
order whereas dehydration to C was in first order.
CH,
ki
CH,
CH,-C=CH-CH,
2-medhyl-2-butene (BÍ
сH, с— сн, — сн,
CH3
ÓH
2-methyl-2-butanol(A)
• CH,=ċ-CH,-CH,
2-methyl-1-butene(C)
Figure 1 Dehydration reaction of liquid 2-methyl-2-butanol
a) Inlet stream consists of pure A with concentration of 40 mol-dm3 and constant volumetric
flowrate of 2 m3.min-1. The concentration of A at the exit stream of reactor one was reduced
to 50%. The composition of product leaving reactor one consists of 60% B and 40% C. If
the size of reactor one is 5 m³ and reactor two is double of reactor one, determine the
composition of remaining A, product B and C in the exit stream of reactor two.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 24 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- REACTION ENGINEERING Consider a heterogeneous gas-phase catalytic reaction:AB(g)→A(g)+B(g) (Catalyst) The surface reaction mechanism follows three steps: AB(g) +S <----> AB*S (Adsorption)AB*S<----> B*S+A(g) (Surface reaction)B*S <---> B(g) + S (Desorption) (a) Derive the rate law assuming (1) surface reaction is rate limiting, and (2) desorption is rate-limiting. Express the overall reaction rate (- Tan) in terms of total number of sites on the surface, C. partial pressures of the gas species (ie., Pab Pa and Pb), rate constants of adsorption, the surface reaction, and desorption (ka,ks, and kd), and the equilibrium constants of adsorption, the surface reaction, and desorption (ie., Ka. Ks and Kd).arrow_forwardBalance the following redox reaction in an acidic solution: UO22+(aq)+Zn(s)->U4+(aq)+Zn2+(aq)arrow_forwardGive answer all questions with explanationarrow_forward
- Problem 3 Dibutyl phthalate (diester) is produced in a CSTR operated isothermally at 112°C. The rate of formation of the di-ester from phthalic anhydride and butanol being very fast, the controlling step, in the presence of sulphuric acid catalyst, is the conversion of mono-ester to the diester. The liquid phase reaction is: СЫН.(СООCН:)CООН + CН,ОН A C6H4(COOC4H6)2 + H2O D B The rate of the reaction is given by the expression -TA = kC; gmol/L.h where CA is the concentration of the mono-ester in gmol/L. The value of the apparent rate constant is given by: k = 0.7628 x 10ol1.965- L/gmol.h where T is the reaction temperature in K. The initial concentration of the mono-ester is 2.84 gmol/L and the density of the reaction mixture is 0.984 kg/L. (Molar mass of diester = 278) 1. In an existing plant consisting of a CSTR of 1.1 m diameter and 1.6 m height, the volumetric feed rate is 10 L/min. (a) Find the conversion achieved in an ideal CSTR. (b) If the conversion achieved in practice 68.5%…arrow_forwardNow, let's use what we know about chemistry to infer how much acetic acid was in our sample. Let's look closely at the equation for the reaction we performed. HC2H3O2(aq) + NaHCO3(s) → NaC2H3O2(aq) + H2O(1) + CO2(g) Based on this balanced chemical reaction, we can see that for every one mole of CO2 that was produced one mole of acetic acid was consumed. Based on this, calculate the moles of acetic acid and grams of acetic acid that must have reacted in each sample. Sample Data for Vinegar Lab moles CO2 Produced Moles HC2H3O2 Consumed g HC2H302 Consumed by by Reaction by Reaction Reaction -2 g NaHCO3 0.0329 -4 g NaHCO3 0.0464 -6 g NaHCO3 0.0523 -8 g NaHCOз 0.0477 -10 g NaHCO3 0.0489arrow_forwardwhen acetone is heated in the gas phase, decomposition into ketene and methane takes place according to: (CH3)2CO > CH2-CO + CH4 the reaction is irreversible and first order. The rate constant is 1.047 s-1 vid 725 C. Calculate the turnover of acetone obtained in an isothermal and isobaric tube reactor under the following operating conditions. The reactor is made up of 20 parallel connected tubes, each with a length of 10 meters and an inner diameter of 10 cm. The working pressure is 4 atm and the temperature is 725 C. The acetone supply amounts to 120 mol/s.arrow_forward
- When N2O5(g) is heated it dissociates into N2O3(g) and O2(g) according to the following reaction: N2O5(g)⇌N2O3(g)+O2(g)Kc=7.75N2O5(g)⇌N2O3(g)+O2(g)Kc=7.75 at a given temperature. The N2O3(g) dissociates to give N2O(g) and O2(g) according the following reaction: N2O3(g)⇌N2O(g)+O2(g)Kc=4.00N2O3(g)⇌N2O(g)+O2(g)Kc=4.00 at the same temperature. When 4.00 mol of N2O5(g) is heated in a 1.00-L reaction vessel to this temperature, the concentration of O2(g) at equilibrium is 4.50 mol/L. A. Find the concentration of N2O5 in the equilibrium system. B. Find the concentration of N2O in the equilibrium system C.Find the concentration of N2O3 in the equilibrium system.arrow_forwardi need help with all parts in this question asaparrow_forward11.4 mole dichloromethane (CH2Cl2) enter a reactor with 20.6 mole hydrogen (H2) and 38.6 mole oxygen (O2). The following reaction takes place: CH2Cl2 + H2 + 3/2 O2 → COCl2 + 2 H2O The extent of the reaction is 6.8. Calculate the mole of H2O that are produced.arrow_forward
- Consider the pair of reactions in which ethylene is oxidized either to ethylene oxide (desired) or to carbon dioxide (undesired) in the furnace: C₂H4+0₂-C₂H4O C₂H₂ +30₂-2 CO₂ + 2H₂O The feed mixture and air are fed at a temperature To. All gaseous effluents are at temperature T emerging from the non-isothermal reactor. a) Calculate the number of degrees of freedom of the process. How would the answer differ if the reactor were adiabatic? b) Outline a manual calculation procedure to determine the compositions of all streams.arrow_forwardPls do Asap...!arrow_forwardDirect dehydrogenation of ethylbenzene to styrene is carried out in the vapor phase with steam over a catalyst consisting primarily of iron oxide. The reaction is endothermic, and can be accomplished either adiabatically or isothermally. Both methods are used in practice. The major reaction is the reversible, endothermic conversion of ethylbenzene to styrene and hydrogen: C6H3CH₂CH CoHsCHCH₂ + H₂ AH= 124.9 kJ/mol Competing thermal reactions degrade ethylbenzene to benzene C6H3CH₂CH3C6H6+ C₂H4 AH 101.8 kJ/mol Styrene also reacts catalytically to toluene: CH3CH₂CH3 + H2 CH3CH3 + CH4 AH=64.5 kJ/mol The reactions take place at 620°C. The costs are as shown in Table 1. The production rate of styrene is 200 mol/h. Chemical name Formula Cost (S/kmol) Ethylbenzene C6H5CH₂CH3 57.1 Styrene C.HSCHCH₂ 75.9 Benzene C6H6 32.8 Toluene C6H5CH3 25.8 Hydrogen H₂ 1.2 (as fuel) Methane CH4 4.0 (as fuel) Ethylene C₂H4 6.7 (as fuel) Correlation for the product selectivity and distribution are given as…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780133887518
Author:H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781285061238
Author:Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780072848236
Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The