
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
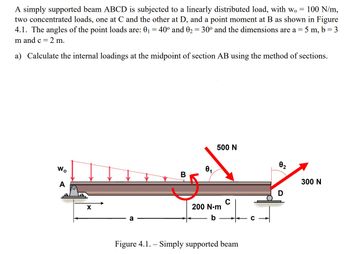
Transcribed Image Text:100 N/m,
A simply supported beam ABCD is subjected to a linearly distributed load, with wo
two concentrated loads, one at C and the other at D, and a point moment at B as shown in Figure
4.1. The angles of the point loads are: 0₁ = 40° and 0₂ = 30° and the dimensions are a = = 5m, b = 3
m and c =
2 m.
a) Calculate the internal loadings at the midpoint of section AB using the method of sections.
Wo
A
X
a
B
1
500 N
의
200 N·m
b
Figure 4.1. - Simply supported beam
0₂
2
300 N
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Could you please help me answer these questions. thank youarrow_forward3. An I beam column with fixed ends (at x = 0 and x = 12 m) is braced at midpoint C as shown below and loaded in compression by a force P. Buckling can potentially occur in either xy plane or xz plane (out of the page). The bracing acts as a simple support (i.e. pinned support) in the xy plane, and there is no such midspan support for buckling in the xz plane. Iyy Izz B = 282 x 106 (mm)4 6 m 6 m a. Which plane is more likely to buckle and why? Include relevant calculations to support your choice. b. Given your answer to part a, find the allowable axial force P assuming a safety factor of 2. Material Properties: E = 200 GPa; Sy = 280 MPa Important properties of the cross-section: A = 27.5 x 10³ (mm)² = 712 x 106 (mm)4 Z yarrow_forwardA simply supported beam carrying floor joist shown in Figure 6.22 is made of rectangular wood having a dimension of 50mm x 100mm. Compute the bending stress in tension and compression.arrow_forward
- A simply supported beam of a total length ll is shown in Figure Q5, where point A is supported by a pin connection and point C is supported by a roller support. The concentrated load is P=mgP=mg at the location of l1l1. Note that l1/l=l1/l= 0.65. Determine the shear-force and bending-moment distributions produced in the beam by the concentrated load PP.arrow_forwardHi there sir/madam I need help on this question A beam with a solid homogeneous rectangular section is simply supported at A and B. A concentrated load F = 150 kilonewtons (kN) acts at point C where distance L1 (A to C) = 2.50 metres (m) and distance L2 (C to B) = 1.65 metres (m). The dimensions of the rectangular section of the beam are breadth, b = 35 mm and depth d = 125 mm. Calculate the maximum bending stress and give your answer in N/mm2 to two decimal placesarrow_forwardThe beam is subjected to a point load and a distribution load as shown in Figure 2-1 below, and the right end is a build-in support. (1ft=12inch, ksi=kilo lb/in2)(a) Find the reaction in build-in support C.(b) Draw a Shear Force Diagram in the beam BC interval.(c) Draw a Moment Diagram in the beam BC interval.(d) Find the maximum shear stress mmax in the beam BC interval.(e) Find the maximum tensile flexural stress mmax, T and maximum compressive flexural stress mmax, C in the beam BC interval, respectively.arrow_forward
- A 5.1 m long simply supported wood beam carries a uniformly distributed load of 11.3 kN/m, as shown in Figure A. The cross-sectional dimensions of the beam as shown in Figure B are b = 205 mm, d = 460 mm, yH = 77 mm, and yx = 162 mm. Section a-a is located at x = 1.3 m from B. (a) At section a-a, determine the magnitude of the shear stress in the beam at point H. (b) At section a-a, determine the magnitude of the shear stress in the beam at point K. (c) If the allowable shear stress for the wood is 850 kPa, what is the largest distributed load w that can be supported by the beam? х В L Figure Aarrow_forwardFind the centroidarrow_forwardA built-in cantilever beam with a hollow rectangular cross-section is subjected to a uniformly distributed load as shown in Figure Q1 below. Which of the following statements best describes the shear force variation along the length, in the x direction, using the sign conventions provided in lectures? Figure Q1 O a ltis constant and positive throughout the length. Ob.it is constant and negative throughout the length. Ocit begins as a negative value and increases linearly to reach a positive value of the same magnitude. Od. None of the provided answers are correct. Oelt begins with a positive constant value for half the length, then suddenly decreases to a negative value, remaining constant for the remaining length. Of. It increases linearly from zero, then continues at a constant value before decreasing linearly to reach a value of zero again. Og It begins as a positive value and decreases linearly to reach a value of zero at the end of the length of the beam.arrow_forward
- Consider the beam in the figure below. Take w = 4 kip/ft and P = 12 kip. Point E is just to the left of the 12-kip load A) Determine the magnitude of the resultant internal normal force in the beam at cross-section through point E. B) Determine the magnitude of the resultant internal shear force in the beam at cross-section through point E. C) Determine the magnitude of the resultant internal bending moment in the beam at cross-section through point E.arrow_forwardA cantilever beam has a cross-section and concentrated loads P1 = 30 kN and P2 = 10 kN, as shown. a. Compute for the maximum tensile bending stress (in MPa). b. Compute for the maximum compressive bending stress (in MPa) c. Compute for the bending stress (in MPa) 2m to the right of point A and 30mm from the top of the beam. d. Find the maximum shear stress (in MPa) for the beam and cross-sectionarrow_forwardA beam AB with overhanging is 6 m in length and made from steel as shown in Figure 2. It is supported by a pin at A and a roller at B. The beam carries a linearly distributed load of 35 kN/m alongAB and uniformly distributed load of 8 kN/m along CD. A moment of 8 kNm is acting at D. Thebeam has a cross-section x-x as shown in Figure 3.a) By using shear-force and bending-moment equations, determine the magnitude of the shear force and bending moment at points A, B, C, and D.b) Construct the shear force and bending moment diagrams for the beam. State all the important values and location of inflection point (if any).c) Calculate the maximum bending stress of the point where located at the inflection point.d) Determine the maximum shear stress and shear stress at point Y.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY