
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
Please answer parts B, C and D.

Transcribed Image Text:A simple random sample of size n is drawn from a population that is normally distributed. The sample mean, x, is found to be 110, and the sample standard deviation,
s, is found to be 10.
(a) Construct an 80% confidence interval about u if the sample size, n, is 15.
(b) Construct an 80% confidence interval about u if the sample size, n, is 28.
(c) Construct a 90% confidence interval about u if the sample size, n, is 15.
(d) Could we have computed the confidence intervals in parts (a)-(c) if the population had not been normally distributed?
Click the icon to view the table of areas under the t-distribution.
(a) Construct an 80% confidence interval about u if the sample size, n, is 15.
Lower bound: 106.5 ; Upper bound: 113.5
(Use ascending order. Round to one decimal place as needed.)
(b) Construct an 80% confidence interval about u if the sample size, n, is 28.
Lower bound:
; Upper bound:
(Use ascending order. Round to one decimal place as needed.)
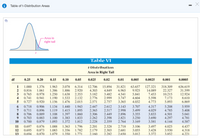
Transcribed Image Text:Table of t-Distribution Areas
-Area in
right tail
Table VI
t-Distribution
Area in Right Tail
df
0.25
0.20
0.15
0.10
0.05
0.025
0.02
0.01
0.005
0.0025
0.001
0.0005
12.706
127.321
318.309
22.327
1
1.376
1.963
3.078
6.314
15.894
31.821
63.657
9.925
5.841
4.604
1.000
636.619
1.386
1.250
1.190
1.156
14.089
7.453
5.598
2.920
6.965
0.816
0.765
0.741
1.061
0.978
0.941
1.886
1.638
1.533
4.303
3.182
2.776
4.849
3.482
2.999
2.757
31.599
12.924
2.353
2.132
2.015
4.541
3.747
3.365
10.215
7.173
5.893
4
8.610
5
0.727
0.920
1.476
2.571
4.032
4.773
6.869
1.134
1.119
2.447
2.365
3.143
2.998
2.896
2.821
2.764
0.718
0.906
3.707
5.959
1.440
1.415
1.397
1.383
1.372
1.943
2.612
2.517
2.449
2.398
2.359
4.317
5.208
3.499
3.355
3.250
5.408
5.041
4.781
4.587
7
0.711
0.896
1.895
4.029
2.306
2.262
2.228
4.785
4.501
4.297
4.144
1.108
8
0.706 0.889
9
0.703
0.700
0.883
0.879
1.860
1.833
3.833
3.690
1.100
10
1.093
1.812
3.169
3.581
0.697
3.497
1.363
1.356
1.350
3.106
3.055
3.012
11
4.025
0.876
0.873
0.870
1.088
1.796
1.782
1.771
2.201
1.083
1.079
2.328
2.303
2.718
2.681
2.650
4.437
4.318
4.221
12
0.695
2.179
3.428
3.930
13
0.694
2.160
2.282
3.372
3.852
23
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Organize each item into the appropriate folder.arrow_forwardUse the following information to answer the next three questions. A bag contains five different balls colored Red, Yellow, Blue, Green, and Orange. You cannot see into the bag and you cannot tell the balls apart by feel.arrow_forwarda. 0 b. -2,0, 2 c. 2 JU d. -2,2arrow_forward
- Rachael has 20 thin rods whose lengths, in centimetres, are 1,2,3,…,201,2,3,…,20. Any two rods can be connected at their ends. Rachael selects three rods to make a triangle, then three other rods to make a second triangle, and so on. only one of rachel's rods cannot be the side of a triangle. determine which one.arrow_forwardanswer b and c ...arrow_forwardThe first angle of a triangle is four times the third angle; the second angle is twenty degrees less than three times the third angle. Let the measure of the third angle be C.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman