
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
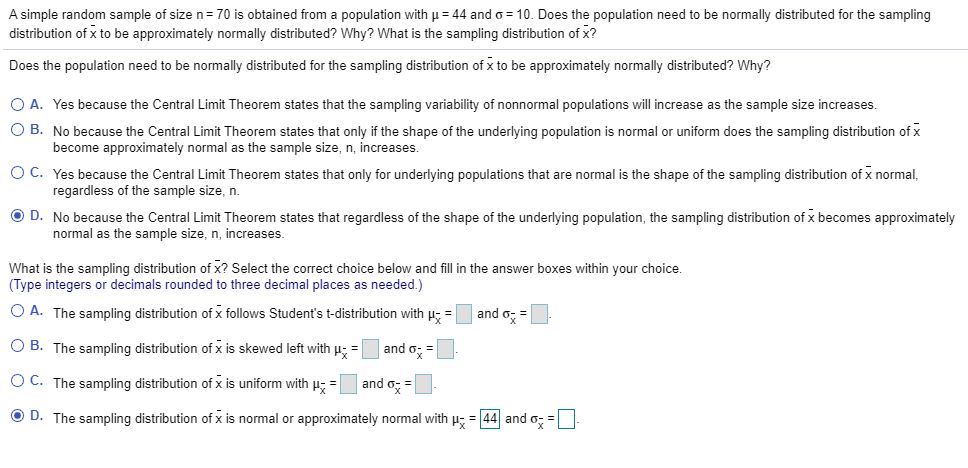
Transcribed Image Text:A simple random sample of size n= 70 is obtained from a population with u = 44 and o = 10. Does the population need to be normally distributed for the sampling
distribution of x to be approximately normally distributed? Why? What is the sampling distribution of x?
Does the population need to be normally distributed for the sampling distribution of x to be approximately normally distributed? Why?
O A. Yes because the Central Limit Theorem states that the sampling variability of nonnormal populations will increase as the sample size increases.
O B. No because the Central Limit Theorem states that only if the shape of the underlying population is normal or uniform does the sampling distribution of x
become approximately normal as the sample size, n, increases.
O C. Yes because the Central Limit Theorem states that only for underlying populations that are normal is the shape of the sampling distribution of x normal,
regardless of the sample size, n.
O D. No because the Central Limit Theorem states that regardless of the shape of the underlying population, the sampling distribution of x becomes approximately
normal as the sample size, n, increases.
What is the sampling distribution of x? Select the correct choice below and fill in the answer boxes within your choice.
(Type integers or decimals rounded to three decimal places as needed.)
O A. The sampling distribution of x follows Student's t-distribution with u- =
and o; =
O B. The sampling distribution of x is skewed left with p; =
and o; =
O C. The sampling distribution of x is uniform with p =
and o; =
O D. The sampling distribution of x is normal or approximately normal with u; = 44 and o; =
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Recall that Benford's Law clalms that numbers chosen from very large data files tend to have "1" as the first nonzero digit disproportionately often. In fact, research has shown that if you randomly draw a number from a v leading digit is about 0.301. Now suppose you are the auditor for a very large corporation. The revenue file contains millons of numbers in a large computer data bank. You draw a random sample of n = 229 numbers from this file and r 85 have a first nonzero digit of 1. Let p represent the population proportion of all numbers in the computer file that have a leading digit of 1. large data file, the probability of getting a number with "1" as the () Test the dalm that p is more than 0.301. Use a 0.10. (a) what is the level of signifcance? State the null and alternate hypotheses. O Hg: p = 0.301; H p> 0.301 O Hgi P = 0.301; Hip 0.301; Hp- 0.301 O Ho: P= 0.301; H: p- 0.301 (b) what sampling distribution will you use? O The Student's t, since np > 5 and ng > 5. O The…arrow_forwardA random sample X1,X2,...,Xn is drawn from the normal distribution. i. Suppose μ is a known parameter. Find the maximum likelihood estimator for σ. ii. Find the bias and variance of the obtained estimatorarrow_forwardLet x be a random variable that has a distribution with mean μ = 150 and standard deviation σ = 15.3. For samples of size n = 36 the sampling distribution of i s with mean = and standard deviation = .arrow_forward
- R2arrow_forwardA simple random sample of size n= 32 is obtained from a population that is skewed left with u = 58 and o = 10. Does the population need to be normally distributed for the sampling distribution of x to be approximately normally distributed? Why? What is the sampling distribution of x? Does the population need to be normally distributed for the sampling distribution of x to be approximately normally distributed? Why? O A. Yes. The central limit theorem states that the sampling variability of nonnormal populations will increase as the sample size increases. O B. Yes. The central limit theorem states that only for underlying populations that are normal is the shape of the sampling distribution of x normal, regardless of the sample size,n. O C. No. The central limit theorem states that regardless of the shape of the underlying population, the sampling distribution of x becomes approximately normal as the sample size, n, increases. O D. No. The central limit theorem states that only if the…arrow_forward3. If x1, X2, X3, ..., Xn is a random sample from a normal 1 distribution N (µ, 1) show that t= E xí is an unbiased estimator of n i = 1 H² + 1.arrow_forward
- 4. The pmf of a geometric distribution with parameter p is given by S p(1 – p)" n= 0, 1, 2, ... otherwise. Pn = Assume p> 0. Show that the variance is (1 – p)/p². Hint: Σ Eng" (1 – q)² n=0 for |g| < 1.arrow_forwardOnly need part farrow_forward#4: Suppose that X1,... , X7n is an i.i.d. random sample drawn from a U[a, 1] uniform distribution, where 0a < 1. Suppose that you want to find an unbiased estimator, â, for a. (a) By definition, what relation must be satisfied for â to be an unbiased estimator of a (b) Use the first-order statistic to find an unbiased estimator of a. Recall that the first-order statistic has the p.d.f: п-1 g(yn)nf(yn) f(x)da Уп where f is the p.d.f. of each of the X;'s. (c) Find an alternative unbiased estimator â of a, which is still based on the random sample (hint: think of a common statistic we calculate from the random sample)arrow_forward
- QUESTION 1 a) Let X₁, X2, X3,..., Xn be a random sample of size n from population X. Suppose that X follows an exponential distribution with parameter and Y = =-=1X₁. 19 iii) What is the value of sample size n, if P(|Y - 2n| < 40) ≥ 0.025? iv) Use the Central Limit Theorem to compute P(100arrow_forwardP(p<0.33)arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosarrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman