
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
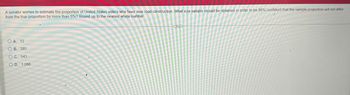
Transcribed Image Text:A senator wishes to estimate the proportion of United States voters who favor new road construction. What size sample should be obtained in order to be 98% confident that the sample proportion will not differ
from the true proportion by more than 5%? Round up to the nearest whole number.
O A. 12
OB. 385
O C. 543
O D. 1,086
CHET
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- You will be applying what you have learned in this course by gathering data and running a statistical analysis. 1) To study about the relationship between height and the weight, you need to collect a sample of nine (9) people using a systematic sampling method. a. What is the population of people? b.Where and how are you going to collect your sample? c. Does your sample accurately represent your population? Why or why not? d. Collect the sample and record the data. 2) (CLO 1) Construct a confidence interval to estimate the mean height and the mean weight by completing the following: a. Find the sample mean and the sample standard deviation of the height. b. Find the sample mean and the sample standard deviation of the weight. c. Construct and interpret a confidence interval to estimate the mean height. d. Construct and interpret a confidence interval to estimate the mean weight. 3) (CLO 2) Test a claim that the mean height of people you know is not equal to 64 inches using the…arrow_forwardYou are the operations manager for an airline and you are considering a higher fare level for passengers in aisle seats. How many randomly selected air passengers must you survey? Assume that you want to be 95% confident that the sample percentage is within 5.5 percentage points of the true population percentage. Complete parts (a) and (b) below. a. Assume that nothing is known about the percentage of passengers who prefer aisle seats. n = (Round up to the nearest integer.) b. Assume that a prior survey suggests that about 34% of air passengers prefer an aisle seat. n = IDound un to the nearest integer)arrow_forwardYou are the operations manager for an airline and you are considering a higher fare level for passengers in aisle seats. How many randomly selected air passengers must you survey? Assume that you want to be 90% confident that the sample percentage is within 4.5 percentage points of the true population percentage. Complete parts (a) and (b) below. a. Assume that nothing known about the percentage of passengers who prefer aisle seats. n= 335 (Round up to the nearest integer.) b. Assume that a prior survey suggests that about 38% of air passengers prefer an aisle seat. (Round up to the nearest integer.)arrow_forward
- Statistics Questionarrow_forwardYou are the operations manager for an airline and you are considering a higher fare level for passengers in aisle seats. How many randomly selected air passengers must you survey? Assume that you want to be 99% confident that the sample percentage is within 4.5 percentage points of the true population percentage. Complete parts (a) and (b) below. a. Assume that nothing is known about the percentage of passengers who prefer aisle seats. n = 820 (Round up to the nearest integer.) b. Assume that a prior survey suggests that about 39% of air passengers prefer an aisle seat. n=0 (Round up to the nearest integer.) Carrow_forwardA programmer plans to develop a new software system. In planning for the operating system that he will use, he needs to estimate the percentage of computers that use a new operating system. How many computers must be surveyed in order to be 90% confident that his estimate is in error by no more than five percentage points question marks? Complete parts (a) through (c) below. a) Assume that nothing is known about the percentage of computers with new operating systems.arrow_forward
- You are the operations manager for an airline and you are considering a higher fare level for passengers in aisle seats. How many randomly selected air passengers must you survey? Assume that you want to be 90% confident that the sample percentage is within 5.5 percentage points of the true population percentage. Complete parts (a) and (b) below. a. Assume that nothing is known about the percentage of passengers who prefer aisle seats. (Round up to the nearest integer.) b. Assume that a prior survey suggests that about 38% of air passengers prefer an aisle seat. (Round up to the nearest integer.)arrow_forwardYou want to obtain a sample to estimate a population proportion. Based on previous evidence, you believe the population proportion is approximately 56%. You would like to be 98% confident that your estimate is within 3.5% of the true population proportion. How large of a sample size is required?arrow_forwardA. What is the total with the disease? B. What is the number with the disease that test positive? C. What is the number without the disease that test positive. D. Determine P(Have the Disease | Tested Positive). Please help and answer all parts using the chart attachedarrow_forward
- Some states now allow online gambling. As a marketing manager for a casino, you need to determine the percentage of adults in those states who gamble online. How many adults must you survey in order to be 90% confident that your estimate is in error by no more than one percentage point? Complete parts (a) and (b) below. a. Assume that nothing is known about the percentage of adults who gamble online. n=0 (Round up to the nearest integer.) b. Assume that 18% of all adults gamble online. n= (Round up to the nearest integer.)arrow_forward4)arrow_forwardThe FBI wants to determine the effectiveness of their 1010 Most Wanted list. To do so, they need to find out the fraction of people who appear on the list that are actually caught. Step 1 of 2 : Suppose a sample of 283283 suspected criminals is drawn. Of these people, 9393 were captured. Using the data, estimate the proportion of people who were caught after being on the 1010 Most Wanted list. Enter your answer as a fraction or a decimal number rounded to three decimal places.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman