
Database System Concepts
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780078022159
Author: Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
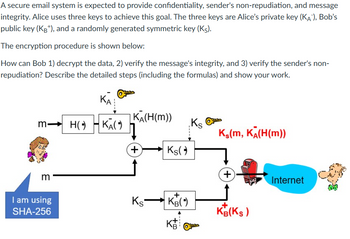
Transcribed Image Text:A secure email system is expected to provide confidentiality, sender's non-repudiation, and message
integrity. Alice uses three keys to achieve this goal. The three keys are Alice's private key (KA), Bob's
public key (KB+), and a randomly generated symmetric key (Ks).
The encryption procedure is shown below:
How can Bob 1) decrypt the data, 2) verify the message's integrity, and 3) verify the sender's non-
repudiation? Describe the detailed steps (including the formulas) and show your work.
m- H(-)
m
I am using
SHA-256
КАН
KA()
KA(H(M))
+
Ks
Ks()
+
KB(*)
Ks
Ks(m, KA(H(m))
+
KB (Ks)
Internet
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Alice sets up an RSA public/private key, but instead of using two primes, she chooses three primes p, q, and r and she uses n=pqr as her RSA-style modulus. She chooses an encryption exponent e and calculates a decryption exponent d. Encryption and Decryption are defined: C ≡ me mod n and m ≡ Cd mod n where C is the ciphertext corresponding to the message m. Decryption: de ≡ 1 mod φ(n) | Let p = 5, q = 7, r = 3, e = 11, and the decryption exponent d = -13. n = 105 & φ(n) = 48 Q: Alice upgrades to three primes that are each 200 digits long. How many digits does n have?arrow_forwardQuestion # 3 Assume that Dominique and Pricilla agreed to use an auto key cipher with initial keyvalue k1 = 11. Now Dominique wants to send Pricilla the following message“THE CLASS IS CANCELLED”. Encrypt the message before transmitting it over the Internet Remember: i need a Mathematics solution not computer program You must show all the steps of your workarrow_forwardSuppose Alice has a public key with modulus 815153 and encryption exponent 91. Eve intercepts a ciphertext 766247from Bob that was encrypted using this key. She calculates 766247⋅941^91(mod815153)=143804 and asks Alice to decrypt this message as an authentication test. Alice responds with the decrypted message 167698 Find the plaintext without factoring Alice’s modulus.arrow_forward
- Computer Science Assume we use transposition cipher to encrypt the data, and the original message is stored in a 8 by 5 matrix (8 rows and 5 columns). If the ciphertext is shown below, what is the original plaintext?WMHPSCATEEEUCELELTCTIASLOTMRNCAarrow_forwardPart 2: Perform encryption and decryption using the RSA algorithm for the following. Show all your steps. 1. p = 3;q=11, e = 7; M = 5 2. p=5;q=11, e = 3; M = 9arrow_forwardIn an RSA system, the public key (n,e) of a given user is (323, 11). 1. What is the value of the exponent in the private key (n, d), of this user? 2. Suppose you want to send this user the message m = 45, write down the expression to generate the ciphertext for this message. 3. Suppose that your ciphertext, c, is 5, write down the expression to generate the plaintext matching this ciphertext. 4. Can you encrypt the message m=322 with this public key? O a. Yes O b. Noarrow_forward
- Alice and Bod have decided to use a symmetric encryption algorithm. They have some assumptions about their messages:- Messages only contain capital letters (i.e. A to Z)- The length of their shared key must be greater than or equal to the length of the plaintext- They assign each letter a number as follows: (A,0), (B,1), (C,2), (D,3),…, (Z,25)Their algorithm combines the key and the message using modular addition. The numerical values of corresponding message and key letters are added together, modulo 26. For example, if the plain text is “HELLO” and the key is “SECRET” then the encrypted message is calculated as following:Since the length of the plaintext is 5, we just need the first 5 letters of the key (i.e. “SECRE”), then for each letter, we should add corresponding letters in both the plaintext and the key modulo 26.Plaintext: H (7) E (4) L (11) L (11) O (14)Key: S (18) E (4) C (2) R (17) E(4)Cipher: Z (25) I (8) N(13) C(2) S (18) Write a program in Python, C/C++ or JavaScript to…arrow_forwardPerform Encryption and decryption using the RSA algorithm for the following: a. p=5; q = 11; e = 3; M = 12 b. p= 3; q = 17; e = 7; M = 2 c. p=7; q = 19; e = 11; M = 5 d. p= 7; q = 13; e = 11; M = 8 e. p= 13; q = 23; e = 5; M = 10arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780134444321
Author:Tony Gaddis
Publisher:PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780132737968
Author:Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780133976892
Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337627900
Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education