
Concept explainers
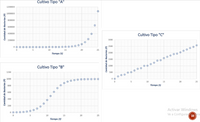
A scientist is studying three different cultures of bacteria {labeled "A", "B" and "C"} and wants to mathematically model the bacterial change of each type. To do this, the scientist decides to collect data for 25 consecutive days and builds the following
Help the scientist decide which mathematical model (initial value problem) to use for each of the three types of crops. To do this, associate each of the graphs above with one of the following initial value problems.
Crop type A
a) dP/dt = k with P(0)=P0 and k>0.
b) dP/dt = k with P(0)=P0 and k<0.
c) dP/dt = kt with P(0)=P0 and k>0.
d) dP/dt = kt with P(0)=P0 and k<0.
e) dP/dt = kP with P(0)=P0 and k>0.
f) dP/dt = kP with P(0)=P0 and k<0.
g) dP/dt = kP(1-P/M) with P(0)=P0 and M, k>0.
h) dP/dt = kP(1-P/M) with P(0)=P0 and M, k<0.
Crop type B
a) dP/dt = k with P(0)=P0 and k>0.
b) dP/dt = k with P(0)=P0 and k<0.
c) dP/dt = kt with P(0)=P0 and k>0.
d) dP/dt = kt with P(0)=P0 and k<0.
e) dP/dt = kP with P(0)=P0 and k>0.
f) dP/dt = kP with P(0)=P0 and k<0.
g) dP/dt = kP(1-P/M) with P(0)=P0 and M, k>0.
Crop type C
a) dP/dt = k with P(0)=P0 and k>0.
b) dP/dt = k with P(0)=P0 and k<0.
c) dP/dt = kt with P(0)=P0 and k>0.
d) dP/dt = kt with P(0)=P0 and k<0.
e) dP/dt = kP with P(0)=P0 and k>0.
f) dP/dt = kP with P(0)=P0 and k<0.
g) dP/dt = kP(1-P/M) with P(0)=P0 and M, k>0.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

- You were asked to help with analysis of birth weights (BW) of 10,000 infants born in NYC during a certain period of time. The aim of the analysis is to see whether the birth weights of the infants are associated with mothers AGE at birth (continuous variable in years) and mothers smoking status (the maternal smoking status MSS contains 4 categories “Non-smoker”, “Past-smoker”, “Passive-smoker”, “Smoker”) and NYC boroughs (the BOROUGH variable contains 5 categories “Manhattan”, “Bronx”, “Brooklyn”, “Queens” and “State Island”). Write down the population model that assumes the effect of mother’s AGE at birth on infant weight BW is DIFFERENT for different levels of maternal smoking status (MSS) when adjusted for BOROUGH variable. Specify the name of each predictor in the model and/or what it means. Make sure that it is clear what each predictor means.arrow_forwardPlease show workarrow_forwardYou were asked to help with analysis of birth weights (BW) of 10,000 infants born in NYC during a certain period of time. The aim of the analysis is to see whether the birth weights of the infants are associated with mothers AGE at birth (continuous variable in years) and mothers smoking status (the maternal smoking status MSS contains 4 categories “Non-smoker”, “Past-smoker”, “Passive-smoker”, “Smoker”) and NYC boroughs (the BOROUGH variable contains 5 categories “Manhattan”, “Bronx”, “Brooklyn”, “Queens” and “Staten Island”). Questions: 1.Write down the population model that estimates BW based on variables AGE and BOROUGH(with the dummy variables). Make sure that it is clear what each predictor means. 2.How many parallel lines are computed by model from population model you created above? 3.Write down the population model that estimates BW based on variables AGE, MSS(with their dummy variables) and BOROUGH(with their dummy variables). Also write down the number of parrallel lines.…arrow_forward
- The best predicted vLue of y when x =8arrow_forwardhow can i calculatearrow_forwardA researcher is studying the intensity of hurricanes that entered the Gulf of Mexico between 1975-2015 and the average water temperature of the Gulf of Mexico at the hurricane's peak strength. What is the independent and dependent variable in this study?arrow_forward
- Range of ankle motion is a contributing factor to falls among the elderly. Suppose a team of researchers is studying how compression hosiery, typical shoes, and medical shoes affect range of ankle motion. In particular, note the variables Barefoot and Footwear2. Barefoot represents a subject's range of ankle motion (in degrees) while barefoot, and Footwear2 represents their range of ankle motion (in degrees) while wearing medical shoes. Use this data and your preferred software to calculate the equation of the least-squares linear regression line to predict a subject's range of ankle motion while wearing medical shoes, ?̂ , based on their range of ankle motion while barefoot, ? . Round your coefficients to two decimal places of precision. ?̂ = A physical therapist determines that her patient Jan has a range of ankle motion of 7.26°7.26° while barefoot. Predict Jan's range of ankle motion while wearing medical shoes, ?̂ . Round your answer to two decimal places. ?̂ = Suppose Jan's…arrow_forwardFind the regression line of the points: (1, 9), (2, 8), (8, 4), (9, 2)arrow_forwardAn agricultural field trial compares the yield of two varieties of corn. The researchers divide in half each of 8 fields of land in different locations and plant each corn variety in one half of each plot. After harvest, the yields are compared in bushels per acre at each location. The 8 differences (Variety A - Variety B) give x¯=3.07 and s=5.11. Does this sample provide evidence that Variety A had a higher yield than Variety B? (a) State the null and alternative hypotheses: (Type "mu" for the symbol μμ , e.g. mu > 1 for the mean is greater than 1, mu < 1 for the mean is less than 1, mu not = 1 for the mean is not equal to 1)H0 : Ha : (b) Find the test statistic, t = 7,6arrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





