
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
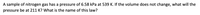
Transcribed Image Text:A sample of nitrogen gas has a pressure of 6.58 kPa at 539 K. If the volume does not change, what will the
pressure be at 211 K? What is the name of this law?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Three gases are mixed into one container. The partial pressure of gas D is 820.1 mmHg. The partial pressure of gas E is 217 mmHg. The partial pressure of gas F is 445.3 mmHg. Determine the total pressure of the gases in a different unit, atm. Do not round until you have finished the problem. 1.00 atm = 760.0 mmHg Your answer should contain one decimal place. Ex: If your answer is 4.435, you would use 4.4 Include the correct units.arrow_forward.What is the final temperature if a sample of ammonia gas, initially at a pressure of 3.00 atmospheres, a temperature of 500 K, and a volume of 275 L is changed to a volume of 200 L and a pressure of 2.50 atm?arrow_forwardA gas-filled weather balloon has a volume of 57.0 L at ground level, where the pressure is 767 mmHg and the temperature is 23.9 °C. After being released, the balloon rises to an altitude where the temperature is –5.32 °C and the pressure is 0.0688 atm. What is the weather balloon's volume at the higher altitude? L V =arrow_forward
- If a 20.0 L cylinder at 19°C is charged with 5.00 g each of sulfur dioxide (SO2) and oxygen gas, what is the partial pressure of each gas? What is the total pressure?arrow_forwardAn experimenter had a gas container that could change its volume. Several times, after setting the container to different volumes and letting the temperature reach room temperature, he measured the pressure at each different volume. Sketch what a graph of volume vs. pressure would look like.arrow_forwardA sample of argon gas in an elastic container has a pressure of 2.0 atm and a volume of 4.0 L. If the pressure is increased to 3.75 atm, what will the new volume be?arrow_forward
- A gas is at a pressure of 97.0 kPa has a volume of 0.4 L. If the pressure is increased to 78 kPa, what will be the new volume?arrow_forward4. Two containers are attached together as shown with a valve between the containers. The 26.0 L flask contains gas at a pressure of 4.25 atmospheres. The 47.0 L container does not contain any gas. The value between the two containers is opened and the gas in the 26.0 L container then also fills the 47.0 L container. What is the resulting pressure of the gas in the two containers?arrow_forwardA sample of argon gas at 308 K and 0.985 atm occupies a volume of 3.18 L. If the pressure of the gas is increased, while at the same time it is heated to a higher temperature, the final gas volume could be larger or smaller than 3.18 L depending on the final pressure and temperature. will be larger than 3.18 L. will be smaller than 3.18 L.arrow_forward
- The gas in a 225.0 mL piston experiences a change in pressure from 1.35 atm to 2.50 atm. What is the new volume (in mL) assuming the moles of gas and temperature are held constant?arrow_forwardSuppose you had a 3.60-L sample of neon gas at 21°C and a pressure of 0.913 atm. What would be the volume of this gas if the pressure were increased to 1.240 atm while the temperature remained constant? Volumearrow_forwardThe pressure of a sample of argon gas was increased from 1.57 atm to 6.41 atm at constant temperature. If the final volume of the argon sample was 14.3 L, what was the initial volume of the argon sample? Assume ideal behavior. Larrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY