
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
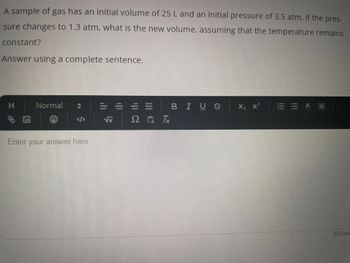
Transcribed Image Text:A sample of gas has an initial volume of 25 L and an initial pressure of 3.5 atm. If the pres-
sure changes to 1.3 atm, what is the new volume, assuming that the temperature remains
constant?
Answer using a complete sentence.
H
Normal
@
Enter your answer here
|||
2 0 1
BIUS
X₂ X²
EEAA
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A sample of nitrogen gas at a pressure of 0.978 atm and a temperature of 21.1 °C, occupies a volume of 18.0 liters. If the gas is allowed to expand at constant temperature to a volume of 24.8 liters, the pressure of the gas sample will be atm.arrow_forwardA sample of nitrogen gas at 310 K and 1.01 atm occupies a volume of 1.51 L. If the gas is compressed into a smaller volume, while at the same time it is cooled to a lower temperature, the final gas pressure ? will be lower than 1.01 atm. ? will be higher than 1.01 atm. ? could be higher or lower than 1.01 atm depending on the final volume and temperature.arrow_forwardConsider a gas sample with an initial pressure of 533 torr and a volume of 10.5 L. What is the pressure of the gas when the volume of the gas increases by a factor of 2.21, as the temperature of the gas remains constant.arrow_forward
- A sample of hydrogen gas that occupies a volume of 31.9 L at a temperature of 0 °C and a pressure of 1 atm contains ___ moles of gas.arrow_forward[Review Topics] [References] Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. A sample of hydrogen gas occupies a volume of 8.88 L at 48.0°C and 0.550 atm. If it is desired to increase the volume of the gas sample to 11.7 L, while decreasing its pressure to 0.399 atm, the temperature of the gas sample at the new volume and pressure must be Submit Answer Retry Entire Group 9 more group attempts remaining Prus Email instructior Save and Exitarrow_forwardA flexible container at an initial volume of 7.14 L contains 9.51 mol of gas. More gas is then added to the container until it reaches a final volume of 12.1 L. Assuming the pressure and temperature of the gas remain constant, calculate the number of moles of gas added to the container. number of moles of gas: molarrow_forward
- A gas sample has an initial pressure of 593 mmHg and an initial volume of 0.511 L What is the pressure (in atm) when the volume of the sample is decreased to 244 mL? (Assume constant temperature and constant number of moles of gas.)arrow_forwardThe initial pressure of a gas system is 43.0 atm and the initial volume is 5.75 L. If the pressure is decreased to 0.700 atm, what is the new volume?arrow_forwardA gas occupying a volume of 18.5 L has a pressure of 329 torr. The pressure is decreased. The volume ends up being 42.7 L. What will be the new pressure?arrow_forward
- A sample of gas contains has a pressure of 1.40 atm at 40.0 mL. What is the pressure of the sample in atmospheres if the volume decreases to 11 mL under constant moles and temperature? Do not include units when entering your answer.arrow_forwardA sample of neon gas at a pressure of and a temperature of, occupies a volume of. If the gas is cooled at constant pressure to a temperature of, the volume of the gas sample will be L.arrow_forwardIf a sample of gas at a pressure of 6.91 atm occupies a volume of 56.3 L, determine the volume of the sample (in L) when the pressure is 7.94 atmarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY