
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question

Transcribed Image Text:A sample of 16 items provides a sample standard deviation of 9.5. Test the following hypotheses using a = 0.05. What is your conclusion? Use both the p-value approach and the critical value approach.
Ho: ²50
H₂ : ² > 50
Test statistic =
p-value low from table=
p-value high from table=
X0.05 =
Reject Ho if x² >
- Select your answer -
Hide Feedback
Incorrect
(to 2 decimals)
(to 3 decimals)
(to 3 decimals). Use Table 11.1.
(to 3 decimals). Use Table 11.1.
(to 3 decimals)
Hint(
Hint(
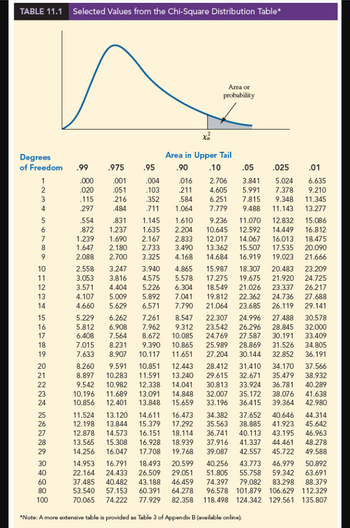
Transcribed Image Text:TABLE 11.1 Selected Values from the Chi-Square Distribution Table*
Degrees
of Freedom
LEAST ONE THAT * *** 9888
2
3
4
5
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
40
80
.99 .975
.000
.001
.020
.051
.115
216
.297
484
.554
.872
1.239
1.647 2.180
2.088 2.700
2.558 3.247
3.053 3.816
3.571
4.107
4.660
6.408
7.015
7.633
5.229 6.262
5.812 6.908
7.564
11.524
12.198
.95
.831
1.145
1.237
1.635
1.690 2.167
12.878
13.565
14.256
.004
.103
.352
.711
3.940
4.575
4.404 5.226
5.009
5.892
5.629
6.571
7.261
7.962
8.672
8.231
9.390
8.907 10.117
8.260
9.591
10.851
8.897 10.283 11.591
9.542 10.982
12.338
10.196
11.689 13.091
10.856
12.401
2.733
3.325 4.168
.016
.211
.584
1.064
Area in Upper Tail
.90
.10
2.706
4.605 5.991
6.251
7.779
4.865
5.578
6.304
7.041
7.790
1.610
2.204
2.833
12.017 14.067
16.013
3.490 13.362 15.507 17.535
14.684 16.919 19.023
8.547
9.312
Xa
10.085
10.865
11.651
Area or
probability
14.848
13.848 15.659
.05 .025
3.841 5.024
7.378
7.815 9.348
9.488 11.143
9.236 11.070 12.832
15.086
10.645 12.592 14.449 16.812
18.475
15.987
18.307 20.483
17.275
19.675 21.920
18.549 21.026 23.337
19.812 22.362 24.736
21.064 23.685 26.119
12.443
13.240
14.041 30.813
24.996
27.488
26.296 28.845
27.587 30.191
.01
6.635
9.210
11.345
13.277
22.307
23.542
24.769
25.989 28.869
31.526 34.805
27.204 30.144 32.852 36.191
13.120 14.611 16.473
34.382
13.844
15.379
17.292
35.563
14.573
16.151
18.114 36.741 40.113
15.308
16.928
18.939 37.916
16.047
17.708 19.768
20.090
21.666
100
*Note: A more extensive table is provided as Table 3 of Appendix B (available online).
23.209
24.725
26.217
27.688
29.141
28.412 31.410 34.170 37.566
29.615 32.671 35.479 38.932
33.924 36.781
40.289
32.007 35.172 38.076
41.638
33.196
36.415 39.364
42.980
30.578
32.000
33.409
37.652
40.646
44.314
38.885 41.923 45.642
43.195
46.963
44.461
48.278
41.337
39.087 42.557 45.722
49.588
14.953
16.791
18.493 20.599
40.256 43.773 46.979 50.892
51.805 55.758 59.342 63.691
22.164
24.433
26.509 29.051
37.485 40.482 43.188 46.459 74.397 79.082 83.298 88.379
53.540 57.153 60.391 64.278 96.578 101.879 106.629 112.329
70.065 74.222 77.929 82.358 118.498 124.342 129.561 135.807
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Claim: The mean systolic blood pressure of all healthy adults is less than than 125 mm Hg. Sample data: For 258 healthy adults, the mean systolic blood pressure level is 124.72 mm Hg and the standard deviation is 15.18 mm Hg. The null and alternative hypotheses are Ho: μ = 125 and H₁ : µ< 125. Find the value of the test statistic. The value of the test statistic is (Round to two decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardA baseline of calibrated length 400.009 m is observed repeatedly with an EDM instrument. After 25 observations, the average of the observed distance is 400.012 m with a standard deviation of ±0.003 m. Is the distance observed significantly different from the distance calibrated at a 0.05 level of significance? Here you must write: 5.1. The two hypothesis. 5.2. The value of the test statistic. 5.3. The rejection region. 5.4. The conclusion.arrow_forwardA simple random sample of size n= 40 is drawn from a population. The sample mean is found to be 103.6, and the sample standard deviation is found to be 21.7. Is the population mean greater than 100 at the a =0.10 level of significance? Determine the null and alternative hypotheses. Ho: H= 100 H: u> 100 Compute the test statistic. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) %3D to Enter your answer in the answer box and then click Check Answer. Check Answer Clear All 2 parts remaining MacBook Air 10 888 F7 FS F4 F3 esc F2 FT & de 8 9 @ 2 3 4 1 P Y Q W E cab K F S > lock Darrow_forward
- On average, Americans have lived in 4 places by the time they are 18 years old. Is this average more for college students? The 52 randomly selected college students who answered the survey question had lived in an average of 4.18 places by the time they were 18 years old. The standard deviation for the survey group was 0.5. What can be concluded at the αα = 0.05 level of significance?arrow_forwardI. A study reports that teenagers spend 27 hours a week online (www.telegraph.co.uk). A researcher wanted to check if this claim is true. A random sample of 200 teenagers taken showed that they spend an average of 25.7 hours per week online with a standard deviation of 8.2 hours. Perform a hypothesis test with the alternate hypothesis that teenagers spend less than 27 hours per week online. Use c = 0.05. Perform all of the steps outline in your notes and write a complete conclusion in words. Assume the distribution of hours spent online is normally distributed.arrow_forwardYou wish to test the following claim (HaHa) at a significance level of α=0.001α=0.001. Ho:μ=53.4 Ha:μ<53.4You believe the population is normally distributed, but you do not know the standard deviation. You obtain the following sample of data: What is the test statistic for this sample? (Report answer accurate to three decimal places.)test statistic = What is the p-value for this sample? (Report answer accurate to four decimal places.)p-value = 45.6 39.8 42.3 45.4 33.4 46.6arrow_forward
- Arandom sample of 15 observations taken from a population that is normally distributed produced a sample mean of 42.4 and a standard deviation of 8. Find the range for the p-value and the critical and observed values of t for each of the following tests of hypotheses using, a= 0.01 Use the distribution table to find a range for the pvalue. Round your answers for the values of decimal places. H0: mean =46 versus H1: mean<46. = <p-value <p-value t critical=t observed= b. H0: mean=46 versus H1: mean≠46 = < p-value < t critical left=t critical right=t observed=arrow_forwardMany people believe that the average number of Facebook friends is 150. The population standard deviation is 37.6. A random sample of 46 high school students in a particular county revealed that the average number of Facebook friends was 159. At =α0.01, is there sufficient evidence to conclude that the mean number of friends is greater than 150? A. State the hypotheses and identify the claim with the correct hypothesis. :H0 ▼claim or not claim :H1 ▼claim or not claimThis hypotheses test is a ▼one-tailed or two-tailed test B. Find the critical value(s) (c)Compute the test value. z= (d)Make the decision. reject or accept (e)Summarize the results. is there enough evidence to support the claimarrow_forwardA large milling machine produces steel rods to certain specifications. The machine is considered to be running normally if the standard deviation of the diameter of the rods is at most 0.15 millimeters. The line supervisor needs to test the machine is for normal functionality. The quality inspector takes a sample of 25 rods and finds that the sample standard deviation is 0.19. What are the null and alternative hypotheses for the test? A. H0 : σ = 0.0225 and H1 : σ ≠ 0.0225 B. H0 : σ ≥ 0.15 and H1 : σ < 0.15 C. H0 : σ2 > 0.15 and H1 : σ2 ≤ 0.15 D. H0 : σ2 ≤ 0.0225 and H1 : σ2 > 0.0225arrow_forward
- The average scores in a pre-final examination scored by under graduate students in the previous year was 63. A tutor, after conducting the weekly tests, wishes to check whether that average has increased this year. For a sample of 70 students, the mean score was 68 with a standard deviation of 15.State the null and the alternative hypotheses. Group of answer choices H0: μ = 63 vs. Ha: μ ≥ 63 H0: μ = 63 vs. Ha: μ ≠ 63 H0: μ = 63 vs. Ha: μ ≤ 63 H0: μ = 63 vs. Ha: μ > 63 H0: μ = 63 vs. Ha: μ < 63arrow_forwardA taxi company claims that its drivers have an average of at least 12.4 years' experience. In a study of 15 taxi drivers, the average experience was 11.2 years. The standard deviation was 2. At a = 0.10, is the number of years' experience of the taxi drivers really less than the taxi company claimed. State the hypotheses and identify the claim.Identify the statistical test to be used. a. Find for the critical value(s). b. Sketch a curve with the rejection and non-rejection region. Computer for the test value. c. Make the decision. Interpret the results.arrow_forwardTwo samples are taken with the following sample means, standard deviations, and sample sizes. We have no reason to assume the variance are equal. T1 = 20 81 = 3 n₁ = 50 F₂ = 27 82 = 2 n₂ = 65 Estimate the difference in population means using a 88% confidence level in interval notation. Round answers to 2 decimal places. -7.770 -6.23 Xarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman