
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
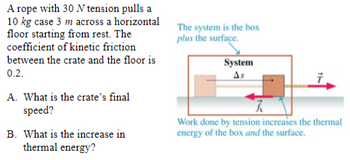
Transcribed Image Text:A rope with 30 N tension pulls a
10 kg case 3 m across a horizontal
floor starting from rest. The
coefficient of kinetic friction
between the crate and the floor is
0.2.
A. What is the crate's final
speed?
B. What is the increase in
thermal energy?
The system is the box
plus the surface.
System
As
Work done by tension increases the thermal
energy of the box and the surface.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In the attached image, the mass is 3.20 kg, and theta=37 degrees. The surface does have friction, with static coefficient=0.45 and kinetic coefficient=0.39.If a person takes hold of the rope and, pulling at this angle with a force of T=23 N, drags the box 3.8 meters... a. How much work is done on the box by person pulling? b. How much work is done on the box by the force of friction? c. What is the net work done on the box?arrow_forwardThere is a 23.1 kg box that starts with an initial velocity of 23.5 m/s. The box moves up a hill where it encounters a frictional force of 319 Newtons over the course of 6 meters. It then moves down a shorter hill.A.How much work was done on the box? JoulesB.What is the box's final velocity? m/sarrow_forward1. A 10 kg at a mail facility slides down a 10-meter sorting chute. The height of the chute is 2 meters. The speed of the package at the top of the chute is 5 m/s, and it is moving at 3 m/s when it reaches the bottom. Let g = 10 m/s². Write the relations you use symbolically before substituting in numbers. a. What is the change in the kinetic energy of the package when it slides down the chute? Be careful with the sign (+/-)! 2m Normal Force: M e. What is the magnitude of the frictional force? b. Determine whether the work done by gravity and the normal force on the package is positive, negative, or zero. Hint: Draw each force vector and displacement vector with their tails together. Think about angle between the force and displacement. Gravity: 20 m 9.8 m What is the work done by gravity as the package slides down the chute? Be careful with the sign (+/-) d. How much mechanical energy became thermal energy during this process, i.e., what is AEtherm? Use the work- energy relation with…arrow_forward
- A 5.00 gram bullet moving horizontally with a speed of 400 m/s collides with a wooden block. After moving 2.00 cm into the block the bullet stops moving. Was work done on the bullet? If so describe the type of work and the force that did the work. a. yes, negative work, force is in the opposite direction as the initial velocity of the bullet b. yes, positive work, force is in the same direction as the initial velocity of the bullet c. yes, positive work, force is in the opposite direction as the initial velocity of the bullet d. No work was done on the bullet e. yes, negative work, force is in the same direction as the initial velocity of the bulletarrow_forwardA box is pulled 2.0 meters along a rough surface at constant velocity using 100 N of force inclined at 30° above the horizontal. a. How much work is done by the: gravitational force, normal force, and frictional force? b. If the force applied, Fa, is doubled but the frictional force remains the same (this is unlikely to occur in practice since Fn changes), will the net work be the same? c. If Fa is doubled with the frictional force unchanged, how much kinetic energy would the block have after being pulled 2.0 m?arrow_forward2. A 900 kg elevator is raised by an electric motor up from the basement to the third floor, a vertical distance of 9.9 m, over the course of 5 s. There's a friction force of 125 N between the elevator and the elevator shaft. A. Draw a free body diagram of the elevator. Which forces are conservative? Which forces are dissipative? Which are external? B. How much potential energy does the elevator gain as its lifted? C. What is the work done by friction on the elevator? Is it positive or negative?arrow_forward
- A spring with spring constant k is attached to the floor, standing vertically. You place a box of mass m on the spring and, from rest, release it. The spring bounces up and down a few times and comes to rest (both its velocity and acceleration are zero). Find the thermal energy generated in this process in terms of m, g, and k. Answer Options: A. mg/k B. m^2 g/k C. m^2 g^2/k D. m^2 g^2/ 2k E. mg/2karrow_forward8. A ball has a 17 J of kinetic energy and its mechanical energy is 25 J. Find the potential energy of the ball. a. b. If the ball has a mass of 3.2 kg, what is its height above the ground? c. What is the speed of the ball?arrow_forwardA block of mass 2.28 kg starts sliding from rest down an incline plane for 25 cm. If the block has a velocity of 1.14 m/s, and the incline has an angle measured from the +x axis of 37 degrees then: a. How much work did kinetic friction do on the block? b. What is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the incline?arrow_forward
- There is trampoline which is connected to spring on the bottom. The spring constant is 1000 N/m. You are holding a mass of 27 kg at 5.0 m above the top of the trampoline.a.Calculate the potential energy of the mass with respect to the trampoline top. b. Now you decide to drop the mass to the trampoline, calculate velocity when it hits the trampoline? C If trampoline spring compresses 9 cm down, calculate the spring potential energy?arrow_forwardI need help with these questionsarrow_forwardA bicycler is moving at 8m/s when they reach the top of a 20m high hill. They coast 15m to the bottom of the hill. They are moving 15m/s when they reach the bottom of the hill. The combined mass of the bicycler and the bicycle is 95kg. a. Calculate the work done by friction on the bicycler. b.Calculate the magnitude of the force of friction acting on the bicycle.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON