
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
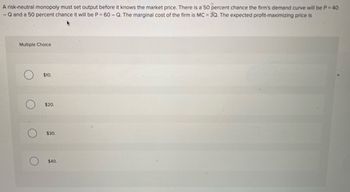
Transcribed Image Text:A risk-neutral monopoly must set output before it knows the market price. There is a 50 percent chance the firm's demand curve will be P = 40
-Q and a 50 percent chance it will be P = 60 - Q. The marginal cost of the firm is MC = 3Q. The expected profit-maximizing price is
Multiple Choice
$10.
$20.
$30.
$40.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A price taker options: is a seller who can set whatever price they want. is a seller who has no control over the price they charge. is a buyer who has no control over the price they pay. is common in a monopoly.arrow_forwardA monopoly company has an average variable cost of $6 average fixed cost of $8, marginal cost of $9, and elasticity of demand -4. In the short run, the company will: set P=$9. earn negative profit so shut down earn negative profit but still produce. set P-$12. set P=$14. earn positive profit. set P-$6. earn zero profit.arrow_forwardHow do you find the profit maximizing PRICE (not level of output) on a graph for a monopoly with demand, marginal revenue, marginal cost, and average total cost curves. Group of answer choices Find the minimum point on the ATC curve and go straight over to the price axis. Find the point where MR = MC and go straight over to the price axis. Find the point where MR = MC, go straight up until you hit the demand curve, and then go straight over to the price axis. Find the point where demand hits marginal cost and go straight over to the price axis.arrow_forward
- The figure below represents the cost and revenue structure for a monopoly firm. Cost and Revenue($) Pot Q₂ Q₂ Q₂Q₂ Quantity A profit-maximizing monopoly's total revenue is equal to: a. P3 x Q₂ b. P₂ x Q4 C. (P3-Po) x Q₂ d. (P3-Po) x Q4arrow_forwardA monopoly is operating at a quantity where average total cost is $70, marginal revenue is $50, and the price is $65. If the monopoly's ATC curve is U-shaped and is currently at its minimum level, then to maximize profits, this business should: Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer. a raise quantity produced. b lower quantity produced. not change the quantity produced since it is already maximizing profits. d. shut down.arrow_forwardFor a monopoly firm, marginal revenue when demand is price inelastic. when demand is price elastic and is Falling ; rising Negative ; positive Rising ; falling Positive ; negativearrow_forward
- Price II. Q2 is the profit maximizing point. III. Q3 is the perfectly competitive output level. Multiple Choice I only Ill only Q₁ Q2 Q3 II and III only This graph shows the cost and revenue curves faced by a monopoly. Which of the following statements is true? I. Q1 is the efficient point. I and II only 4 MC MR ATC Quantityarrow_forwardThe monopolist is productively-efficient, because, like the perfect competitor, it operates at minimum ATC is the long-run. True Falsearrow_forwardYou are the manager of a monopoly that sells a product to two groups of consumers in different parts of the country. Analysts at your firm have determined that group 1’s elasticity of demand is −6, while group 2’s is −2. Your marginal cost of producing the product is $80. a. Determine your optimal markups and prices under third-degree price discrimination. markup for group 1: price for group 1: markup for group 2: price for group 2:arrow_forward
- The demand curve facing a monopoly firm is given by P=200-5Q a) What is the maximum revenue the firm can earn? b) What is the marginal cost when the profit maximizing quantity is 15? c) What is the profit maximizing quantity when the marginal cost is increased to K100? d) At a quantity of 10, what is the percentage change in demand when the price is increased from K150 to K151.5?arrow_forwardNo written by hand solutionarrow_forwardA price discriminating monopoly sells in two markets whose demand scehules are: p1=12.5-0.0625q1 , p2=7.2-0.002q2 and faces the horizontal marginal cost schedule MC=5. what price and output should it choose for each market?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education