
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
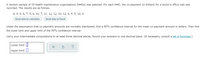
Transcribed Image Text:A random sample of 19 health maintenance organizations (HMOS) was selected. For each HMO, the co-payment (in dollars) for a doctor's office visit was
recorded. The results are as follows.
8, 9, 9, 8, 7, 5, 6, 10, 7, 11, 12, 12, 10, 12, 8, 5, 5, 10, 9
Send data to calculator
Send data to Excel
Under the assumption that co-payment amounts are normally distributed, find a 90% confidence interval for the mean co-payment amount in dollars. Then find
the lower limit and upper limit of the 90% confidence interval.
Carry your intermediate computations to at least three decimal places. Round your answers to one decimal place. (If necessary, consult a list of formulas.)
Lower limit: ||
Upper limit:
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- given data: 2.1, 2.8, 3.7, 4.1, 4.6, 5.8, 6.3, 7.4, 8.2, 8.5, 9.6, 10.1, 10.3, 10.9, 11.0, 11.8, 12.4, 13.6, 13.9, 14.3, 14.6, 15.5, 15.9, 16.7, 16.9 Can someone help me with this series of questions please... 5a) Calculate the percentile of the data value 7.4. b) What value represents the 65th percentile? c) What does it mean for a data value to be in the 65th percentile?arrow_forwardCreate a stem plot for the following 26 numbers: 1, 13, 28, 31, 32, 32, 37, 37, 37, 38, 39, 3, 53, 55, 58, 62, 62, 63, 65, 65, 65, 66arrow_forwardThe following are the annual incomes (in thousands of dollars) for 24 randomly chosen, U.S. adults employed full-time. 28, 31, 32, 33, 34, 36, 38, 38, 38, 38, 41, 42, 43, 43, 44, 47, 48, 50, 54, 55, 61, 82, 96, 107 Send data to calculator Send data to Excel Frequency 15 10+ 15 6 5. 25 45 65 1 1 1 85 105 125 Annual income (in thousands of dollars) Answer the questions below. (a) For these data, which measures of central tendency take more than one value? Choose all that apply. Mean Median Mode ☐ None of these measures Mean (b) Suppose that the measurement 28 (the smallest measurement in the data set) were ☐ Median replaced by 10 Which measures of centralarrow_forward
- given data: 2.1, 2.8, 3.7, 4.1, 4.6, 5.8, 6.3, 7.4, 8.2, 8.5, 9.6, 10.1, 10.3, 10.9, 11.0, 11.8, 12.4, 13.6, 13.9, 14.3, 14.6, 15.5, 15.9, 16.7, 16.9 Can I get help with... 6a) Two data sets both have a mean of 50. One has a standard deviation of 2 and the other has a standard deviation of 10. Describe what is different about these two data sets. b) Since the mean and the median both describe the same characteristic, explain why they are not always the same. (no formulas) c) When and why would the mean be better to use than the median?arrow_forwardDetermine whether the following examples are discrete or continuous data sets. Write "DISCRETE" for discrete and "CONTINUOUS" for continuous. (without quotations - use for instance copy and paste to avoid typos) (a) The number of voters who vote Democratic. answer: (b) The number of customers waiting in line at the grocery store. answer: (c) The temperature in any given location. answer: (d) The length of time needed for a student to complete a homework assignment. answer:arrow_forwardFind the range, variance and standard deviation of the ff 10, 17, 15, 20, 13, 11, 19, 12, 14, 16 Excel form needarrow_forward
- Determine whether the following examples are discrete or continuous data sets. Write "DISCRETE" for discrete and "CONTINUOUS" for continuous. (without quotations - use for instance copy and paste to avoid typos) (a) The number of voters who vote Democratic answer. (b) The temperature in any given location. answer. (C) The distance traveled by a city bus each day. answer. (d) The length of time needed for a student to complete a homework assignment. answerarrow_forwardA mother is creating the family budget for next year and wants to come up with a single value to estimate the cost of the water bill every month based on the total from last year divided by 12 months. Which descriptive statistic should she use? O Mode O Median O Meanarrow_forwardPlease help!arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman