
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
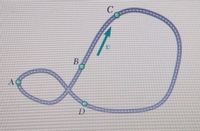
A race car travels around the track shown at a constant speed. At which point will the race car have the largest acceleration?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Match the following to True/False. A. GPS devices are an example of mobile traffic sensors For the time-space diagram of a single-lane one-way road, the vehicle trajectories do not intersect with each other unless there is a crash. Pneumatic tubes detect vehicle presence by sending an electric signal to a roadside device. B. Space mean speed may be greater than time mean speed in certain situations. A. True B. Falsearrow_forwardAs a car comes around a bend onto a straight road moving at 80 km/hr the driver suddenly notices another slower car ahead, a distance d = 50 m ahead, moving at 30 km/hr. At this moment, in order to avoid hitting the slow-moving car ahead the driver slows down but takes .25 seconds to react relative to first noticing the car 50 m ahead. Assuming the car decelerates at a constant rate, above what minimum magnitude of the deceleration avoids a rear-end collision? can you solve this with a detailed explanationarrow_forwardA motorcyclist drives at 21 m/s in a direction 46° east of north relative to a car, and at 9.5 m/s due north relative to the Earth. What is the magnitude of the car's velocity relative to Earth, VC relative to E? What is the direction of the car's velocity relative to Earth, measured as an angle counterclockwise from due east? VC relative to E = 0 = m/sarrow_forward
- Assume you are observing traffic in a single lane of a highway at a specific location. You measure the average headway and average spacing of passing vehicles as 3.2 seconds and 20 m, respectively. Calculate the flow, average speed, and density of the traffic stream in this lane.arrow_forwardSpeedometer readings for a vehicle (in motion) at 4-second intervals are given in the table. t (sec) 0 4 8 12 16 20 24 v (ft/s) 0 5 17 31 39 38 28 Estimate the distance traveled by the vehicle during this 24-second period using L6, R6 and M3.L6 = R6=M3=arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning