
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
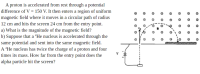
Transcribed Image Text:A proton is accelerated from rest through a potential
difference of V = 150 V. It then enters a region of uniform
magnetic field where it moves in a circular path of radius
12 cm and hits the screen 24 cm from the entry point.
a) What is the magnitude of the magnetic field?
b) Suppose that a “He nucleus is accelerated through the
same potential and sent into the same magnetic field.
A *He nucleus has twice the charge of a proton and four
times its mass. How far from the entry point does the
alpha particle hit the screen?
O O o o
O o o o
O O O
O o o' o
o o io
O O
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is one of the most useful and rapidly growing medical imaging tools. It non-invasively produces two-dimensional and three-dimensional images of the body that provide important medical information with none of the hazards of x-rays. MRI is based on an effect called nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) in which an externally applied magnetic field interacts with the magnetic fields of nuclei of certain atoms, particularly those of hydrogen (protons). The external magnetic field is created by a large coil. This field interacts with the hydrogen atoms in the patient's body to form images. a) To see why an MRI utilizes iron to increase the magnetic field created by a coil, calculate the current needed in a 420-loop-per-meter circular coil 0.66 m in radius to create a 1.3 T field (typical of an MRI instrument) at its center with no iron present. /= A Introducing ferromagnetic materials inside coils greatly increases the magntic field inside the coil for a small…arrow_forward4. An ionized deuteron (a particle with a +e charge) passes through a velocity selector whose magnetic and electric fields have magnitudes of 40.0 mT and 6.70 kV/m, respectively. Find the speed of the ion to undeflected. m/s VISS (9JS 09.09 $$160 ssfove through the selectorarrow_forwardWhat is the force acting on a 1.6(10)–19 C charge when it is moving at 3(10)7m/s perpendicular to a magnetic field whose strength is 0.02 T? What is the radius of the particle’s trajectory if the mass of the particle is 3.3(10)-27 kg?arrow_forward
- The Bainbridge spectrometer works by ionizing particles, sending them through a velocity selector, and then detecting a given charge-to-mass ratio based on its trajectory in a uniform magnetic field (See Ch 11.7 in your book). Suppose your spectrometer works by altering the electric field of the velocity selector to scan for ions. If a singly-charged ion of mass 140.9 amu required an electric field of 1.9 N/C, what electric field would be necessary to detect a doubly-charged ion of mass 161.9? Give your answer in units of N/C.arrow_forwardA proton travels clockwise in the plane of the page under the influence of a magnetic field of 3T a) If the particle has an energy of 10-15J, find the radius of the circle b) What is the direction of the field? c) A long wire carries a current of 10A. A closed loop, in the form of a rectangle with the dimensions in the figure carries a current of 4 A. The side of the loop nearest the wire is 1mm from the wire. Find the force on the loop.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON