
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
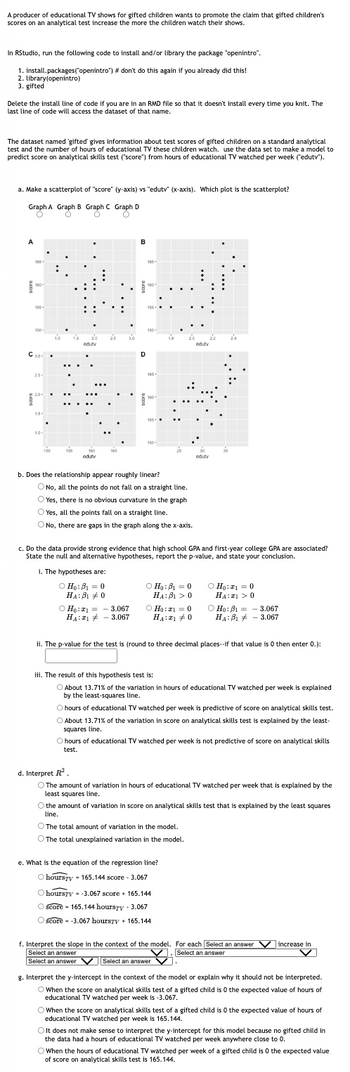
Transcribed Image Text:A producer of educational TV shows for gifted children wants to promote the claim that gifted children's
scores on an analytical test increase the more the children watch their shows.
In RStudio, run the following code to install and/or library the package "openintro".
1. install.packages("openintro") # don't do this again if you already did this!
2. library(openintro)
3. gifted
Delete the install line of code if you are in an RMD file so that it doesn't install every time you knit. The
last line of code will access the dataset of that name.
The dataset named 'gifted' gives information about test scores of gifted children on a standard analytical
test and the number of hours of educational TV these children watch. use the data set to make a model to
predict score on analytical skills test ("score") from hours of educational TV watched per week ("edutv").
a. Make a scatterplot of "score" (y-axis) vs "edutv" (x-axis). Which plot is the scatterplot?
Graph A Graph B Graph C Graph D
C
A
165-
160-
155-
150-
C 3.0
25-
22.0-
1.5-
10-
150
1.0
156
1.5
edutv
160
edutv
165
3.0
D
165-
160-
O Ho: ₁3.067
HA: 3.067
156-
150-
165-
160-
155-
150-
b. Does the relationship appear roughly linear?
O No, all the points do not fall on a straight line.
OYes, there is no obvious curvature in the graph
O Yes, all the points fall on a straight line.
O No, there are gaps in the graph along the x-axis.
○ Ho: B₁ = 0
HA:B10
c. Do the data provide strong evidence that high school GPA and first-year college GPA are associated?
State the null and alternative hypotheses, report the p-value, and state your conclusion.
i. The hypotheses are:
Ho: B₁0
HA:B10
Ho: a = 0
HA: 0
:
edutv
edutv
Ho: 1 = 0
HA: >0
ii. The p-value for the test is (round to three decimal places--if that value is 0 then enter 0.):
Ho: B₁- 3.067
HA:B 3.067
iii. The result of this hypothesis test is:
O About 13.71% of the variation in hours of educational TV watched per week is explained
by the least-squares line.
O The total amount of variation in the model.
The total unexplained variation in the model.
O hours of educational TV watched per week is predictive of score on analytical skills test.
O About 13.71% of the variation in score on analytical skills test is explained by the least-
squares line.
e. What is the equation of the regression line?
O hoursty - 165.144 score - 3.067
O hoursry -3.067 score 165.144
O score - 165.144 hoursty - 3.067
O score = -3.067 hoursTV + 165.144
O hours of educational TV watched per week is not predictive of score on analytical skills
test.
d. Interpret R²
O The amount of variation in hours of educational TV watched per week that is explained by the
least squares line.
O the amount of variation in score on analytical skills test that is explained by the least squares
line.
f. Interpret the slope in the context of the model. For each Select an answer V increase in
Select an answer
V. Select an answer
V
Select an answer
Select an answer V.
g. Interpret the y-intercept in the context of the model or explain why it should not be interpreted.
O When the score on analytical skills test of a gifted child is 0 the expected value of hours of
educational TV watched per week is -3.067.
O When the score on analytical skills test of a gifted child is 0 the expected value of hours of
educational TV watched per week is 165.144.
O It does not make sense to interpret the y-intercept for this model because no gifted child in
the data had a hours of educational TV watched per week anywhere close to 0.
O When the hours of educational TV watched per week of a gifted child is 0 the expected value
of score on analytical skills test is 165.144.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- You may need to use the appropriate appendix table to answer this question. Alexa is the popular virtual assistant developed by Amazon. Alexa interacts with users using artificial intelligence and voice recognition. It can be used to perform daily tasks such as making to-do lists, reporting the news and weather, and interacting with other smart devices in the home. In 2018, the Amazon Alexa app was downloaded some 2,800 times per day from the Google Play store.† Assume that the number of downloads per day of the Amazon Alexa app is normally distributed with a mean of 2,800 and standard deviation of 860. (a) What is the probability there are 1,900 or fewer downloads of Amazon Alexa in a day? (Round your answer to four decimal places.) (b) What is the probability there are between 1,600 and 2,400 downloads of Amazon Alexa in a day? (Round your answer to four decimal places.) (c) What is the probability there are more than 2,900 downloads of Amazon Alexa in a day? (Round…arrow_forwardMartha is in a statistics course in which each exam has a total of 100 points possible. Martha currently has an average score of 88 on her statistics exams. If she earns a score of 95 on her final exam, Martha's averagearrow_forwardDefine interset.arrow_forward
- Could you please answer number 3 and number 4?arrow_forwardThe scores of a test for an engineering class of 30 students are shown here. (Due to the nature of this problem, do not use rounded intermediate values in your calculations-including answers submitted in WebAssign.) Scores: 81, 54, 55, 56, 96, 86, 98, 61, 90, 52, 92, 76, 66, 84, 79, 70, 71, 88, 62, 74, 53, 65, 55, 78, 79, 58, 60, 72, 51,80 (a) Determine the frequency (f), midpoint (x), and xf for each range and fill in the table below. (First, organize the scores into the following ranges: 50-59, 60-69, 70-79, 80-89, and 90-99.) (b) Using the following equation, determine the mean value (x) and fill in the table below. Σ(XA) n X = (c) Calculate (x − x) for each range and fill in the table below. (d) Calculate (x - x)²f for each range and fill in the table below. Range Frequency f Midpoint x 50-59 60-69 70-79 80-89 90-99 S = Enter a number. S = (e) Using the following equation, compute the standard deviation of the class scores. Σ(x-x) ²f n - 1 Σ(x-x) ²4 n - 1 = xf 29 X X - X (x - x)²farrow_forwardPlease answer the questions carefully to get the correct answers.arrow_forward
- Find the mode for the following variables 2,12,5,8,5,12,6,3,6,12,12arrow_forwardWhat is the range of the 2,3,-5,4,14arrow_forwardThere are five numbers in a data set. They are 3, 1, 16, 20 and x, where x is one of the largest two number of the five. What value does x need to be so that the median of the five numbers equals the mean of the five numbers?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman