
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781337093347
Author: Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
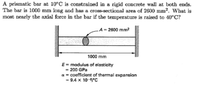
Transcribed Image Text:A prismatic bar at 10°C is constrained in a rigid concrete wall at both ends.
The bar is 1000 mm long and has a cross-sectional area of 2600 mm². What is
most nearly the axial force in the bar if the temperature is raised to 40°C?
A = 2600 mm?
1000 mm
E= modulus of elasticity
- 200 GPa
a = coefficient of thermal expansion
9.4 x 10-erc
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A wine of length L = 4 ft and diameter d = 0.125 in. is stretched by tensile forces P = 600 lb. The wire is made of a copper alloy having a stress-strain relationship that may be described mathematically by =18,0001+30000.03(=ksi) in which is nondimensional and has units of kips per square inch (ksi). (a) Construct a stress-strain diagram for the material. (bj Determine the elongation, of the wire due to the Forces P. (c) IF the forces are removed, what is the permanent set of the bar? (d) If the forces are applied again, what is the proportional limit?arrow_forwardAn elastomeric bearing pad consisting of two steel plates bonded to a chloroprene elastomer (an artificial rubber) is subjected to a shear force V during a static loading test (see figure). The pad has dimensions a = 125 mm and b = 240 mm, and the elastomer has a thickness t = 50 mm. When the Force V equals 12 kN, the top plate is found to have displaced laterally S.O mm with respect to the bottom plate. What is the shear modulus of elasticity G of the chloroprene?arrow_forwardA steel bar 600mm long and having 30mm diameter, is turned down to 25mm diameter for one fourth of its length. It is heated at 30 °C above room temperature, clamped at both ends and then allowed to cool to room temperature. If the distance between the clamps is unchanged, the maximum stress in the bar (a = 12.5 x 10-6,°c and E = 200o GN/m3) is 75 MPa 25 MPa 40 MPa 50 MPaarrow_forward
- 3. A circular bar rigidly fixed at its both ends is 1.2 m long. It uniformly tapers from 100 mm at one end to 75 mm at the other. What is the maximum stress induced in the bar, when its tempera- ture is raised through 25 K? Take E as 200 GPa and a as 12 x 10/K. [Ans. 80 MPa] unifor from 00 to 60arrow_forwardthis question is from thermal stressarrow_forwardAn AISI 1020 steel rod 12 feet long is anchored between two rigid supports. At 68 degrees the rod has a stress of 6,000 psi. At what temperature will the rod have no stress? (assume the rod is in tension) Could someone please help me solve this question?arrow_forward
- A vinyl [E = 2.85 GPa; v = 0.41] block with width b = 50 mm, depth d = 100 mm, and height h = 270 mm rests on a smooth rigid base. A load P is applied to a rigid plate that rests on top of the block. Calculate the change in the depth dimension d of the block after a load of P = 100 kN is applied. Rigid plate Answer: Ad i P Width Depth d b eTextbook and Media Save for Later Height h Rigid base mm Attempts: 0 of 5 used Submit Answerarrow_forwardQuestion 2 Consider the bar in figure 2, it has cross sectional area A 1.10-4m², modulus of elasticity E = = 200GPa, and length 1.5 m. The bar is fixed to a wall on its left hand side, and has a constant loading of 1(x) = −10 kN/m applied along its length. x=0.0 |(x) = -10 kN/m 1.5 m X x=1.5 Figure 2: diagram of bar subject to applied force along its length a) The displacement of the bar u(x) is governed by the equation ə du(x) AE dx dx +1(x) 0 x = [0, 1.5], state the two boundary conditions for this bar problem, and give a short reasoning for your answer (maximum 2 sentences for each boundary condition).arrow_forwardA 2.5m steel rod with a cross sectional area of 1250m^2 is secured between rigid supports at both ends. If there is no stress of 30°C, E = 200000MPa. (a)Compute the stress when the temperature drops to 0°C, if it has a coefficient of thermal expansion of 0.0000117 m/m°C. (b)Compute the strain of the rod if the rod supports yield by 0.800mm as temperature drops. (c)Compute the stress in the rod if the support yield and moves together a distance of 0.800mm as the temperature drops.arrow_forward
- 3. The bar shown below is composed of two pieces, AC and CD. The bar is attached to the wall at point A. The length L = 10 in. The cross sectional areas are: AAC = 4 in? and AcD = 2 in?. The Young's Moduli are: EAC =20 Msi and Ecd= 15 Msi Two forces are applied at points B and D: PB = 50 kips and PD = 20 kips. Determine: (a) the reaction force at A (specify –→ or +) and (b) the deflection of point D (specify → or +). (Hint for (b): Think about how many pieces you must subdivide the rod into.) Ans: RA = 30 kips (+), dp = 7.9167×10-3 in (E) A В C D Pp L 2L Larrow_forwardQuestion (4): A plastic bar ACB having two different solid circular cross sections is held between rigid supports as shown in the figure. The diameters in the left and right-hand parts are 50 mm and 75 mm, respectively. The corresponding lengths are 225 mm and 300 mm. Also, the modulus of elasticity E is 6.0 GPa, and the coefficient of thermal expansion a is 100 x 10-6/°C. The bar is subjected to a uniform temperature increase of 30°C.Calculate the following quantities: (1) the compressive force N in the bar; (2) the maximum compressive stress oc; and (3) the displacement 8 of point C. JA 50 mm C -225 mm- + -2251 175 mm B -300 mm-arrow_forwardAs shown in the figure, there is a gap between the aluminum bar and the rigid slab that is supported by two copper bars. At 10°C, A = 0.18 mm. The temperature in the assembly is increased to 95'C. Neglect the mass of the slab. For each copper bar, A = 500 mm², E = 120 GPa, and acopper = 16.8 x 10° m/(m.'C). For Aluminum bar, A = 400 mm', E = 70 GPa, and aaluminum = 23.1 x 10°m /(m.'C). %3D %3D Determine the stress in the aluminium bar in MPa. Determine the stress of copper in MPa. ww OSL addo) Aluminum Jaddo)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning