
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
please help solve, I am not sure what I am doing wrong
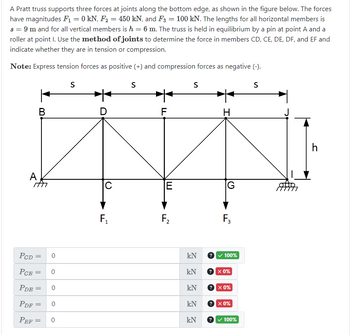
Transcribed Image Text:A Pratt truss supports three forces at joints along the bottom edge, as shown in the figure below. The forces
have magnitudes F₁ = 0 kN, F₂ = 450 kN, and F3 = 100 kN. The lengths for all horizontal members is
s = 9 m and for all vertical members is h = 6 m. The truss is held in equilibrium by a pin at point A and a
roller at point I. Use the method of joints to determine the force in members CD, CE, DE, DF, and EF and
indicate whether they are in tension or compression.
Note: Express tension forces as positive (+) and compression forces as negative (-).
B
S
D
S
F
S
H
A
C
E
G
F₁
பட்
F₂
F3
PCD =
0
kN
100%
PCE =
0
kN
? × 0%
PDE =
0
kN
? × 0%
PDF
PEF
=
=
0
0
kN
? × 0%
kN
100%
S
h
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- I need answer within 20 minutes please please with my best wishesarrow_forwardWhich of the following statement is incorrect? Select one: Friction causes objects to move faster Friction is high for dry surface Friction causes objects to slow down Friction force acts opposite to motionarrow_forwardنقطة واحدة B)) The vertical height of * ? point A from point B 40 m/s a=g= 10ms 20 m 18.75 m O 10.75 m 0.0 Sec O 1.5 m O 1.25 m 5.25 m Oarrow_forward
- Tire manufacturers recommend that you check your tire pressure monthly to avoid unnecessary tire wear and enhance safety. This is best done when the tires are cold meaning; the car has not been driven for at least 2 hours. Since you leave for work before the sun comes up you decide to inflate your tires to the recommended pressure right after you get home from work in the afternoon when the tires are still warm. What would you find if you rechecked your tire pressure after the tires have cooled down? A.Tire pressure has decreased because there is a decrease in kinetic energy of themolecules resulting in more collisions with the inside walls of the tire thusincreasing the pressure inside the tire. B.Tire pressure has increased because there is a decrease in kinetic energy of the molecules resulting in fewer collisions with the inside walls of the tire thus decreasing the pressure inside the tire. C.Tire pressure has increased because there is an increase in kinetic energy of the…arrow_forwardWhich statement is correct?arrow_forwardPaula has worked for Brindle Corporation for 3 years. During this time, she has worked as a machine operator/cell leader in various work cells. Recently, the plant went to mandatory 12-hour shifts and plans to remain on this schedule for several months. Paula’s present work cell is manufacturing 3-inch diameter exhaust tubes that are made from stainless steel. These tubes get a hole punched in them, a flange welded on, and burrs ground off. The pipe then gets placed into a gage to check that it was made correctly. (The tubes weigh about six pounds.) Paula has been performing the welding operation. She leans into the machine and loads the part into a fixture then positions the flange. Both pieces are clamped (using hand clamps) into position and the machine is cycled by depressing two palm buttons. The gaging operation requires placing the finished part into the gage and clamping it (using hand clamps) into place. A pin is depressed to verify the position of the hole and a…arrow_forward
- Why is it a good idea to bend you legs as you land on the ground after jumping down from a ledge (that is, say, a few feet higher than the ground)?arrow_forwardTe-Learning Portal Courses Reports e-Services Which of the following statement is correct Select one: of O Fiction is very bad at rough surfaces ion O Friction is zero for smooth surfaces O Friction is good at smooth surfaces O Friction is high for rough surfacesarrow_forwardkindly create a conclusion regarding Tesla Cars and its factoryarrow_forward
- Paula has worked for Brindle Corporation for 3 years. During this time, she has worked as a machine operator/cell leader in various work cells. Recently, the plant went to mandatory 12-hour shifts and plans to remain on this schedule for several months. Paula’s present work cell is manufacturing 3-inch diameter exhaust tubes that are made from stainless steel. These tubes get a hole punched in them, a flange welded on, and burrs ground off. The pipe then gets placed into a gage to check that it was made correctly. (The tubes weigh about six pounds.) Paula has been performing the welding operation. She leans into the machine and loads the part into a fixture then positions the flange. Both pieces are clamped (using hand clamps) into position and the machine is cycled by depressing two palm buttons. The gaging operation requires placing the finished part into the gage and clamping it (using hand clamps) into place. A pin is depressed to verify the position of the hole and a…arrow_forwarduse this logo and explain for safteyarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY