
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
A point charge of 33 uC is placed at a distance of 36 cm from another identical charge. A charge of -1.5 uC is transferred from point a to point b as shown in the figure. Determine:
a) The change in electrical potential energy
b) If the -1.5 uC charge has an initial velocity of zero. What is its final velocity if it has a mass of 5.0 x 10-15 kg?
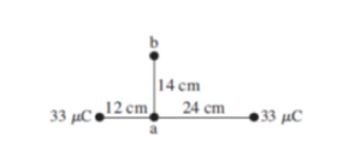
Transcribed Image Text:33 μC 12 em
14 cm
24 cm
33 д
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- There are three point charges in a system. The first is -2.9uC and is located at (0,0.4) m. The second is 3.29uC and is located at (85.9,0) m. The third is -9.83uC and is located at (86.4,50.4) m. What is the potential (in V) at the origin due to these three charges?arrow_forwardV is the energy (in J) required to bring the two charges from infinite distance separation to distance r (in nm).Q1 and Q2 are the charges in terms of electrons.(i.e. the constant in the above expression is 2.31×10-19 J nm electrons-2) For a group of "point" charges (e.g. ions) the total energy of interaction is the sum of the interaction energies for the individual pairs. Calculate the energy of interaction for the square arrangement of ions shown in the diagram below.arrow_forwardPlease type clear thank youarrow_forward
- An immovable charge Q₁ = +2.0µC is placed in fixed location at the origin on an (x, y) coordinate system. Another charge, Q₂ = +4.0μC is allowed to move near the first charge. How much work does it take to move this charge from it's starting location of (-3cm, 4cm) to the following locations and if the time to make this change is 10 ms how much power was output during each process: (a) (-1.5cm, 2cm) (b) (-6cm, 8cm) (c) (3cm, 4cm)arrow_forwardA bare helium nucleus has two positive charges and a mass of 6.64-10-27 (a) Calculate its kinetic energy in joules at 2.5% of the speed of light. KE = J (b) What is this in electron volts? KE = eV (c) Assume that the nucleus starts from rest and accelerates through a potential difference V, what quantity is conserved? O A. Mechanical Energy O B. Kinetic Energy O C. Potential Energy O D. None of those quanitites are conserved kg. (d) What voltage would be needed to obtain this energy? V = Varrow_forwardA square of particlesFour particles are attached to the four corners of a square whose edge measures L (see image). Particles A and B each have a positive charge q and particles C and D each have a negative charge -q. (a) What is the electrical potential energy of the system? (b) Is this energy positive or negative?arrow_forward
- Shown below is a configuration of charges that has been formed into a right triangle. We shall consider the process of the work required to assemble this collection of charges in the manner shown. To do so, we shall start with empty space and then add into that space one charge at a time until we have completely assembled the triangle of three charges. The legs of the right triangle have dimensions dx = 6.8e-02 meters and dy = 1.38e-02 meters. dy 9₁ The charges are as follows: • 91 = -7.64e-06 Coulombs. 92 2.21e-06 Coulombs. = ● 92 ● 93 = -5.2e-06 Coulombs. d₁ Determine the work required to place only q1 into the position shown: Determine the work required to ADD 92 into the picture: Determine the work required to ADD 93 into the picture: Determine the total work required to complete all the above steps: Joules Joules 93 Joules Joulesarrow_forwardAn oil droplet (q = 5e-) is suspended between two parallel, charged plates (V = 175 V). If an oil droplet of the same mass but with a charge of 3e- is to be suspended between the same plates, what potential difference would be necessary?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON