
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
A plot of pH vs volume of 0.05 M NaOH solution was obtained for titrating 0.4055 g of a dried solid sample of a weak, monoprotic acid.
- Determine the molar mass of the acid in its solid, crystalline form.
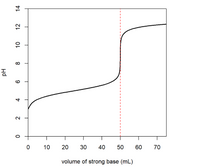
Transcribed Image Text:T
0 10
20
30
40
50
60
70
volume of strong base (mL)
14
12
4.
Hd
2.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The student Louise continued the analysis of acetic acid using half - neutralization technique. She titrates this acetic acid solution using 0.984 M NaOH titrant solution. When the volume of NaOH reaches 14.34 mL, she stopped titration. The averaged pH value is measured to be 4.75. - Calculate the molar concentration of H3O ^+.arrow_forwardA solution of the weak acid HA is prepared by dissolving 2.70 g of HA in 100.0 mL water. The solution is titrated, and the equivalence point is reached after 31.0 mL of 0.500 M NaOH is dispensed. Calculate the molar mass of HA. molar mass: g/mol At the equivalence point in this titration, how can the solution pH be described? acidic neutral basicarrow_forwarda. A student massed out 0.175 g of an unknown diprotic acid on an analytical balance, and then dissolved it in 100mL of deionized water. The acid was then titrated with 0.111 M NaOH solution. The second equivalence point showed the sharpest change in pH, and so it was used to determine the molar mass of the unknown acid. The volume of NaOH needed to reach the second equivalence point was 27.77 mL b. If the volume required to reach the second equivalence point is 38.18 mL, what is the volume required to reach the first equivalence point? Report your answer to 2 digits behind the decimal point, and do not include units in your answer. c. if the volume to reach the second equivalence point in a titration is 24.53 mL, What is the volume to reach the midpoint between the first equivalence point and the second equivalence point? Report your answer to 2 digits behind the decimal point and do not include units d. If pKa1 = 3.18 what is the value for Ka1? Report your answer in…arrow_forward
- Consider the following information to answer the questions below. A volume of 10.00 mL of 0.100 M acetic acid (HC2H3O2) is titrated with 0.107 M sodium hydroxide solution. Given the chemical equation below. Calculate the volume (in milliliters) of NaOH needed to reach the equivalence point of the titration. HC2H3O2(aq) + NaOH(aq) -> H2O (l) + NaC2H3O2(aq)arrow_forwardA 0.328 g sample of an unknown monoprotic acid, HA, is dissolved in water and titrated with a standardized 0.1261M NaOH. If 28.10 mL of the basic solution is required to reach the equivalence point, calculate the molar mass of the acid.arrow_forwardA solution of the weak acid HA is prepared by dissolving 2.20 g of HA in 100.0 mL water. The solution is titrated, and the equivalence point is reached after 31.1 mL of 0.500 M NaOH is dispensed. Calculate the molar mass of HA. molar mass: g/mol At the equivalence point in this titration, how can the solution pH be described? acidic basic O neutralarrow_forward
- In a titration with 25.00 mL of a 0.1300 M diprotic acid, 40.00 mL of NaOH is used to reach the equivalence point. What is the concentration of the NaOH solution?arrow_forwardA chemistry graduate student is given 450. mL of a 0.70 M chlorous acid (HCIO2) solution. Chlorous acid is a weak acid with K=1.1 x 10^-2 . What mass of KClO, should the student dissolve in the HCIO, solution to turn it into a buffer with pH = 2.24? You may assume that the volume of the solution doesn't change when the KCIO, is dissolved in it. Be sure your answer has a unit symbol, and round it to 2 significant digits.arrow_forward50.00 mL of a buffer solution contains 0.280 M HClO and 0.450 M NaClO. If 25.00 mL of water is added to the buffer, what are the new concentrations of HClO and NaClO?arrow_forward
- A 30.00 mL sample of 0.400 M HNO3 is titrated with 0.600 M KOH. What is the balanced neutralization chemical reaction? What volume of base (in mL) must be added to reach the equivalence point? Is the pH of the equivalence point acidic, basic, or neutral?arrow_forwardA student prepares a solution for titration by adding a 10.00 mL aliquot of a solution saturated with Ca(OH)2 at 82.9°C to 25.0 mL of deionized water. This solution is titrated with a standardized 0.01252 M HCl solution. The equivalence point is observed after 17.94 mL of the HCl solution has been added. Use this data to answer the questions below. Calculate the moles of OH- in the 10.00ml sample. (Hint, moles of OH- at the equivalence point = moles HCl) Your answer should have 4 sig figs. Enter answers in scientific notationarrow_forwardA student is making a titration curve. To do so, they added 25.00 mL of 0.1390 M HCl to a flask. They then added 36.78 mL of 0.1080 M KOH to the flask. What is the pH at this point in the titration curve?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY