
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
q1b

Transcribed Image Text:(b) A plastic rod AB of length L = 520 mm has a diameter d = 30 mm as shown in Figure
Q2(b). A plastic sleeve CD of length c = 300 mm and outer diameter d2 = 45 mm is
securely bonded to the rod so that no slippage can occur between the rod and the sleeve.
The rod is made of an acrylic with modulus of elasticity E1 = 3.1GPA and the sleeve is
made of a polyamide with E2 = 2.5GP .
(i)
Calculate the elongation & of the rod when it is pulled by axial forces P=15KN .
(ii)
If the sleeve is extended for the full length of the rod, what is the elongation?
(iii) If the sleeve is removed, what is the elongation?
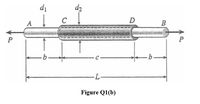
Transcribed Image Text:di
d2
C
D
A
B
b
C
L-
Figure Q1(b)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- p=(18−6x+4y)kPa. Suppose that p1 = 18 kPa, p2 = 27 kPa, p3 = 9 kPa a = 3 mm, b = 2.25 mm. Part 1 Determine the magnitude of the resultant force Part 2 Deteremine the x coordinate of the point where the line of action of the resultant force intersects the plate Part 3 Determine the y coordinate of the point where the line of action of the resultant force intersects the plate.arrow_forwardThe force acting on the gear tooth is F=45 KN. Resolve this force into two components acting along the lines aa and bb * F. 80° 50° F_a=65.46 KN, F_b=D35 KN none of above O F_a=32.46 KN, F_b=D40 KN F_a=45.17 KN, F_b=45 KN O F_a=57.85 KN, F_b=45 KNarrow_forward2.107 - This question asks to be solved using the ‘Dot Product’arrow_forward
- Please answer 1-2arrow_forwardThe particle has a mass of 0.45 kg and is confined to move along the smooth horizontal slot due to the rotation of the arm OA. Assume the particle contacts only one side of the slot at any instant. The arm has an angular acceleration of 0 = 3 rad/s² when 0 = 2 rad/s at 0 = 30° (Figure 1) Figure 6 = 2 rad/s 99°F Sunny r A 0.5 m 1 of 1 < Rearrow_forwardIn (Figure 1), F = 4 kN. Figure 60° 45° X 2 kN 1 of 1 Part A Determine the magnitude of the resultant force acting on the screw eye. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. FR = Submit Part B μA OR = Value Units You have already submitted this answer. Enter a new answer. No credit lost. Try again. Previous Answers Request Answer Determine the direction of the resultant force acting on the screw eye measured clockwise from the x axis. Express your answer in degrees to three significant figures. ? VAΣo↓↑vec You have already submitted this answer. Enter a new answer. No credit lost. Try again. Submit Previous Answers Request Answer ? 0arrow_forward
- Part A The pole is subjected to the forc F which has components F = 1.4 kN and F₂ = 1.05 kN. If 3 = 84°, determine the magnitude of Fy. Express your answer with the appropriate units. F₂ = Submit Part B O μA Request Answer Determine the magnitude of F. Express your answer with the appropriate units. НА F= Value Unit Submit Request Answer Units ? ? XB F Farrow_forward6 kN A 2KN 2M 2M 2M Solve for the force magnitude and direction in member AB, to the nearest 0.01 kN. 2M twitarrow_forwardIn (Figure 1). F-39 lb. Figure 60 F-25 lb 1 of 1 Part A Determine the magnitude of the projection of the force F₁ along the line of action of F₂. Express your answer in pounds to three significant figures. VAXO I vec F12= Submit Previous Answers Request Answer x Incorrect; Try Again; 5 attempts remaining Provide Feedback ? lb Next >>arrow_forward
- A technician states that the master cylinder has a piston radius of .75" and the caliper piston has a diameter of 1.25" If he pushes the master cylinder with a force of 15 ft/lbs and the master cylinder input shaft travels 2.5%, what is the force at the caliper piston? (in decimal form rounded to three decimal place, sood 250arrow_forward1.Impulse of a force is the integral of the force with respect to time over the time the force is applied. Impulse of a force is the integral of the force with respect to time over the time the force is applied. True Falsearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY