
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
A piping system is to be installed at place where the pump will transfer the fluid from tank A to tank B. There are two suggested piping designs available to carry the fluid efficiently. Compute and determine which of the available piping arrangement will experience the less pumping power
with given flow conditions. Discuss the results.
Flow conditions are same for both type of designs and given as:
Pipe material: stainless steel
Volume flow rate: 40 L/sec
Assume the working fluid is water at standard atmosphere temperature and both tanks are
open to atmosphere.
Pipe inlet is sharp-edged and bends are sharped without vanes.
Elevations are as ?? = ?? ? and ?? = ?? ?
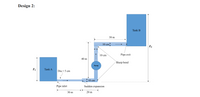
Transcribed Image Text:Design 2:
Tank B
30 m
10 cm
Z2
10 cm
Pipe exit
40 m
Sharp bend
Pump
Tank A
Dia = 5 cm
† 10 cm
Pipe inlet
Sudden expansion
30 m
20 m
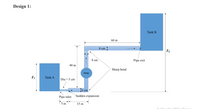
Transcribed Image Text:Design 1:
Tank B
60 m
8 cm
Z2
8 cm
Pipe exit
40 m
Sharp bend
Pump
Z1
Tank A
Dia = 5 cm
†8 cm
Pipe inlet Sudden expansion
5 m
15 m
Activate Window
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Calculate the resistance coefficient K for a check valve swing type placed in a 6 inch schedule 40 steel pipe if water at 100º F flowing with a velocity of 10 ft/sarrow_forwardA pumping system has the following characteristics, f=0.015 length of thepipe = (2500 ft) pipe diameter 6 in, losses less than 0.5, the pipeis cast iron, and the system curve is:Hp= 34+ 5.47Q2Knowing that the system curve and the pump curve intersect at 12 cfsa. Determine Operation headb. Determine dischargec. Plot the system curvearrow_forwardAs shown in the figure, the water flows from the ground floor of a three-storey house to the second floor through pipes of 20 mm diameter (average roughness of the pipe material = 0.0015 mm) at a volumetric flow rate of 0.75 L / s. Water is discharged from the system to atmospheric pressure through a tap with a 12 mm diameter outlet. There are 4 winged elbows, one ball valve and one faucet throughout the installation. Calculate the effective pressure at point 1. (psu=998 kg/m3, usu=1.12x10-3 Pa s, g=9.81 m/s2)arrow_forward
- As shown in the picture blew, a pump can deliver volume flow rate of of water through a vertical lift of . The inlet to the pump is just below the water surface and the discharge is to the atmosphere through a DN50 schedule 40 steel pipe. The energy loss . (1) Calculate velocity at the exit of point 2__________m/sarrow_forwardA pressurized tank and piping system are shown in the figure. The tank pressure is maintained at 175 kPa. The line is made of 12 m of 1 std type M copper tubing and it conveys gasoline (octane). What is the expected flow rate through the line? All fittings are soldered (same as flanged) and regular. 4 m 175 kPa 1 marrow_forwardThe water is pumped from a 40 sch pipe that has 750 ft lenght, 6 in. nominal diameters. Height difference between exit and entry planes is stated as 50 ft. The yield of waterpump, 80% the power of pump motor is 20 horsepowers. Friction losses are stated as 50ft-lbf/lbm. Please calculate the flow rate in pipe line.arrow_forward
- Example -5.2- It is required to pump cooling water from storage pond to a condenser in a process plant situated 10 m above the level of the pond. 200 m of 74.2 mm i.d. pipe is available and the pump has the characteristics given below. The head loss in the condenser is equivalent to 16 velocity heads based on the flow in the 74.2 mm pipe. If the friction factor = 0.003, estimate the rate of flow and the power to be supplied to the pump assuming n = 0.5 Q (m³/s) 0.0028 0.0039 0.005 0.0056 0.0059 Ah (m) 23.2 21.3 18.9 15.2 11.0arrow_forwardQ:/ Discuss the relation between the head pressure and flow rate for the benefits of connecting the pumps in parallel ?arrow_forwardDiscuss the relation between the head pressure and flow rate for the benefits of connecting the pumps in series?arrow_forward
- For the hydraulic system of Figure 8, the following data are given: The pump is adding2.984kW to the fluid.(a) Pump flow is 0.00158 m3(b) The pipe inside diameter is 0.0254m.(c) The specific gravity of the oil is 0.9.(d) The oil tank is vented to the atmosphere.(e) The head loss HL between station 1 and 2 is 12.19m.(f) The elevation difference between stations 1 and 2 is 6.096m.Find the pressure available at the inlet to the hydraulic motor(station 2).arrow_forwardCompute points on the velocity profile from the tube wall to the centerline of a standard hydraulic steel tube, 50 mm OD x 1.5 mm wall, if the volume flow rate of SAE 30 oil (sg = 0.89) at 110°C is 25 L/min. Use increments of 4.0 mm and include the velocity at the centerline.|arrow_forwardA duct system layout is shown in the figure below, it is supplied with air from a central air conditioning unit. The ducts require to be rectangular with a maximum height of 10in due to ceiling limitations. Maximum air duct velocities are: main = 1200fpm; branches = 800 fpm. Determine the sizes of the rectangular ducts and the static pressure at the AHU. Use Velocity reduction method. AHU- AIR HANDLING UNIT (CENTRAL AIRCON)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY