
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question

Transcribed Image Text:A pharmaceutical company is about to launch a new manufacturing process in addition to the existing one.
The quality control manager believes that the new method results in a different variation in the weights of
the capsules. To verify the claim, the samples from each production line were obtained and the results are
below (in mg):
Production Line 1:
100.7 104.7 101.9 101.6 98.9
101 98.8 99.4
101
100.3
(Note: The average and the standard deviation of the data are respectively 100.83 mg and 1.731 mg.)
Production Line 2:
101.6 100.4
99.1
99
98.6
100
97.5
99.5
102 97.6 99.9
102.5 100.4 98.6
99.1 100.8 99.3
Part 1 of 5
(Note: The average and the standard deviation of the data are respectively 99.76 mg and 1.416 mg.)
Use a 1% significance level to test the claim that the standard deviation of the capsule weights in the
production line 1 is greater than the standard deviation of the capsule weights in the production line 2. If
normality plots are not provided assume that the samples are from normal populations.
Procedure: Select an answer
Assumptions: (select everything that applies)
Population standard deviation are unknown
Paired samples
Sample sizes are both greater than 30
The number of positive and negative responses are both greater than 10 for both samples
Simple random samples
Normal populations
Population standard deviation are unknown but assumed equal
Independent samples
Population standard deviations are known
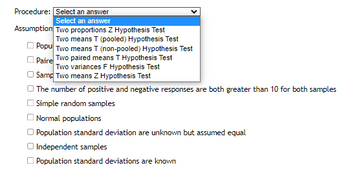
Transcribed Image Text:Procedure: Select an answer
Select an answer
Assumption Two proportions Z Hypothesis Test
Two means T (pooled) Hypothesis Test
Popu Two means T (non-pooled) Hypothesis Test
Paire Two paired means T Hypothesis Test
Two variances F Hypothesis Test
Samp Two means Z Hypothesis Test
The number of positive and negative responses are both greater than 10 for both samples
Simple random samples
Normal populations
Population standard deviation are unknown but assumed equal
O Independent samples
Population standard deviations are known
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
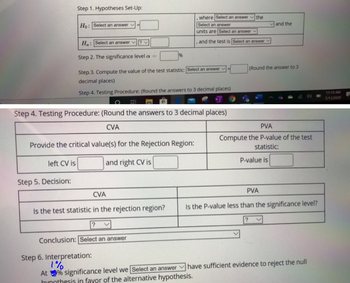
Transcribed Image Text:Step 1. Hypotheses Set-Up:
Ho: Select an answer
Ha: Select an answer
Step 2. The significance level =
Provide the critical value(s) for the Rejection Region:
left CV is
and right CV is
Step 5. Decision:
where Select an answer the
Select an answer
units are Select an answer
Step 3. Compute the value of the test statistic: Select an answer
decimal places)
Step 4. Testing Procedure: (Round the answers to 3 decimal places)
CVA
Is the test statistic in the rejection region?
?
Conclusion: Select an answer
.
and the test is Select an answer
Step 4. Testing Procedure: (Round the answers to 3 decimal places)
CVA
Step 6. Interpretation:
1%
At % significance level we [Select an answer
hypothesis in favor of the alternative hypothesis.
E
and the
(Round the answer to 3
PVA
Compute the P-value of the test
statistic:
P-value is
PVA
Is the P-value less than the significance level?
have sufficient evidence to reject the null
11:19 AM
7/11/2020
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question

Transcribed Image Text:Step 1. Hypotheses Set-Up:
Ho: Select an answer
Ha: Select an answer
Step 2. The significance level =
Provide the critical value(s) for the Rejection Region:
left CV is
and right CV is
Step 5. Decision:
where Select an answer the
Select an answer
units are Select an answer
Step 3. Compute the value of the test statistic: Select an answer
decimal places)
Step 4. Testing Procedure: (Round the answers to 3 decimal places)
CVA
Is the test statistic in the rejection region?
?
Conclusion: Select an answer
.
and the test is Select an answer
Step 4. Testing Procedure: (Round the answers to 3 decimal places)
CVA
Step 6. Interpretation:
1%
At % significance level we [Select an answer
hypothesis in favor of the alternative hypothesis.
E
and the
(Round the answer to 3
PVA
Compute the P-value of the test
statistic:
P-value is
PVA
Is the P-value less than the significance level?
have sufficient evidence to reject the null
11:19 AM
7/11/2020
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Epistasis is a phenomenon in which one gene controls the expression of another. In one case, a dihybrid cross should yield a 9:3:4 ratio. You collect the following data on mice: black coat: 138 brown coat: 46 white coat: 60 Is there any reason to doubt the ratio of 9 black : 3 brown : 4 white?arrow_forwardA local college cafeteria has a self-service soft ice cream machine. The cafeteria provides bowls that can hold up to 16 ounces of ice cream. The food service manager is interested in comparing the average amount of ice cream dispensed by male students to the average amount dispensed by female students. A measurement device was placed on the ice cream machine to determine the amounts dispensed. Random samples of 85 male and 78 female students who got ice cream were selected. The sample averages were 7.23 and 6.49 ounces for the male and female students, respectively. Assume that the population standard deviations are 1.22 and 1.17 ounces, respectively. Using the 1% significance level, can you conclude that the average amount of ice cream dispensed by male college students is larger than the average amount dispensed by female college students? What is the type of test to be used?arrow_forwardA consumer organization was concerned about the differences between the advertised sizes of containers and the actual amount of product. In a preliminary study, six packages of three different brands of margarine that are supposed to contain 500 ml were measured. The differences from 500 ml are listed here. Brand 1 Brand 2 Brand 3 1 1 3 2 3 4 4 3 2 1 4 4 What is the test value? Use 5% level of significance. a) 0.60 ОБ) 1.69 c) 2.69 d) 0.21 e) None of the answers are correct 2.arrow_forward
- Six samples of each of four types of cereal grain grown in a certain region were analyzed to determine thiamin content, resulting in the following data (µg/g). Wheat 5.2 4.4 6.1 6.2 6.6 5.8 Barley 6.5 7.9 6.0 7.6 6.0 5.7 Maize 5.8 4.6 6.4 4.9 6.0 5.2 Oats 8.4 6.2 7.8 7.1 5.4 7.2 USE SALT Does this data suggest that at least two of the grains differ with respect to true average thiamin content? Use a level α = 0.05 test. State the appropriate hypotheses. | H₂: M₁ = H₂ = H3 = H4 H₂: all four μ's are unequal • Ho: M₁ = H₂ = H3 = H4 H₂: at least two μ's are unequal ⒸH₂² H₁ H₂ H3 H4 # H: all four μ's are equal O Ho: M₁ #M₂ #H3 H4 H₂: at least two μ's are equal Compute the test statistic value. (Round your answer to two decimal places.) f = What can be said about the P-value for the test? O P-value > 0.100 O 0.050 < P-value < 0.100 O 0.010 < P-value < 0.050 O 0.001 < P-value < 0.010 O P-value < 0.001 State the conclusion in the problem context. O Reject Ho. There is not significant evidence…arrow_forwardIn automobile mileage and gasoline-consumption testing, 13 automobiles were road tested for 300 miles in both city and highway driving conditions. The following data were recorded for miles-per-gallon performance. City: 16.7 17.2 16.4 14.9 13.7 15.8 17.3 16.5 16.6 15.8 15.7 15.8 16.7 Highway: 20.0 21.2 18.9 19.2 19.8 18.0 17.8 19.2 19.6 21.7 20.0 19.1 19.3 Calculate the mean, median, and mode for City and Highway gasoline consumption (to 1 decimal). City Highway Mean Median Mode The data are bimodal: andarrow_forwardPlease help me in answering the following practice question:Given a random sample of the amount of protein (in gram) in one bag of snack food: 0.95, 0.85, 0.92, 0.95, 0.93, 0.86, 1, 0.92, 0.85, 0.81, 0.78, 0.93, 0.93, 1.05, 0.93, 1.06, 1.06, 0.96, 0.81, 0.96 Here, it is assumed that the amount of protein in the snack is normal. How would I calculate a 98% two-sided confidence interval for the average amount of protein in one bag?Thank you for your help in advance!arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman