
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780133923605
Author: Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
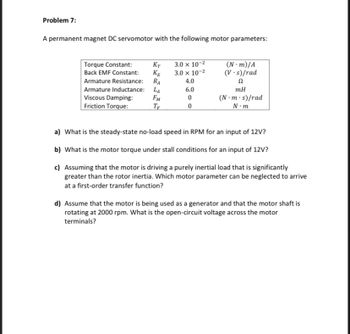
Transcribed Image Text:Problem 7:
A permanent magnet DC servomotor with the following motor parameters:
Torque Constant:
Back EMF Constant:
KT
KE
Armature Resistance:
RA
Armature Inductance: LA
Viscous Damping:
FM
Friction Torque:
TE
3.0 x 10-²
3.0 x 10-²
4.0
6.0
0
0
(N-m)/A
(V.s)/rad
Ω
mH
(N.m.s)/rad
N.m
a) What is the steady-state no-load speed in RPM for an input of 12V?
b) What is the motor torque under stall conditions for an input of 12V?
c) Assuming that the motor is driving a purely inertial load that is significantly
greater than the rotor inertia. Which motor parameter can be neglected to arrive
at a first-order transfer function?
d) Assume that the motor is being used as a generator and that the motor shaft is
rotating at 2000 rpm. What is the open-circuit voltage across the motor
terminals?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A permanent-magnet dc motor hasRA = 1.0 Ω. With no load, it operatesat 1000 rpm and draws 1.0 A from a 15 Vsource. Assume that rotational power lossis proportional to speed. Find the outputpower and efficiency for a load that dropsthe speed to 950 rpm.arrow_forward× 4:03 K s.eng.ruh.ac.lk □ Û 8. Figure 4 shows the core of a simple dc motor. The magnetization curve for the metal in this core is given by Figure 5 and Figure 6. Assume that the cross-sectional area of each air gap is 18 cm² and that the width of each air gap is 0.05 cm. The effective diameter of the rotor core is 4 cm. L It is desired to build a machine with as great a flux density as possible while avoiding excessive saturation in the core. What would be a reasonable maximum flux density for this core? ii. What would be the total flux in the core at the flux density of part (i)? iii. The maximum possible field current for this machine is I A. Select a reasonable number of turns of wire to provide the desired flux density while not exceeding the maximum available current. Flux Density, B (T) 2.8 སྤྲ ཤཱ ཀ ཀཱ བྷ ཀ ཡཱཾ བ ་ 1.2 1.0 0.4 0.2 4-48cm Figure 4 0 10 20 30 40 50 100 → Depth 4 cm -0.05 cm 200 300 500 1000 2000 Magnetizing Intensity, H (A.turns/m) Figure 5 Magnetization curve…arrow_forward
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,