
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
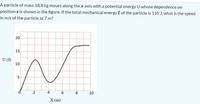
Transcribed Image Text:A particle of mass 18.8 kg moves along the x-axis with a potential energy U whose dependence on
position x is shown in the figure. If the total mechanical energy E of the particle is 110 J, what is the speed
in m/s of the particle at 7 m?
15
U (J)
10
V.
5
4
8
10
X (m)
00
6.
20
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A particle of mass m = 2.00 kg moves along one dimension at a speed v = 1.00 m/s. The particle is subject to a single force, whose potential energy function is given by U(x)=13x3−32x2+2x+3U(x)=13x3−32x2+2x+3 (where U is measured in Joules and x is measured in meters). If the particle's initial position is in stable equilibrium, what is that position, in meters? What is the magnitude of the force (in newtons) felt by the particle when it is at position x = 5?arrow_forwardWhen an 85.4-kg adult uses a spiral staircase to climb to the second floor of his house, his gravitational potential energy increases by 2.03 x 103 J. By how much does the potential energy of a 15.6-kg child increase when the child climbs a normal staircase to the second floor?arrow_forwardA particle of mass 2.0 kg moves under the influence of the force F(x) = (3/√x) N. If its speed at x = 2.0 m is v = 6.0 m/s, what is its speed at x = 7.0 m?arrow_forward
- You throw a ball of mass 15.0 kg straight upward into free fall with an initial kinetic energy of 7.00 J. At its maximum height, the ball stops moving. What is the gravitational potential energy of the ball relative to its starting point at its maximum height in SI units?arrow_forwardAn object with a mass of m = 3.00 kg is traveling with an initial velocity of vi = (5.40î − 1.60ĵ) m/s. (a) Determine its initial kinetic energy. (Give your answer to at least one decimal place.) J(b) Determine the amount of work that must be done on the object in order to change its velocity to vf = (6.00î + 7.00ĵ) m/s. Jarrow_forwardA horizontal, frictionless spring has a spring constant k = 440 N/m. How much work does it take to stretch the spring from x1 = 0.23 m to x2 = 0.46 m?arrow_forward
- In a simple pendulum, energy is stored by lifting the pendulum some height "h" away from the pull of gravity. If the pendulum has gained 10 Joules of gravitational potential energy when it is lifted to position "A", how much kinetic energy will it have at position "B"? A B C D PE = 103 KE =O PE KE = PE=2J KE= -- PE =0 KE= a O Joules 2 Joules 8 Joules 10 Joulesarrow_forwardWhen an 81.0 kg adult uses a spiral staircase to climb to the second floor of his house, his gravitational potential energy increases by 2.00×10³ J. By how much does the potential energy of a 18.0 kg child increase when the child climbs a normal staircase to the second floor?arrow_forwardA particle moving along the a-axis has the potential energy PE = 200/x2 J, where x is in meters. What is the x-component of the force on the particle at x = 7 m.arrow_forward
- A basketball player throws a basketball m = 1 kg straight up with an initial speed of v0 = 9.5 m/s. The ball leaves his hand at shoulder height h0 = 2.2 m. Let gravitational potential energy be zero at ground level. Give the total mechanical energy of the ball E in terms of maximum height hm it reaches, the mass m, and the gravitational acceleration g.arrow_forwardA particle, mass 8 kg, moves along the y axis with a speed of 3.3 m/s. It experiences a force of 16 N directed along the x axis. What power is imparted to the particle by the force 9.69 J/s x 9.69arrow_forwardThe figure here shows a plot of potential energy U versus position x of a 6-kg particle that can travel only along an x axis. Nonconservative forces are not involved. When the particle is at x = 1 m, it is moving in the +x direction with a kinetic energy of 100 J. Potential Energy Versus x Potential Energy U(U) 100 20 0 1 2 3 7 Position x (m) 4 5 6 8 9 10 11 12 a. What is the acceleration of the particle at x = 3.5 m? Include a plus or minus sign to indicate direction.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON